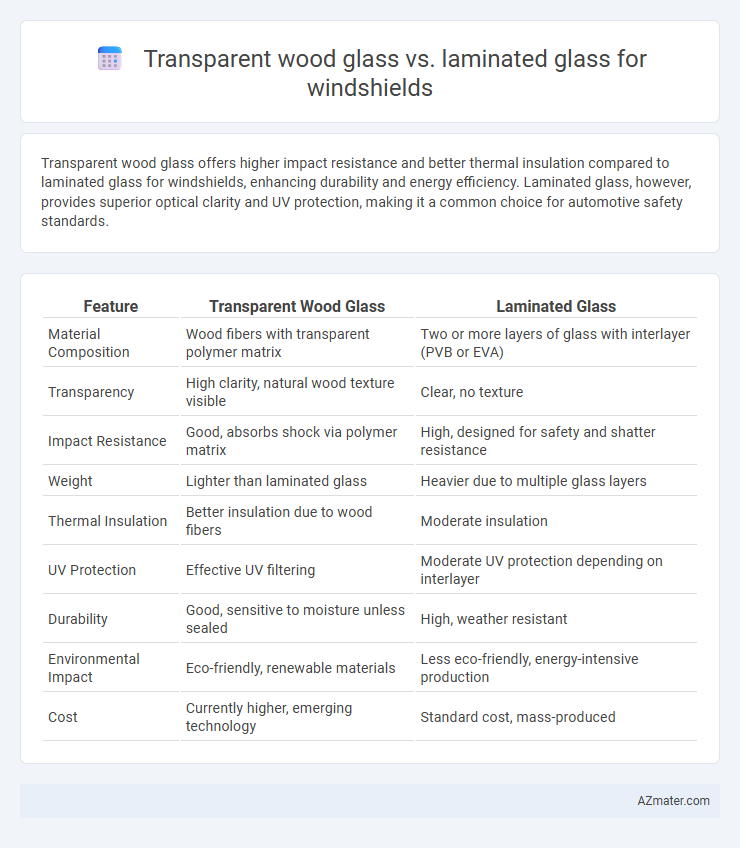
Transparent wood glass offers higher impact resistance and better thermal insulation compared to laminated glass for windshields, enhancing durability and energy efficiency. Laminated glass, however, provides superior optical clarity and UV protection, making it a common choice for automotive safety standards.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transparent Wood Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood fibers with transparent polymer matrix | Two or more layers of glass with interlayer (PVB or EVA) |
| Transparency | High clarity, natural wood texture visible | Clear, no texture |
| Impact Resistance | Good, absorbs shock via polymer matrix | High, designed for safety and shatter resistance |
| Weight | Lighter than laminated glass | Heavier due to multiple glass layers |
| Thermal Insulation | Better insulation due to wood fibers | Moderate insulation |
| UV Protection | Effective UV filtering | Moderate UV protection depending on interlayer |
| Durability | Good, sensitive to moisture unless sealed | High, weather resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, renewable materials | Less eco-friendly, energy-intensive production |
| Cost | Currently higher, emerging technology | Standard cost, mass-produced |
Introduction to Automotive Windshield Technologies
Transparent wood glass offers a novel alternative to traditional laminated glass for automotive windshields by combining high strength with enhanced optical clarity and reduced weight. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded with a polymer interlayer, provides proven impact resistance and shatterproof safety benefits widely adopted in automotive applications. Advances in transparent wood composites focus on improving durability and UV resistance while maintaining superior sustainability and energy efficiency compared to conventional laminated windshield glass.
What is Transparent Wood Glass?
Transparent wood glass is an innovative material made by removing lignin from wood and infiltrating the porous structure with a transparent polymer, resulting in a lightweight, strong, and optically clear panel. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of multiple glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer to provide impact resistance and safety, transparent wood glass offers superior flexibility, better impact absorption, and enhanced thermal insulation. This emerging technology has potential applications in automotive windshields due to its combination of transparency, durability, shatter resistance, and eco-friendly attributes.
Understanding Laminated Glass
Laminated glass for windshields consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety by preventing shattering upon impact. This construction improves durability and maintains visibility under stress, making it the industry standard for automotive windshields. Compared to transparent wood glass, laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and clarity critical for driver safety and performance.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Transparent wood glass offers superior optical clarity with minimal distortion due to its natural cellulose structure, enabling high light transmission levels up to 85-90%. Laminated glass typically achieves light transmission around 80-85% but can suffer from slight haze or irregularities caused by interlayer materials. The unique composition of transparent wood glass allows clearer visibility and better light diffusion compared to the multilayered structure of laminated glass in windshield applications.
Strength and Impact Resistance Comparison
Transparent wood glass exhibits high tensile strength and superior impact resistance due to its layered cellulose structure combined with polymer infiltration, offering enhanced durability against shattering. Laminated glass, traditionally used in windshields, consists of two glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing excellent impact absorption and preventing glass fragmentation upon impact. While laminated glass ensures reliable safety and clarity, transparent wood glass presents a promising alternative with potentially greater strength-to-weight ratio and improved energy dissipation under impact conditions.
Weight and Fuel Efficiency Implications
Transparent wood glass offers a significantly lighter alternative to traditional laminated glass for windshields, reducing vehicle weight by up to 30%. This weight reduction translates to improved fuel efficiency, with studies showing a potential fuel consumption decrease of approximately 5-7%. Lighter materials enhance overall vehicle performance and contribute to lower carbon emissions through better energy utilization.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Transparent wood glass exhibits superior durability due to its natural lignin and cellulose matrix, offering enhanced impact resistance compared to laminated glass. Its renewable structure provides excellent weather resistance, maintaining clarity and structural integrity under UV exposure and temperature fluctuations. Laminated glass, while effective at shatter resistance, is more prone to delamination and micro-cracking under prolonged environmental stress.
Environmental Sustainability
Transparent wood glass offers superior environmental sustainability compared to laminated glass used in windshields by utilizing renewable wood fibers that reduce reliance on petroleum-based materials. Its production process emits fewer greenhouse gases and allows for enhanced biodegradability at the end of its lifecycle. Unlike laminated glass, transparent wood glass improves energy efficiency through natural insulation properties, contributing to lower vehicle emissions.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Transparent wood glass offers potential cost advantages over laminated glass due to the use of renewable wood-based materials, which can reduce reliance on expensive petrochemical inputs. Manufacturing transparent wood involves processes like delignification and impregnation with resins, which currently require specialized equipment and can increase production complexity compared to the well-established lamination process for laminated glass. While laminated glass benefits from mature, mass-production techniques leading to consistent cost-efficiency, transparent wood's scalability and cost-effectiveness depend on advancements in bio-based material processing technologies.
Future Prospects and Industry Adoption
Transparent wood glass offers innovative potential for windshields by combining high strength, lightweight properties, and enhanced sustainability compared to traditional laminated glass. Research indicates that transparent wood's superior impact resistance and UV protection could lead to safer, more energy-efficient automotive applications, attracting interest from eco-conscious manufacturers. Despite laminated glass's current dominance due to established manufacturing processes and regulatory approval, increasing environmental regulations and material advancements are driving gradual industry adoption of transparent wood alternatives in next-generation windshield designs.
Infographic: Transparent wood glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com