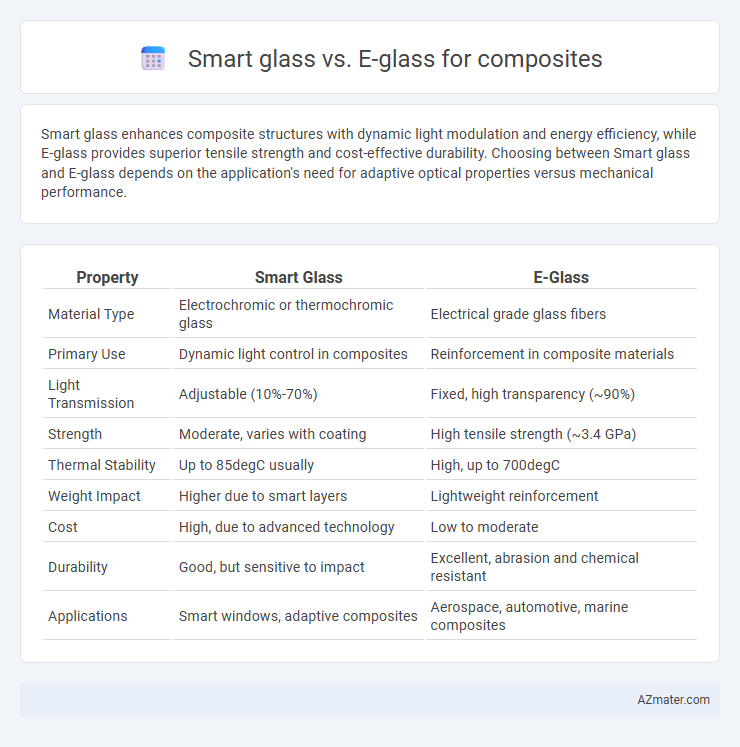
Smart glass enhances composite structures with dynamic light modulation and energy efficiency, while E-glass provides superior tensile strength and cost-effective durability. Choosing between Smart glass and E-glass depends on the application's need for adaptive optical properties versus mechanical performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Smart Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Electrochromic or thermochromic glass | Electrical grade glass fibers |
| Primary Use | Dynamic light control in composites | Reinforcement in composite materials |
| Light Transmission | Adjustable (10%-70%) | Fixed, high transparency (~90%) |
| Strength | Moderate, varies with coating | High tensile strength (~3.4 GPa) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 85degC usually | High, up to 700degC |
| Weight Impact | Higher due to smart layers | Lightweight reinforcement |
| Cost | High, due to advanced technology | Low to moderate |
| Durability | Good, but sensitive to impact | Excellent, abrasion and chemical resistant |
| Applications | Smart windows, adaptive composites | Aerospace, automotive, marine composites |
Understanding Smart Glass and E-Glass: Definitions and Overview
Smart glass, also known as switchable glass, changes its light transmission properties in response to electrical, thermal, or light stimuli, enhancing energy efficiency and privacy in composite applications. E-glass, or electrical glass, is a traditional fiber-reinforced composite material known for its excellent electrical insulation, high tensile strength, and chemical resistance, commonly used in structural and marine industries. Understanding these materials' distinct properties helps optimize composite design for specific performance requirements like durability, transparency control, and electrical insulation.
Material Properties: Smart Glass vs E-Glass
Smart glass exhibits dynamic optical properties with the ability to change transparency under electrical stimuli, offering enhanced energy efficiency and privacy control in composites. E-glass, a traditional fiberglass material, provides excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation, making it a cost-effective reinforcement in composite applications. While smart glass integrates functional intelligence, E-glass emphasizes durability and structural performance in composite materials.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Smart glass composites often involve complex manufacturing processes such as lamination and integration of electrochromic or thermochromic layers, requiring precise temperature and pressure controls to maintain functionality. E-glass composites use traditional methods like hand lay-up, filament winding, or resin transfer molding, prioritizing fiber alignment and resin curing for mechanical strength. The manufacturing of smart glass composites is generally more intricate and costly due to the integration of electronic components alongside the glass-fiber matrix.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Analysis
Smart glass composites exhibit enhanced mechanical strength due to their adaptive properties, allowing for dynamic stress distribution and improved resistance to impact and deformation. E-glass composites provide high tensile strength and excellent durability, characterized by superior resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and UV exposure. Comparative analyses indicate that while E-glass offers consistent long-term durability, smart glass composites deliver advanced performance in applications requiring variable mechanical resilience and self-healing capabilities.
Applications in Composite Structures
Smart glass in composite structures offers dynamic light modulation and energy efficiency, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications requiring adaptive transparency and thermal control. E-glass, composed of alumino-borosilicate fibers, provides high strength, electrical insulation, and chemical resistance, widely used in wind turbine blades, marine vessels, and sporting goods for structural reinforcement. The choice between smart glass and E-glass depends on specific composite performance requirements, with smart glass enhancing functionality and E-glass optimizing mechanical properties.
Energy Efficiency and Smart Features
Smart glass offers superior energy efficiency for composites by dynamically controlling light transmission and heat gain, reducing cooling and heating demands significantly compared to E-glass. E-glass, while durable and cost-effective, lacks the adaptive properties of smart glass, resulting in higher energy consumption in buildings or vehicles where it is used. The integration of smart features such as electrochromic or thermochromic technologies in smart glass enables real-time modulation of transparency and insulation, enhancing user comfort and energy savings beyond the static performance of E-glass composites.
Cost Comparison and Economic Viability
Smart glass in composite applications typically incurs higher initial costs due to advanced manufacturing and embedded technologies, contrasting with the lower price point of traditional E-glass fibers known for their affordability and wide availability. Despite the premium expense, smart glass offers enhanced energy efficiency and adaptive properties that can reduce long-term operational costs and improve overall economic viability in specific sectors such as automotive and construction. E-glass remains economically favorable for large-scale production and structural components where budget constraints are critical, balancing cost-effectiveness with adequate performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Smart glass and E-glass differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability within composite materials. E-glass, a traditional fiberglass, requires high energy for production and generates substantial waste, whereas smart glass incorporates advanced coatings that enhance energy efficiency by controlling light and heat transmission, reducing overall carbon footprints. The recyclability of smart glass composites is improving, promoting longer lifecycle sustainability compared to the limited recyclability of E-glass composites.
Industry Adoption: Case Studies and Trends
Smart glass and E-glass composites are gaining traction in aerospace, automotive, and construction sectors, driven by their unique properties like energy efficiency and durability. Industry adoption highlights case studies such as Boeing's use of smart glass in aircraft windows for passenger comfort and automotive manufacturers integrating E-glass for lightweight, high-strength body panels. Trends indicate a growing preference for smart glass in smart building applications, while E-glass remains dominant in cost-sensitive, high-volume composite manufacturing.
Future Prospects: Innovations and Market Outlook
Smart glass and E-glass composites exhibit distinct future prospects driven by advancements in material science and increasing demand in aerospace, automotive, and construction sectors. Innovations in smart glass focus on enhanced energy efficiency, adaptive transparency, and integration with IoT for smart building applications, while E-glass continues to evolve through improvements in tensile strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness for lightweight structural components. Market outlooks project robust growth for smart glass composites due to rising environmental regulations and smart city developments, whereas E-glass maintains a strong presence as a reliable and scalable solution in mass-produced composite materials.
Infographic: Smart glass vs E-glass for Composite
 azmater.com
azmater.com