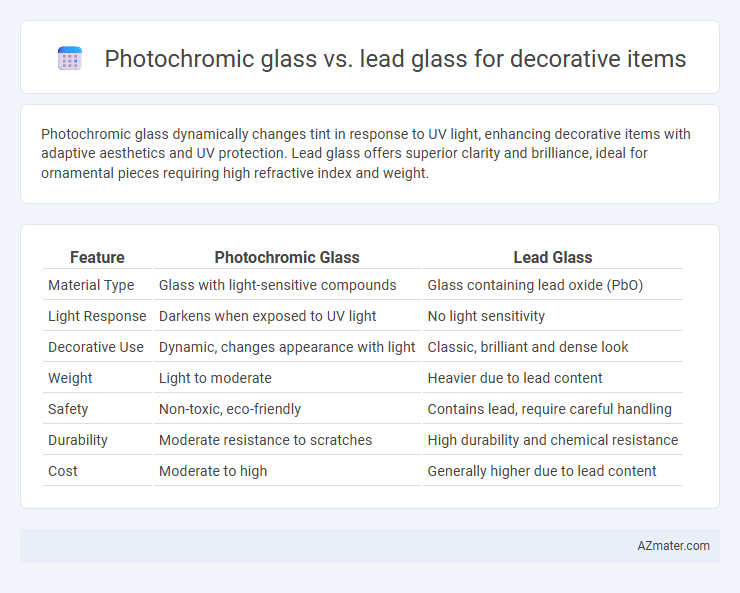
Photochromic glass dynamically changes tint in response to UV light, enhancing decorative items with adaptive aesthetics and UV protection. Lead glass offers superior clarity and brilliance, ideal for ornamental pieces requiring high refractive index and weight.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Photochromic Glass | Lead Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glass with light-sensitive compounds | Glass containing lead oxide (PbO) |
| Light Response | Darkens when exposed to UV light | No light sensitivity |
| Decorative Use | Dynamic, changes appearance with light | Classic, brilliant and dense look |
| Weight | Light to moderate | Heavier due to lead content |
| Safety | Non-toxic, eco-friendly | Contains lead, require careful handling |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to scratches | High durability and chemical resistance |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally higher due to lead content |
Introduction to Photochromic and Lead Glass
Photochromic glass changes its tint based on light exposure, utilizing photochromic molecules to darken in sunlight and return to clear indoors, offering dynamic aesthetic and functional benefits for decorative items. Lead glass, known for its high refractive index and brilliant clarity, contains lead oxide, enhancing brilliance, weight, and durability, making it a classic choice for ornamental pieces. Both materials serve distinct decorative purposes, with photochromic glass providing adaptive visual effects and lead glass delivering timeless elegance and sparkle.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Photochromic glass contains photochromic molecules such as silver halides embedded within its silicon dioxide-based matrix, allowing it to reversibly change color when exposed to ultraviolet light. Lead glass, also known as lead crystal, incorporates a significant proportion of lead oxide (PbO), which increases its density, refractive index, and brilliance, enhancing its decorative appeal. Chemically, photochromic glass exhibits dynamic light-responsive behavior, while lead glass is chemically stable with high weight and enhanced optical properties due to the lead oxide content.
Visual Aesthetics and Color Dynamics
Photochromic glass offers dynamic color changes that respond to light exposure, creating a visually engaging and interactive decorative piece with shifting hues. Lead glass, renowned for its high refractive index and brilliance, provides a classic, sparkling aesthetic with rich clarity and depth. While photochromic glass emphasizes evolving color dynamics, lead glass excels in delivering timeless visual elegance through its crystal-like luminosity.
Durability and Longevity
Photochromic glass offers enhanced durability with scratch-resistant coatings and UV-reactive properties that maintain visual clarity over time. Lead glass, while valued for its brilliance and weight, is more susceptible to surface scratches and may degrade with prolonged exposure to moisture and environmental factors. For decorative items prioritizing longevity, photochromic glass provides a longer-lasting, resilient option compared to traditional lead glass.
Light Responsiveness: Photochromic vs Lead Glass
Photochromic glass dynamically adjusts its tint in response to ultraviolet light, offering enhanced light responsiveness that adds both functional and aesthetic value to decorative items by changing color throughout the day. Lead glass, while prized for its high refractive index and brilliant clarity, remains static in appearance and does not react to light conditions. The adaptability of photochromic glass provides interactive visual effects, making it a superior choice for light-responsive decorative applications compared to the traditional and inert nature of lead glass.
Health and Environmental Impacts
Photochromic glass offers significant health benefits by reducing UV exposure through its light-reactive properties, minimizing potential skin and eye damage in decorative applications, while also being more environmentally friendly due to its non-toxic composition and recyclability. Lead glass, commonly used in decorative items for its brilliance and weight, poses serious health risks from lead leaching and prolonged exposure, contributing to toxic contamination. Environmentally, lead glass is less sustainable, with hazardous waste concerns during manufacturing and disposal, whereas photochromic glass supports eco-friendly practices and safer indoor environments.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Photochromic glass offers dynamic customization by changing tint in response to light, enabling innovative decorative designs that adapt to environmental conditions. Lead glass provides exceptional clarity and brilliance, allowing for intricate patterns and traditional craftsmanship, but lacks the responsive features of photochromic materials. Designers favor photochromic glass for modern, interactive aesthetics, while lead glass is preferred for classic elegance and detailed artistry.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Photochromic glass requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive, pH-neutral solutions to preserve its light-reactive coatings, avoiding harsh chemicals that can degrade its photochromic properties. Lead glass, known for its density and brilliance, demands careful handling to prevent scratches and tarnishing, often necessitating specialized glass cleaners designed for lead crystal surfaces. Both materials benefit from regular dusting and wiping with a soft microfiber cloth to maintain clarity and aesthetic appeal.
Cost Considerations for Decorative Use
Photochromic glass typically incurs higher costs due to advanced chemical treatments and technology required for its light-reactive properties, making it a premium choice for decorative items. Lead glass, by contrast, is generally more affordable and valued for its brilliance and density but involves higher health and environmental precautions in manufacturing and disposal. Cost considerations for decorative use must balance initial investment against aesthetic impact and long-term sustainability requirements.
Choosing the Right Glass for Decorative Items
Photochromic glass offers dynamic light-responsive color changes that enhance decorative items with functional aesthetics and energy efficiency, making it ideal for modern, interactive designs. Lead glass, known for its high refractive index and brilliance, provides exceptional clarity and sparkle, perfect for traditional luxury ornaments and intricate craftsmanship. Choosing the right glass depends on desired visual effects, durability, and the ambiance you want to create in the decorative setting.
Infographic: Photochromic glass vs Lead glass for Decorative item
 azmater.com
azmater.com