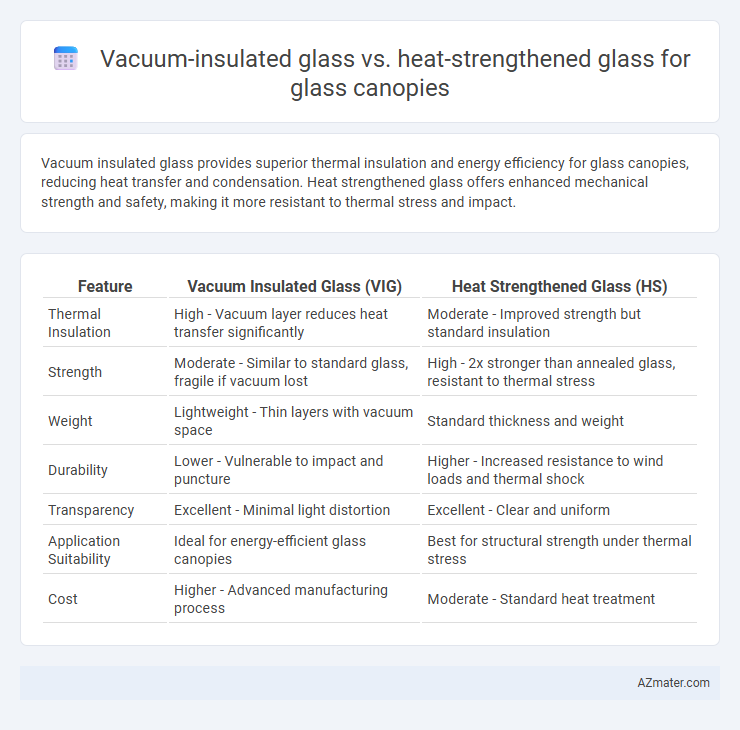
Vacuum insulated glass provides superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency for glass canopies, reducing heat transfer and condensation. Heat strengthened glass offers enhanced mechanical strength and safety, making it more resistant to thermal stress and impact.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) | Heat Strengthened Glass (HS) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High - Vacuum layer reduces heat transfer significantly | Moderate - Improved strength but standard insulation |
| Strength | Moderate - Similar to standard glass, fragile if vacuum lost | High - 2x stronger than annealed glass, resistant to thermal stress |
| Weight | Lightweight - Thin layers with vacuum space | Standard thickness and weight |
| Durability | Lower - Vulnerable to impact and puncture | Higher - Increased resistance to wind loads and thermal shock |
| Transparency | Excellent - Minimal light distortion | Excellent - Clear and uniform |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for energy-efficient glass canopies | Best for structural strength under thermal stress |
| Cost | Higher - Advanced manufacturing process | Moderate - Standard heat treatment |
Introduction to Glass Canopy Solutions
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and reduced condensation for glass canopies, enhancing energy efficiency and durability in architectural applications. Heat strengthened glass provides increased strength and resistance to thermal stress, making it a cost-effective choice for canopy structures exposed to environmental variations. Selecting between these options depends on specific performance requirements such as thermal efficiency and structural safety for glass canopy solutions.
What is Vacuum Insulated Glass?
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum layer that significantly reduces heat transfer, offering superior thermal insulation for glass canopies. Unlike heat strengthened glass, which is mechanically treated to enhance strength and thermal resistance, VIG provides enhanced energy efficiency by minimizing conductive and convective heat loss. This advanced glazing technology improves temperature regulation, reduces condensation, and increases overall comfort and durability in architectural applications such as glass canopies.
Understanding Heat Strengthened Glass
Heat strengthened glass for glass canopies offers enhanced thermal resistance by undergoing controlled heat treatment that increases its strength to about twice that of annealed glass, making it more resistant to thermal stress and breakage. Unlike vacuum insulated glass, which primarily focuses on thermal insulation through a vacuum layer between glass panes, heat strengthened glass provides improved durability and safety without significantly affecting insulation properties. This makes heat strengthened glass a preferred choice for glass canopies exposed to varying temperatures and mechanical loads, ensuring long-term performance and safety.
Key Differences: Vacuum Insulated vs Heat Strengthened Glass
Vacuum insulated glass features a sealed space between two glass panes with a vacuum that significantly reduces heat transfer, providing superior thermal insulation for glass canopies. Heat strengthened glass undergoes controlled thermal treatment to enhance strength and resistance to thermal stress, offering improved safety and durability but less insulation compared to vacuum insulated glass. Key differences include vacuum insulated glass's focus on superior energy efficiency and temperature control, while heat strengthened glass emphasizes mechanical strength and impact resistance.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) outperforms heat strengthened glass in thermal insulation for glass canopies by minimizing heat transfer through its vacuum layer, achieving U-values as low as 0.5 W/m2K. Heat strengthened glass improves durability and thermal stress resistance but offers limited thermal performance, with U-values typically around 5.5 W/m2K. Selecting VIG enhances energy efficiency and indoor temperature regulation, making it superior for climate control under glass canopies.
Durability and Safety Considerations
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and enhanced durability for glass canopies by reducing condensation and preventing thermal stress cracks, making it ideal for environments with extreme temperature variations. Heat strengthened glass provides increased mechanical strength and safety over annealed glass by undergoing controlled heat treatment, which makes it more resistant to impact and thermal stress but less effective than vacuum insulated glass in insulation performance. Safety considerations favor vacuum insulated glass for energy efficiency and long-term performance, while heat strengthened glass is preferred where moderate impact resistance and lower cost are priorities.
Energy Efficiency Impact
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior energy efficiency for glass canopies by minimizing heat transfer through its airless space, significantly reducing heat loss and gain compared to heat strengthened glass. Heat strengthened glass improves durability and thermal resistance but lacks the insulation properties necessary to achieve optimal energy savings. Choosing vacuum insulated glass enhances temperature regulation and lowers energy costs in buildings with glass canopies.
Design Flexibility for Glass Canopies
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal performance and thinner profiles, allowing architects greater design flexibility with expansive glass canopies without compromising energy efficiency. Heat strengthened glass provides enhanced strength and durability, enabling larger spans and complex shapes while maintaining safety under environmental loads. Choosing between these materials depends on balancing design aesthetics, structural requirements, and insulation needs for innovative and resilient glass canopy designs.
Cost Comparison and ROI
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation for glass canopies but comes at a higher initial cost compared to heat strengthened glass, which is more affordable yet provides moderate energy efficiency. The increased upfront investment in VIG can lead to a faster return on investment (ROI) through significant energy savings and reduced HVAC costs over time. Heat strengthened glass presents a lower entry cost with less dramatic energy savings, resulting in a longer payback period despite its durability benefits.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Canopy
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency for glass canopies, reducing heat transfer and condensation risks, which is ideal for climate control. Heat strengthened glass, known for its increased strength and resistance to thermal stress, provides a cost-effective solution with enhanced safety over standard annealed glass. Selecting the right glass depends on factors like environmental exposure, structural requirements, and budget, with vacuum insulated glass excelling in energy performance and heat strengthened glass balancing durability with affordability.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Heat strengthened glass for Glass canopy
 azmater.com
azmater.com