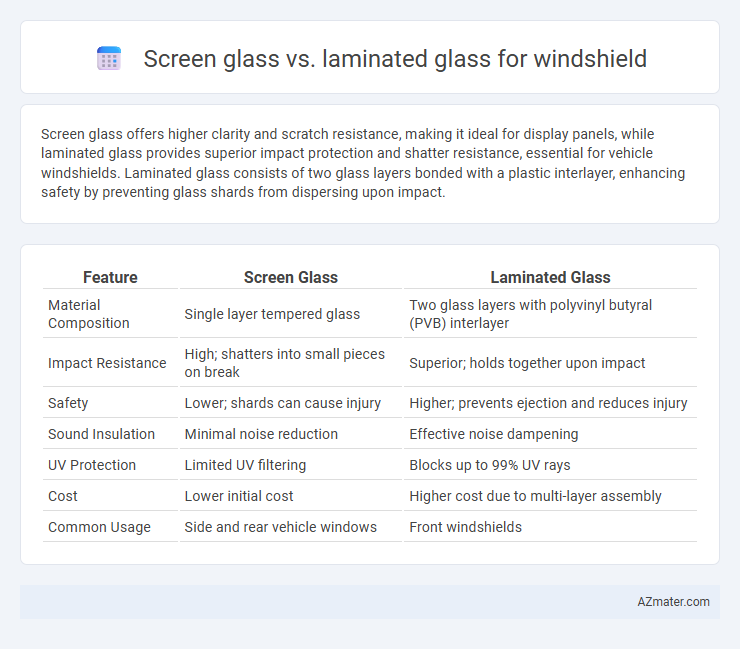
Screen glass offers higher clarity and scratch resistance, making it ideal for display panels, while laminated glass provides superior impact protection and shatter resistance, essential for vehicle windshields. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, enhancing safety by preventing glass shards from dispersing upon impact.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Screen Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Single layer tempered glass | Two glass layers with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Impact Resistance | High; shatters into small pieces on break | Superior; holds together upon impact |
| Safety | Lower; shards can cause injury | Higher; prevents ejection and reduces injury |
| Sound Insulation | Minimal noise reduction | Effective noise dampening |
| UV Protection | Limited UV filtering | Blocks up to 99% UV rays |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher cost due to multi-layer assembly |
| Common Usage | Side and rear vehicle windows | Front windshields |
Introduction: Importance of Choosing the Right Windshield Glass
Choosing the right windshield glass is crucial for vehicle safety, visibility, and durability. Screen glass offers enhanced clarity and resistance to scratches, while laminated glass provides superior impact resistance and shatterproof qualities. Understanding the differences between screen glass and laminated glass helps ensure optimal protection and performance on the road.
What is Screen Glass? Definition and Key Characteristics
Screen glass is a specialized type of glass used primarily in electronic display screens, characterized by its thin, durable, and transparent properties designed to protect underlying components. Unlike laminated glass, which is composed of multiple layers including a plastic interlayer to enhance impact resistance and safety in automotive windshields, screen glass typically lacks this layered construction and focuses more on clarity and touch sensitivity. Key characteristics of screen glass include high optical clarity, scratch resistance, and sometimes flexibility, making it ideal for devices but less suited for the structural safety required in windshields.
What is Laminated Glass? Structure and Composition
Laminated glass for windshields consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, usually polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), that provides enhanced impact resistance and safety. The structure prevents shattering upon impact by holding shards in place, reducing injury risk and maintaining visibility. This composition contrasts with typical screen glass, which lacks a protective interlayer and shatters more easily under stress.
Durability Comparison: Screen Glass vs Laminated Glass
Laminated glass offers superior durability compared to screen glass, featuring a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, significantly enhancing safety. Screen glass, typically used in electronic devices, lacks this interlayer, making it more prone to cracking and shattering under stress. For windshields, laminated glass provides better resistance to impact, weather conditions, and long-term wear, ensuring prolonged structural integrity and vehicle protection.
Safety Performance: Crash Resistance and Protection
Laminated glass offers superior safety performance for windshields due to its crash-resistant properties, as it consists of two glass layers bonded by a plastic interlayer that prevents shattering upon impact. Screen glass, typically used for electronic displays, lacks the structural integrity needed for automotive safety and does not provide adequate protection against collisions. The plastic interlayer in laminated glass absorbs impact energy and reduces the risk of glass penetration, significantly enhancing occupant protection during accidents.
Visual Clarity and Noise Reduction Benefits
Screen glass offers superior visual clarity due to its uniform surface and minimal distortion, enhancing driver visibility and safety. Laminated glass excels in noise reduction by incorporating a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) layer that dampens external sounds and vibrations, providing a quieter cabin experience. Choosing laminated glass for windshields delivers a balance of safety, sound insulation, and reduced glare for optimal driving comfort.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Long-term Value
Screen glass typically offers a lower upfront cost compared to laminated glass for windshields, making it more affordable for immediate replacement. Laminated glass, while initially more expensive, provides superior durability, noise reduction, and enhanced safety, which translates into long-term savings by reducing the likelihood of frequent replacements and repairs. Evaluating windshields based on cost analysis requires balancing the initial affordability of screen glass with the extended lifespan and value retention that laminated glass delivers.
Repair and Replacement Considerations
Screen glass used for windshields offers easier and more cost-effective repair options compared to laminated glass, which often requires full replacement due to its multi-layer structure. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers bonded with an inner plastic interlayer, providing enhanced safety and durability but complicating repair processes. Repair specialists typically recommend replacing laminated windshields rather than repairing chips or cracks, whereas screen glass can often be fixed quickly, minimizing downtime and expenses.
Legal Requirements and Industry Standards
Laminated glass is legally mandated for vehicle windshields in many regions due to its enhanced safety properties, including its ability to hold together upon impact, reducing the risk of injury. Industry standards such as FMVSS 205 in the United States specify the use of laminated glass to meet strength, clarity, and shatter-resistance criteria. Screen glass, often used for side or rear windows, lacks these safety features and does not comply with regulations required for windshield applications.
Conclusion: Which Windshield Glass is Right for You?
Laminated glass is the preferred choice for windshields due to its superior safety features, including enhanced impact resistance and the ability to hold shards together during a collision, reducing injury risk. Screen glass, while offering clearer visibility and scratch resistance, lacks the same level of durability and protection in accidents. Choosing laminated glass ensures compliance with automotive safety standards and provides optimal protection for drivers and passengers.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com