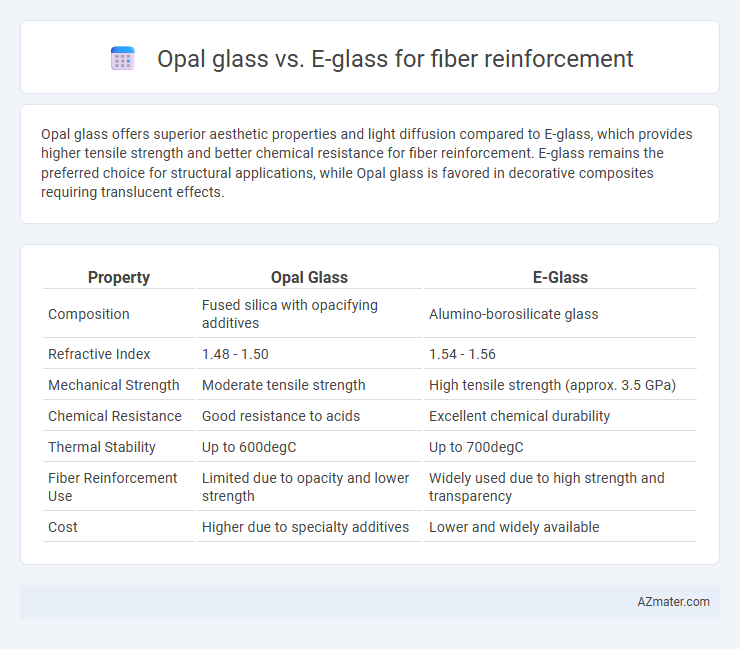
Opal glass offers superior aesthetic properties and light diffusion compared to E-glass, which provides higher tensile strength and better chemical resistance for fiber reinforcement. E-glass remains the preferred choice for structural applications, while Opal glass is favored in decorative composites requiring translucent effects.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Opal Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fused silica with opacifying additives | Alumino-borosilicate glass |
| Refractive Index | 1.48 - 1.50 | 1.54 - 1.56 |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength (approx. 3.5 GPa) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids | Excellent chemical durability |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 600degC | Up to 700degC |
| Fiber Reinforcement Use | Limited due to opacity and lower strength | Widely used due to high strength and transparency |
| Cost | Higher due to specialty additives | Lower and widely available |
Introduction to Fiber Reinforced Materials
Fiber reinforcement enhances composite materials by improving strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. Opal glass fibers provide superior aesthetic qualities and better light diffusion compared to E-glass, which is commonly used for its high tensile strength and cost-effectiveness. The choice between Opal glass and E-glass fibers depends on the specific application requirements such as mechanical performance, optical properties, and budget constraints.
What is Opal Glass?
Opal glass is a type of glass fiber characterized by its milky, translucent appearance due to the dispersion of micro-sized particles within the glass matrix, enhancing its optical properties and providing improved fiber-matrix bonding in composite materials. This glass type offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to standard E-glass, making it suitable for high-performance fiber reinforcement applications in aerospace and automotive industries. The enhanced durability and moisture resistance of opal glass fibers contribute to longer-lasting composite structures with increased mechanical strength and environmental resilience.
What is E-Glass?
E-glass, or electrical-grade glass, is a widely used type of fiberglass known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, high tensile strength, and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it ideal for fiber reinforcement in composites. Unlike opal glass, which is primarily a decorative or optical material, E-glass fibers serve as reinforcement in structural applications such as automotive parts, aerospace components, and marine vessels due to their durability and cost-effectiveness. The high silica content and alumina, boron, and calcium oxide components in E-glass contribute to its thermal stability and mechanical performance in composite materials.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Opal glass fiber reinforcement primarily consists of silica mixed with metal oxides such as aluminum oxide and calcium oxide, resulting in a more opaque and chemically resistant material compared to E-glass, which is predominantly composed of alumino-borosilicate with low alkali content tailored for high strength and electrical insulation. Manufacturing opal glass fibers involves higher melting temperatures and controlled cooling to achieve its distinctive opacity and improved chemical durability, while E-glass fibers are produced through rapid fiber drawing from molten glass to maximize tensile strength and minimize defects. These compositional and manufacturing contrasts influence the selection of opal glass for applications requiring enhanced chemical resistance and E-glass for structural reinforcement due to its superior mechanical properties.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Opal glass fiber reinforcement exhibits superior tensile strength and improved impact resistance compared to conventional E-glass, making it suitable for high-performance composite applications. E-glass fibers offer excellent durability with good resistance to chemical and environmental degradation but typically show lower strength-to-weight ratios than Opal glass. The enhanced mechanical properties of Opal glass, including higher modulus and better fatigue resistance, contribute to increased longevity and reliability in demanding structural uses.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Opal glass fiber exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to E-glass, withstanding higher temperatures up to 1000degC versus E-glass's limit around 700degC. This enhanced heat tolerance makes Opal glass ideal for applications in aerospace and automotive industries where thermal stability is critical. The improved thermal resistance of Opal glass fibers reduces degradation and maintains structural integrity under extreme thermal conditions.
Chemical Resistance and Stability
Opal glass exhibits superior chemical resistance and stability compared to E-glass, making it more suitable for harsh chemical environments and prolonged exposure to alkaline or acidic substances. Its enhanced resistance to hydrolytic degradation ensures longer-lasting performance in corrosive conditions, whereas E-glass is more susceptible to chemical attack and moisture-induced weakening. The improved durability of Opal glass fibers results in better dimensional stability and mechanical strength retention over time in aggressive chemical applications.
Applications in Industry
Opal glass fibers exhibit superior chemical resistance and improved thermal properties, making them ideal for high-stress environments such as aerospace and automotive industries where durability and heat resistance are critical. E-glass fibers, renowned for their excellent tensile strength and cost-effectiveness, dominate applications in construction, marine, and wind energy sectors due to their versatility and widespread availability. The choice between Opal glass and E-glass fibers hinges on balancing performance requirements with economic considerations in industrial composite manufacturing.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Opal glass fiber reinforcement exhibits moderate cost levels and niche availability, primarily used in specialized composite applications due to its unique optical properties. E-glass fibers dominate the market with lower production costs and widespread availability, making them the most economically feasible option for large-scale structural reinforcements. Cost efficiency and global supply chain robustness position E-glass as the preferred material over opal glass in fiber reinforcement industries.
Choosing Between Opal Glass and E-Glass
Choosing between Opal glass and E-glass for fiber reinforcement depends on specific mechanical and thermal properties required in the application. Opal glass fibers offer enhanced chemical resistance and superior aesthetic qualities, making them ideal for decorative composites, while E-glass fibers provide higher tensile strength and better electrical insulation, suitable for structural components and aerospace uses. Consider factors like durability, cost, and environmental exposure when selecting the appropriate glass fiber to optimize performance and longevity in composite materials.
Infographic: Opal glass vs E-glass for Fiber reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com