Opal glass offers superior light diffusion and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for luxury vehicle windshields, while laminated glass provides enhanced safety and impact resistance, commonly used for standard automotive windshields. Laminated glass consists of multiple layers with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, ensuring shatterproof protection and UV filtration.
Table of Comparison
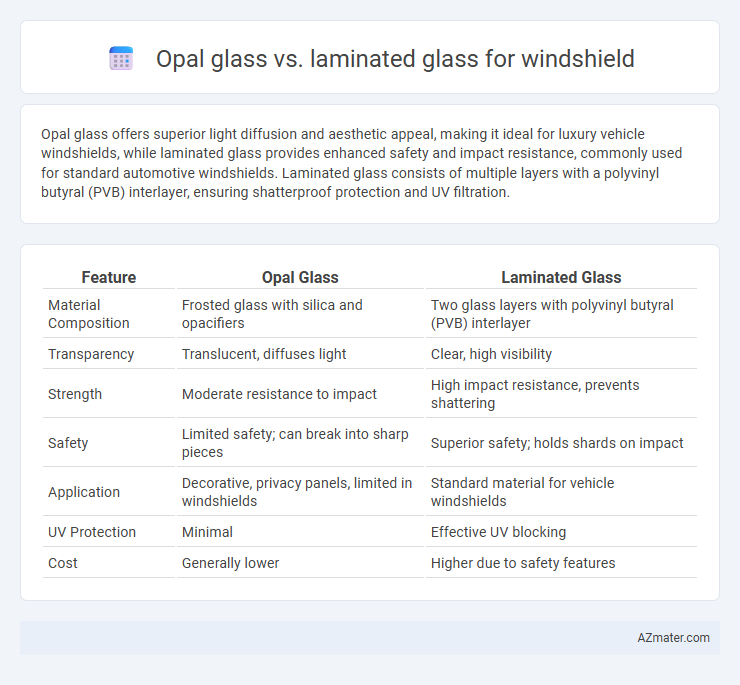
| Feature | Opal Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Frosted glass with silica and opacifiers | Two glass layers with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Transparency | Translucent, diffuses light | Clear, high visibility |
| Strength | Moderate resistance to impact | High impact resistance, prevents shattering |
| Safety | Limited safety; can break into sharp pieces | Superior safety; holds shards on impact |
| Application | Decorative, privacy panels, limited in windshields | Standard material for vehicle windshields |
| UV Protection | Minimal | Effective UV blocking |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to safety features |
Introduction to Windshield Glass Types
Opal glass and laminated glass are two key types used in automotive windshields, each offering distinct safety benefits. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing superior impact resistance and preventing shattering upon collision. Opal glass, often used for its aesthetic qualities, lacks the laminated structure, making laminated glass the preferred choice for enhanced windshield safety and durability in vehicles.
What is Opal Glass?
Opal glass, used in automotive applications, is a type of translucent glass that diffuses light for enhanced privacy and glare reduction while maintaining natural light transmission. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of multiple glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer for increased safety and shatter resistance, opal glass primarily focuses on aesthetic and light-diffusing properties. Its unique composition makes it ideal for windshields requiring soft light diffusion without compromising visibility and structural integrity.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which holds the layers in place even when shattered, enhancing safety and durability. This structure provides superior impact resistance and prevents glass fragments from dispersing upon breakage, making it the preferred material for windshields in vehicles. Compared to opal glass, laminated glass offers increased structural integrity and better protection against penetration and shattering during collisions.
Manufacturing Process: Opal vs. Laminated Glass
Opal glass manufacturing involves a specialized melting process where opacifying agents such as bone ash or tin oxide are added to molten glass to create a translucent or milky appearance, requiring precise temperature control and extended cooling times. Laminated glass production consists of bonding two or more glass layers with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), using heat and pressure to achieve strong adhesion and enhanced safety features like impact resistance and shatter retention. The opal glass process emphasizes optical qualities and diffusion, whereas laminated glass manufacturing prioritizes structural integrity and safety performance for windshield applications.
Safety Features Comparison
Opal glass offers enhanced shatter resistance due to its composite structure, reducing the risk of sharp glass fragments upon impact, while laminated glass includes a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that holds glass shards together, preventing ejection and maintaining windshield integrity during collisions. Laminated glass excels in UV protection and sound insulation, contributing to overall passenger safety and comfort. Both types provide crucial safety benefits, but laminated glass's proven ability to absorb impact energy and maintain visibility under stress makes it the preferred choice for windshield applications.
Optical Clarity and Visibility
Opal glass typically offers superior optical clarity compared to laminated glass, resulting in less distortion and enhanced visibility for drivers. Laminated glass, while providing excellent safety benefits through its impact resistance and shatter-retaining properties, may slightly reduce optical clarity due to its multiple layers and interlayer films. For windshield applications where clear, unobstructed vision is critical, opal glass is often preferred to maximize driver safety and comfort.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Opal glass offers moderate durability but is prone to chipping and cracking under heavy impact, making it less ideal for windshield applications compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer, significantly enhancing impact resistance and preventing shattering upon collision. This laminated structure provides superior durability and safety, ensuring better performance in automotive windshields under high stress conditions.
Cost Differences and Affordability
Opal glass windshields generally cost more than laminated glass due to their advanced light-diffusing properties and enhanced aesthetic appeal. Laminated glass, favored for its safety features and durability, is more affordable and widely used in standard vehicle windshields. When considering cost differences, laminated glass offers better affordability for budget-conscious buyers, whereas opal glass suits those prioritizing design despite higher price points.
Suitability for Modern Vehicles
Opal glass, known for its high clarity and UV resistance, offers excellent visibility and durability for modern vehicle windshields, making it ideal for advanced driver-assistance systems and enhanced safety features. Laminated glass provides superior impact resistance and noise reduction, crucial for urban environments and collision protection in contemporary automotive design. Both materials are engineered to meet strict automotive safety standards, but the choice depends on balancing optical performance with structural integrity for specific vehicle models.
Final Verdict: Which Glass is Better for Windshields?
Opal glass provides superior clarity and aesthetic appeal, while laminated glass offers enhanced safety through its multi-layer construction that prevents shattering. For windshield applications, laminated glass is generally preferred due to its impact resistance, UV protection, and ability to hold together upon impact, reducing injury risk. The final verdict favors laminated glass as the better choice for windshields, prioritizing safety and durability over visual appeal.
Infographic: Opal glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com