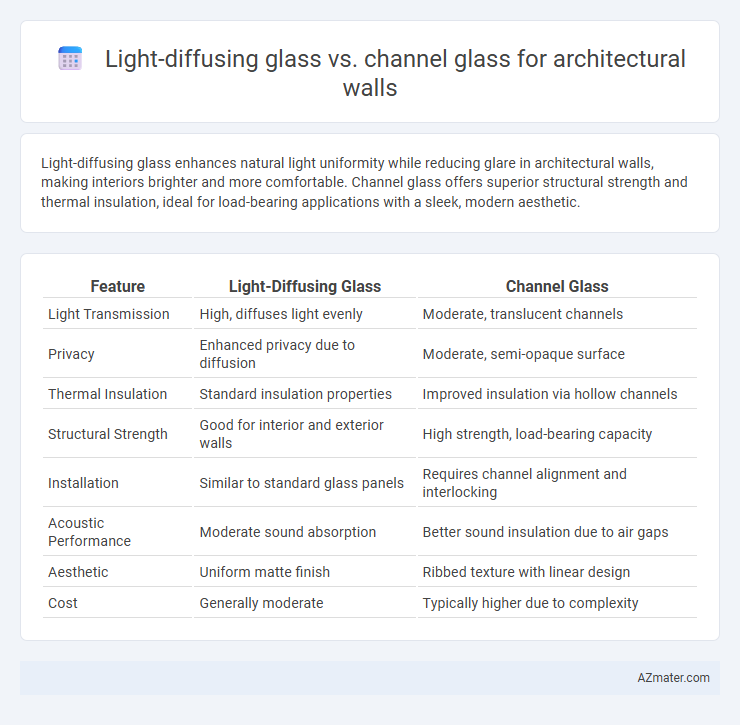
Light-diffusing glass enhances natural light uniformity while reducing glare in architectural walls, making interiors brighter and more comfortable. Channel glass offers superior structural strength and thermal insulation, ideal for load-bearing applications with a sleek, modern aesthetic.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Light-Diffusing Glass | Channel Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Light Transmission | High, diffuses light evenly | Moderate, translucent channels |
| Privacy | Enhanced privacy due to diffusion | Moderate, semi-opaque surface |
| Thermal Insulation | Standard insulation properties | Improved insulation via hollow channels |
| Structural Strength | Good for interior and exterior walls | High strength, load-bearing capacity |
| Installation | Similar to standard glass panels | Requires channel alignment and interlocking |
| Acoustic Performance | Moderate sound absorption | Better sound insulation due to air gaps |
| Aesthetic | Uniform matte finish | Ribbed texture with linear design |
| Cost | Generally moderate | Typically higher due to complexity |
Introduction to Architectural Glass Walls
Architectural glass walls enhance natural light while maintaining privacy and energy efficiency, with light-diffusing glass offering uniform illumination by scattering sunlight to reduce glare and shadows. Channel glass, characterized by its U-shaped vertical sections, provides structural support, thermal insulation, and a textured surface that diffuses light while allowing translucency. Both materials contribute to modern building facades by balancing aesthetics, daylight optimization, and functional performance.
What is Light-Diffusing Glass?
Light-diffusing glass is engineered to scatter transmitted light evenly, reducing glare and enhancing visual comfort in architectural walls while maintaining transparency. This glass type utilizes micro-etched patterns or embedded particles to diffuse sunlight, creating a soft, uniform illumination ideal for office or commercial spaces. Compared to channel glass, which features structural grooves for strength and insulation, light-diffusing glass prioritizes ambient light quality and aesthetic softness in interior environments.
What is Channel Glass?
Channel glass is a structural glazing solution consisting of U-shaped glass profiles that interlock to form continuous, load-bearing walls with excellent translucency. This architectural wall system offers enhanced light diffusion and privacy while maintaining strength and thermal insulation. Compared to light-diffusing glass, channel glass provides superior impact resistance and uniform light distribution, making it ideal for modern facades and office partitions.
Comparison of Light Transmission Properties
Light-diffusing glass offers uniform light distribution by scattering incoming light, reducing glare and creating a soft, even illumination ideal for interior architectural walls. Channel glass, with its ribbed vertical structure, allows higher direct light transmission while providing structural support and enhanced privacy through partial light diffusion. Compared to channel glass, light-diffusing glass typically achieves lower total light transmission but ensures smoother, more homogeneous light diffusion, making it preferable for spaces requiring balanced daylight without harsh shadows.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Light-diffusing glass offers superior aesthetic appeal for architectural walls by scattering natural light evenly, creating a soft, glowing ambiance that enhances interior spaces with privacy and style. Channel glass provides distinct linear patterns and structural rigidity, enabling innovative design flexibility through modular and load-bearing wall applications that emphasize rhythm and texture. Both materials cater to modern architectural trends but differ in visual texture and integration, with light-diffusing glass favoring smooth, ethereal light effects and channel glass supporting bold, geometric design statements.
Structural Performance and Durability
Light-diffusing glass offers enhanced structural performance with uniform load distribution and high impact resistance, making it well-suited for architectural walls requiring consistent natural light without compromising strength. Channel glass provides superior durability by integrating a U-shaped profile that resists wind loads and thermal expansion, ensuring long-term stability and minimal maintenance. Both materials excel in structural applications, but light-diffusing glass prioritizes optical clarity under stress, while channel glass emphasizes robustness against environmental factors.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Capabilities
Light-diffusing glass offers superior thermal insulation due to its ability to scatter natural light while minimizing heat transfer, making it ideal for energy-efficient architectural walls. Channel glass provides excellent acoustic insulation with its hollow, laminated design that effectively reduces noise pollution in urban environments. Both materials contribute to comfortable indoor climates, but light-diffusing glass excels in thermal performance, whereas channel glass is preferred for soundproofing.
Installation Processes and Challenges
Light-diffusing glass offers straightforward installation with standard glazing techniques but requires careful handling to avoid surface damage, while channel glass demands precise alignment within aluminum channels and specialized sealants to ensure weather tightness. The rigid framing system of channel glass often requires skilled labor and longer installation times due to the need for exact positioning and sealing between panels. Both materials present challenges in managing thermal expansion, but channel glass systems typically provide better integrated support, minimizing stress on the glass during installation.
Cost Analysis and Maintenance Needs
Light-diffusing glass typically incurs higher initial costs due to specialized manufacturing processes that enhance natural light distribution, whereas channel glass offers a more budget-friendly option with simpler production. Maintenance-wise, light-diffusing glass demands periodic cleaning to prevent haze buildup that can affect translucency, while channel glass requires minimal upkeep thanks to its durable surface and integrated channels that resist dirt accumulation. Evaluating lifecycle costs, channel glass often provides cost-efficiency through lower maintenance expenses and longer service intervals despite the higher upfront investment of light-diffusing alternatives.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Architectural Wall
Light-diffusing glass evenly disperses natural light, reducing glare and enhancing interior illumination, making it ideal for spaces requiring soft, uniform light distribution. Channel glass offers superior structural strength and thermal insulation, with vertical channels that provide added rigidity and privacy through translucent textures. Selecting the right glass depends on the balance between aesthetic goals, light control needs, and structural requirements of the architectural wall.
Infographic: Light-diffusing glass vs Channel glass for Architectural wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com