Solar control glass reduces heat gain by reflecting and absorbing solar radiation, enhancing energy efficiency in curtain walls. Insulated glass combines multiple panes with air or gas-filled space to improve thermal insulation and reduce heat transfer.
Table of Comparison
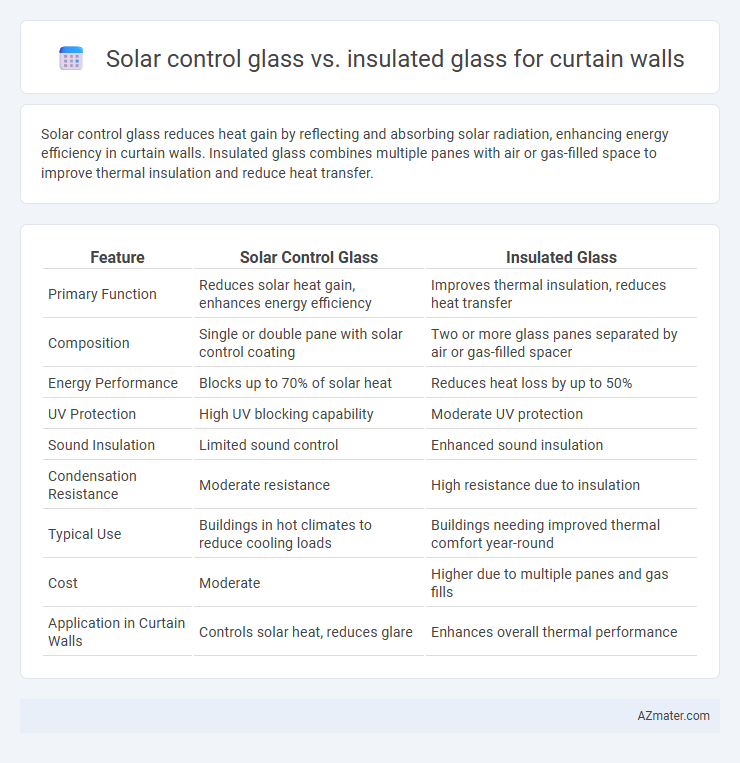
| Feature | Solar Control Glass | Insulated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reduces solar heat gain, enhances energy efficiency | Improves thermal insulation, reduces heat transfer |
| Composition | Single or double pane with solar control coating | Two or more glass panes separated by air or gas-filled spacer |
| Energy Performance | Blocks up to 70% of solar heat | Reduces heat loss by up to 50% |
| UV Protection | High UV blocking capability | Moderate UV protection |
| Sound Insulation | Limited sound control | Enhanced sound insulation |
| Condensation Resistance | Moderate resistance | High resistance due to insulation |
| Typical Use | Buildings in hot climates to reduce cooling loads | Buildings needing improved thermal comfort year-round |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to multiple panes and gas fills |
| Application in Curtain Walls | Controls solar heat, reduces glare | Enhances overall thermal performance |
Introduction to Curtain Walls
Curtain walls are non-structural cladding systems commonly used in modern commercial buildings to enhance aesthetics and control environmental factors. Solar control glass in curtain walls reduces solar heat gain, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort by filtering infrared and ultraviolet rays. Insulated glass units (IGUs) consist of multiple glass panes separated by a spacer and sealed to provide enhanced thermal insulation, reducing heat transfer and condensation for better climate control within the building.
What is Solar Control Glass?
Solar control glass is designed to reduce solar heat gain by reflecting or absorbing a significant portion of the sun's infrared rays while allowing natural light to pass through, enhancing energy efficiency in curtain wall systems. This type of glass typically features a special coating that improves thermal performance without compromising visibility, making it ideal for climates with intense sunlight. Compared to insulated glass, solar control glass primarily targets heat reduction and glare control, optimizing indoor temperature and comfort.
Understanding Insulated Glass Units
Insulated Glass Units (IGUs) consist of two or more glass panes separated by a sealed air or gas-filled space, enhancing thermal insulation for curtain walls by reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency. Solar control glass, integrated within IGUs, incorporates coatings that selectively reflect solar radiation, minimizing heat gain while maintaining visible light transmission. Combining insulated glass technology with solar control coatings results in superior performance for curtain walls, optimizing indoor comfort and reducing HVAC energy consumption.
Key Differences Between Solar Control and Insulated Glass
Solar control glass reduces heat gain by reflecting and absorbing solar radiation, optimizing energy efficiency in curtain walls, while insulated glass primarily minimizes heat transfer through its dual or triple pane design with sealed air or gas-filled spaces. Solar control glass enhances occupant comfort by controlling glare and UV rays, whereas insulated glass improves thermal insulation and soundproofing. The choice depends on climate conditions and building performance goals, with solar control glass suited for hot climates and insulated glass preferred for temperature regulation in variable environments.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Solar control glass reduces heat gain by reflecting and absorbing infrared radiation, significantly lowering cooling loads in curtain wall systems. Insulated glass units (IGUs) provide superior thermal insulation through multiple glass panes separated by a gas-filled gap, minimizing heat transfer between interior and exterior environments. For energy efficiency, solar control glass excels in hot climates by blocking solar heat, while insulated glass enhances overall thermal resistance, making the choice dependent on specific climatic and building performance requirements.
Thermal Performance Analysis
Solar control glass significantly reduces solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), enhancing energy efficiency by blocking up to 60-70% of infrared radiation, which lowers cooling loads in curtain wall systems. Insulated glass units (IGUs) combine multiple glass panes separated by air or inert gas layers, improving thermal resistance (R-value) and minimizing heat transfer through conduction and convection. In curtain wall applications, integrating solar control coatings with insulated glass achieves optimal thermal performance by balancing solar heat reduction and improved insulation, resulting in decreased HVAC energy consumption.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Solar control glass offers excellent aesthetic options with various tints and coatings that enhance energy efficiency while maintaining clear visibility, allowing architects to design sleek, modern curtain walls with minimal glare. Insulated glass provides superior thermal performance through multiple panes and gas fills, enabling thicker units that may limit slim profile designs but offer versatile shapes and sizes for creative facade solutions. Both glass types support diverse design requirements, though solar control glass often delivers greater flexibility for light manipulation and transparency in curtain wall aesthetics.
Cost Implications and ROI
Solar control glass reduces energy costs by minimizing solar heat gain, leading to lower air conditioning expenses, which can increase the return on investment over time despite its higher initial cost. Insulated glass, with its dual or triple glazing, offers improved thermal insulation that decreases heating and cooling demands, often resulting in quicker payback in colder climates due to enhanced energy efficiency. When evaluating curtain wall applications, the choice between solar control glass and insulated glass should consider local climate, energy prices, and long-term savings to optimize cost efficiency and ROI.
Application Suitability for Curtain Walls
Solar control glass offers superior heat reduction and glare control, making it ideal for curtain walls in hot climates and urban settings where energy efficiency and occupant comfort are priorities. Insulated glass excels in thermal insulation, reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy savings, which is particularly suitable for cooler climates and buildings requiring strict temperature regulation. Both types improve building performance, but solar control glass is preferable for controlling solar heat gain, while insulated glass provides better overall thermal insulation in curtain wall applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Solar control glass reduces heat gain and enhances energy efficiency by reflecting infrared rays while allowing visible light to pass, making it ideal for curtain walls in hot climates. Insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation through its dual-pane construction with an air or gas-filled cavity, preventing heat loss in colder environments. Selecting the right glass depends on project-specific factors such as climate, energy performance goals, and budget considerations.
Infographic: Solar control glass vs Insulated glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com