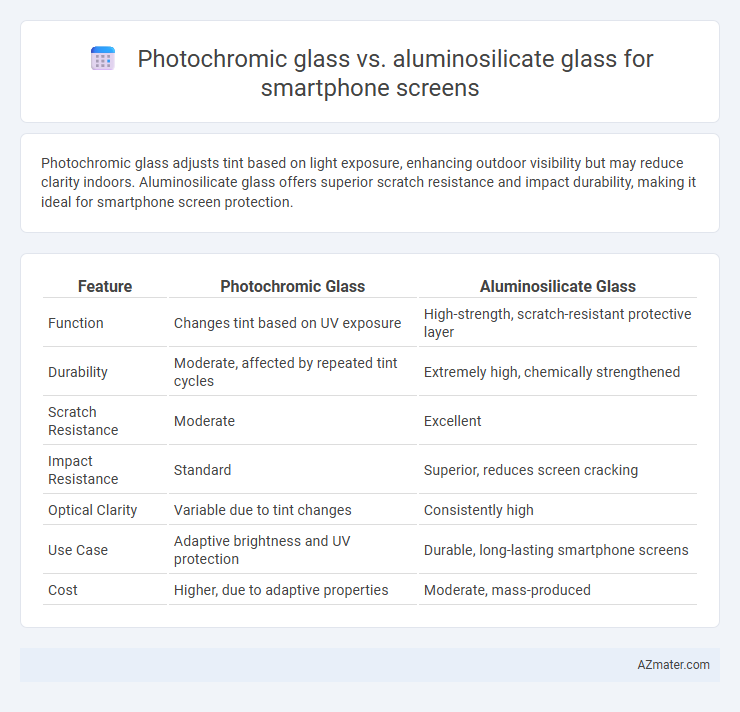
Photochromic glass adjusts tint based on light exposure, enhancing outdoor visibility but may reduce clarity indoors. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior scratch resistance and impact durability, making it ideal for smartphone screen protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Photochromic Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Changes tint based on UV exposure | High-strength, scratch-resistant protective layer |
| Durability | Moderate, affected by repeated tint cycles | Extremely high, chemically strengthened |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Impact Resistance | Standard | Superior, reduces screen cracking |
| Optical Clarity | Variable due to tint changes | Consistently high |
| Use Case | Adaptive brightness and UV protection | Durable, long-lasting smartphone screens |
| Cost | Higher, due to adaptive properties | Moderate, mass-produced |
Introduction to Smartphone Screen Glass Types
Photochromic glass and aluminosilicate glass represent two advanced materials used in smartphone screen technology, each offering distinct benefits. Aluminosilicate glass, renowned for its high scratch resistance and durability, is commonly employed to protect smartphone displays from daily wear and accidental drops. Photochromic glass, featuring light-responsive properties, dynamically adjusts its tint to enhance visibility and reduce glare under varying lighting conditions, improving user experience in outdoor environments.
What is Photochromic Glass?
Photochromic glass is a type of smart glass that changes its tint in response to ultraviolet (UV) light, enhancing screen visibility and reducing glare under bright sunlight. Unlike aluminosilicate glass, known for its exceptional hardness and scratch resistance due to its unique aluminum and silicon oxide composition, photochromic glass prioritizes adaptive light modulation for user comfort. This dynamic light control helps improve outdoor readability while maintaining clarity indoors, making it an innovative choice for smartphone screens seeking both protection and enhanced usability.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a high-strength, chemically toughened glass commonly used in smartphone screens for its superior scratch resistance and impact durability compared to traditional glass types. It consists mainly of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, which create a robust glass matrix ideal for protecting devices against drops and everyday wear. Unlike photochromic glass that changes tint based on light exposure, aluminosilicate glass provides consistent clarity and toughness without altering visual properties.
Key Properties of Photochromic Glass
Photochromic glass used in smartphone screens offers dynamic light modulation by darkening in response to ultraviolet (UV) exposure, enhancing outdoor visibility and reducing glare. Its key properties include excellent UV responsiveness, rapid reversible color change, and high optical clarity that preserves touchscreen sensitivity and display accuracy. Unlike aluminosilicate glass, which prioritizes extreme hardness and impact resistance, photochromic glass integrates adaptive light control while maintaining sufficient durability for mobile devices.
Key Properties of Aluminosilicate Glass
Aluminosilicate glass is renowned for its superior hardness, enhanced scratch resistance, and excellent impact durability, making it ideal for smartphone screens that demand robust protection. Its chemical composition includes aluminum oxide, which increases thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion compared to conventional glass. These properties provide a balanced combination of toughness and optical clarity, outperforming photochromic glass in durability and everyday usability for mobile devices.
Durability Comparison: Photochromic vs Aluminosilicate
Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone screens like Gorilla Glass, offers superior durability with high resistance to scratches, impacts, and bending due to its chemically strengthened structure. Photochromic glass, while providing adaptive light-darkening properties for eye comfort, generally exhibits lower mechanical strength and scratch resistance compared to aluminosilicate glass. For rugged smartphone applications requiring maximum screen protection, aluminosilicate glass remains the more durable choice over photochromic variants.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Photochromic glass offers adaptive tinting but typically has lower scratch resistance compared to aluminosilicate glass, which is engineered for enhanced hardness and durability. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone screens like Gorilla Glass, provides superior impact resistance by utilizing chemical strengthening processes such as ion exchange. The structural composition of aluminosilicate glass results in better protection against drops and abrasions, making it the preferred choice for resilient smartphone displays.
Display Quality and User Experience
Photochromic glass offers dynamic light adaptation, enhancing outdoor visibility by darkening under sunlight, which improves display readability and reduces eye strain. Aluminosilicate glass, known for high durability and scratch resistance, maintains consistent clarity and touch sensitivity, ensuring a smooth user experience. While photochromic glass optimizes natural light conditions, aluminosilicate glass excels in long-term protection, making both materials essential for balancing display quality and user satisfaction in smartphones.
Cost and Manufacturing Differences
Photochromic glass for smartphone screens involves complex chemical treatments to enable light-induced tint changes, resulting in higher production costs due to specialized coating processes and raw materials. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphones, offers superior strength and scratch resistance through an ion-exchange manufacturing method that is more cost-effective and established at scale. The price disparity arises from photochromic glass requiring bespoke manufacturing setups and slower production rates, while aluminosilicate glass benefits from streamlined, mass-production techniques reducing overall expenses.
Which Glass is Better for Your Smartphone?
Photochromic glass offers adaptive tinting that adjusts to light conditions, reducing glare and enhancing outdoor screen visibility, making it ideal for users frequently exposed to sunlight. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its exceptional hardness and scratch resistance, provides superior durability and protection against drops and daily wear, which is crucial for long-term smartphone use. Choosing between photochromic and aluminosilicate glass depends on whether you prioritize dynamic visual comfort or maximum screen protection for your smartphone.
Infographic: Photochromic glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com