Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and infrared transparency, making it ideal for high-temperature protective covers. UV glass provides enhanced ultraviolet filtration, ensuring effective protection against UV radiation in sensitive optical applications.
Table of Comparison
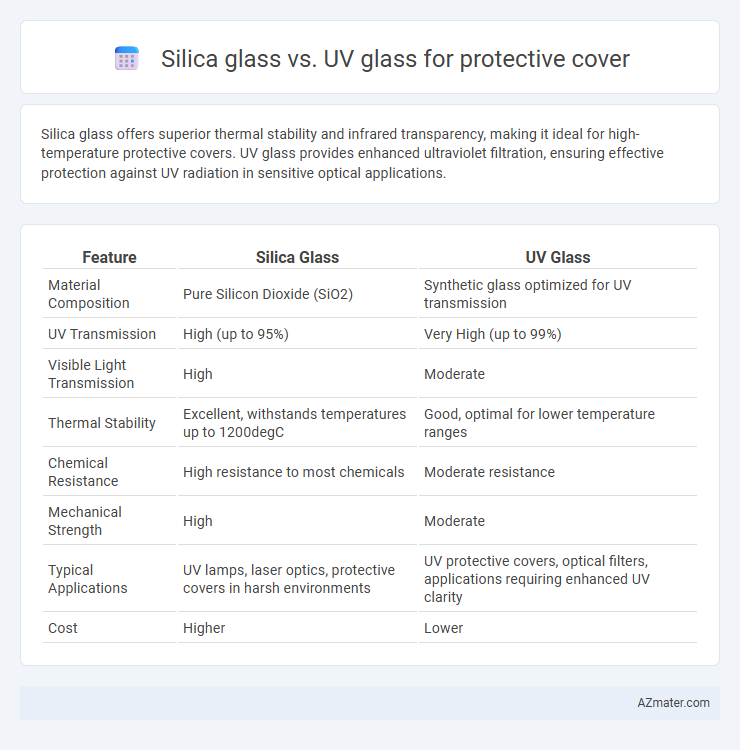
| Feature | Silica Glass | UV Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) | Synthetic glass optimized for UV transmission |
| UV Transmission | High (up to 95%) | Very High (up to 99%) |
| Visible Light Transmission | High | Moderate |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent, withstands temperatures up to 1200degC | Good, optimal for lower temperature ranges |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to most chemicals | Moderate resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Moderate |
| Typical Applications | UV lamps, laser optics, protective covers in harsh environments | UV protective covers, optical filters, applications requiring enhanced UV clarity |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Protective Glass Covers
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and high UV transmission, making it ideal for protective covers in precision optical applications. UV glass is engineered to absorb harmful ultraviolet rays while maintaining clarity, providing enhanced protection for sensitive equipment and displays. Selecting between silica glass and UV glass depends on specific environmental exposure and optical performance requirements for the protective cover.
Composition and Properties of Silica Glass
Silica glass, primarily composed of high-purity silicon dioxide (SiO2), offers exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for protective covers requiring durability and transparency. UV glass, often doped with specific additives to block ultraviolet radiation, provides targeted protection against UV light but typically lacks the high melting point and chemical inertness of silica glass. The inherent purity and robust network structure of silica glass ensure superior scratch resistance and minimal optical distortion under extreme environmental conditions.
Composition and Properties of UV Glass
UV glass is composed primarily of high-purity silica with added dopants like cerium oxide or titanium dioxide to enhance ultraviolet light absorption and resistance. Its unique composition allows UV glass to block harmful UV radiation while maintaining excellent optical clarity and high transparency in the visible spectrum. Compared to standard silica glass, UV glass exhibits superior durability against UV-induced degradation, making it ideal for protective covers in environments exposed to intense ultraviolet light.
Key Differences Between Silica Glass and UV Glass
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and higher purity, making it ideal for high-temperature applications, while UV glass is specifically designed to block ultraviolet radiation, protecting sensitive components from UV damage. Silica glass typically has a wider transmission range in the UV spectrum but lower UV blocking capabilities compared to UV glass, which is engineered to absorb UV rays effectively. The choice between silica glass and UV glass as protective covers depends on the balance between thermal resistance and UV filtration requirements.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Silica glass offers superior optical clarity and high light transmission, making it ideal for protective covers requiring precise visibility and minimal distortion. UV glass specifically filters harmful ultraviolet rays while maintaining good transparency, though it may slightly reduce overall light transmission compared to silica glass. For applications demanding maximum clarity and broad-spectrum light passage, silica glass outperforms UV glass in preserving image quality and brightness.
UV Protection Capabilities Compared
Silica glass offers superior UV protection due to its excellent transmission in the visible range while effectively blocking harmful UV rays below 200 nm, making it ideal for sensitive optical applications. UV glass specifically filters harmful ultraviolet radiation between 200 and 400 nm, providing enhanced protection in environments with intense UV exposure. Compared to UV glass, silica glass typically exhibits higher durability and thermal stability, ensuring long-lasting protection without compromising optical clarity.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Silica glass exhibits superior durability due to its high thermal stability and resistance to environmental factors, making it ideal for long-lasting protective covers. UV glass specializes in blocking ultraviolet rays while maintaining adequate scratch resistance, though it can be slightly more prone to surface damage compared to silica glass. For applications demanding enhanced scratch resistance and extended lifespan, silica glass outperforms UV glass in protective cover performance.
Cost Considerations and Value
Silica glass provides high thermal resistance and excellent UV transmission at a generally higher cost, making it suitable for demanding protective cover applications where durability and performance justify the investment. UV glass, while more affordable, offers effective UV-blocking properties with moderate durability, presenting a cost-effective solution for standard protection needs. Evaluating the balance between material expense and lifespan efficiency is crucial for optimizing value in protective cover selection.
Best Use Cases for Silica vs UV Glass
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments such as laboratory equipment and optical instruments exposed to harsh conditions. UV glass excels in blocking ultraviolet radiation while maintaining high visible light transmission, making it the best choice for protective covers in UV-sensitive applications like photographic filters, UV curing systems, and solar panels. Selecting silica glass ensures durability in extreme conditions, whereas UV glass optimizes protection against UV-induced degradation in sensitive optical devices.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Protective Cover
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and excellent UV transparency, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and long-term exposure to ultraviolet light. UV glass provides effective UV blocking and is generally more cost-efficient, suitable for environments where UV protection outweighs extreme heat resistance. Selecting the right protective cover depends on balancing performance needs, with silica glass favored for high-precision, high-temperature conditions and UV glass preferred for affordable, efficient UV shielding.
Infographic: Silica glass vs UV glass for Protective cover
 azmater.com
azmater.com