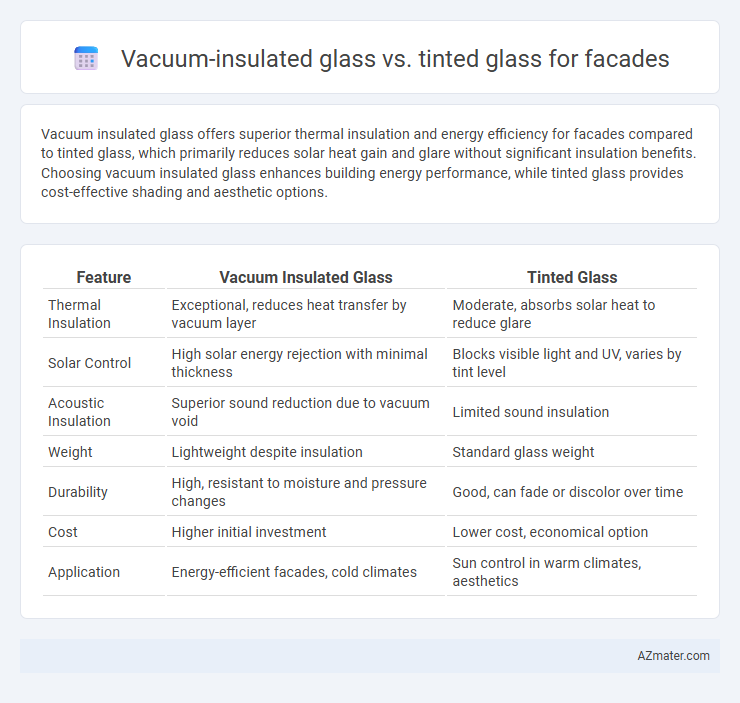
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency for facades compared to tinted glass, which primarily reduces solar heat gain and glare without significant insulation benefits. Choosing vacuum insulated glass enhances building energy performance, while tinted glass provides cost-effective shading and aesthetic options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Exceptional, reduces heat transfer by vacuum layer | Moderate, absorbs solar heat to reduce glare |
| Solar Control | High solar energy rejection with minimal thickness | Blocks visible light and UV, varies by tint level |
| Acoustic Insulation | Superior sound reduction due to vacuum void | Limited sound insulation |
| Weight | Lightweight despite insulation | Standard glass weight |
| Durability | High, resistant to moisture and pressure changes | Good, can fade or discolor over time |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost, economical option |
| Application | Energy-efficient facades, cold climates | Sun control in warm climates, aesthetics |
Introduction to Facade Glass Selection
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency compared to tinted glass, making it ideal for modern facade designs aiming to reduce heating and cooling costs. Tinted glass primarily enhances solar control by reducing glare and heat gain but lacks the advanced insulation properties of vacuum insulated glass. Selecting facade glass depends on balancing factors such as energy performance, daylighting, aesthetic preferences, and climate considerations.
What is Vacuum Insulated Glass?
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum layer that significantly reduces heat transfer, providing superior thermal insulation compared to conventional double glazing. This technology minimizes energy loss and condensation on building facades, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Unlike tinted glass, which primarily reduces solar heat gain and glare, vacuum insulated glass offers advanced insulation properties without compromising natural daylight.
Understanding Tinted Glass for Facades
Tinted glass for facades reduces solar heat gain and glare by incorporating metal oxides or other additives during manufacturing, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort. The spectrum of tint colors allows customization to control visible light transmission and UV protection, which impacts thermal performance and aesthetic appeal. Unlike vacuum insulated glass, tinted glass primarily targets solar control rather than insulation, making it a strategic choice for balancing daylighting and energy efficiency in building envelopes.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by minimizing heat transfer through its vacuum layer, significantly reducing energy loss compared to tinted glass. Tinted glass primarily blocks solar radiation, lowering cooling loads, but does not provide the same level of thermal resistance against conductive heat flow. For facade applications, vacuum insulated glass achieves higher overall energy efficiency by combining low U-values with effective solar heat gain control.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) significantly outperforms tinted glass in energy efficiency due to its superior thermal insulation properties, reducing heat transfer and minimizing energy consumption for heating and cooling. The vacuum layer within VIG eliminates conductive and convective heat loss, resulting in enhanced facade performance and lower HVAC system demands. Tinted glass primarily reduces solar heat gain but lacks the advanced insulation capabilities of VIG, making it less effective for comprehensive energy savings in building facades.
Acoustic Insulation: Which Performs Better?
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) outperforms tinted glass in acoustic insulation due to its unique airless gap that significantly reduces sound transmission, making it ideal for noisy urban facades. Tinted glass primarily serves to control solar heat gain and glare but offers limited noise reduction compared to VIG. For facades requiring superior soundproofing, vacuum insulated glass provides enhanced acoustic performance and thermal efficiency, creating quieter and more comfortable indoor environments.
Visual and Aesthetic Considerations
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior clarity and minimal distortion, enhancing natural light transmission and providing a sleek, modern facade appearance. Tinted glass, while reducing glare and controlling solar heat gain, introduces color variations that can affect uniformity and alter building aesthetics. Choosing between them depends on desired visual impact and energy performance balance, with vacuum insulated glass favoring transparency and tint glass emphasizing shading effects.
Durability and Maintenance Needs
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior durability compared to tinted glass due to its airtight seal which prevents moisture ingress and maintains thermal performance over time. Tinted glass, while effective in reducing solar heat gain, is more prone to surface wear and fading, requiring frequent maintenance and potential replacement. Maintenance needs for VIG are minimal owing to its robust construction and resistance to environmental damage, whereas tinted glass requires regular cleaning and inspection to preserve its aesthetic and functional properties.
Cost Analysis: Vacuum Insulated vs Tinted Glass
Vacuum insulated glass generally incurs higher upfront costs compared to tinted glass due to advanced manufacturing techniques and materials that enhance thermal insulation and energy efficiency. Tinted glass, while initially more affordable, may lead to increased energy expenses over time because it primarily reduces solar heat gain without providing robust insulation. Evaluating lifecycle costs reveals vacuum insulated glass offers greater long-term savings through reduced heating and cooling demands despite its premium price.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Facade
Choosing the right glass for your facade involves comparing vacuum insulated glass (VIG) and tinted glass based on energy efficiency and aesthetic goals. Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation, reducing heat transfer and lowering energy costs, making it ideal for climates with extreme temperature variations. Tinted glass, while providing glare reduction and UV protection, primarily enhances visual comfort and appearance, but does not match VIG's insulation performance for optimal energy savings.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Tinted glass for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com