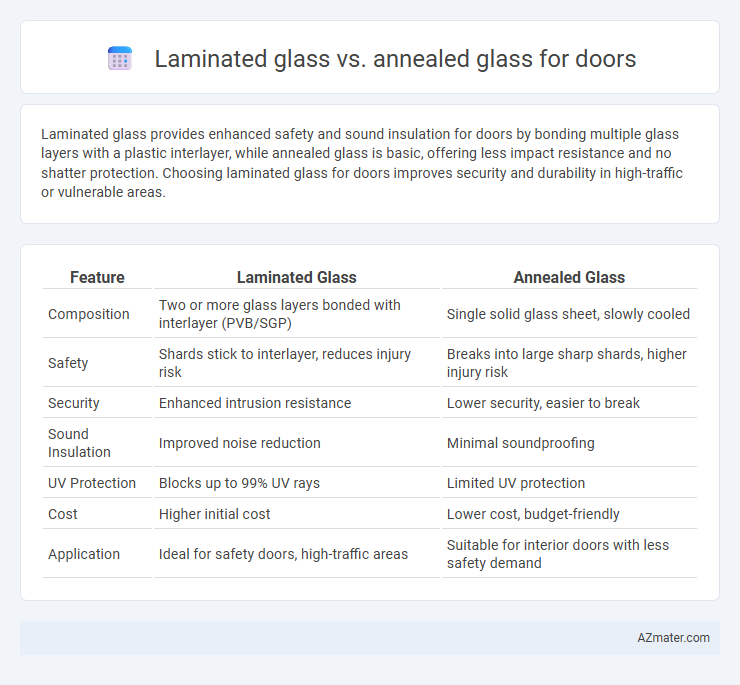
Laminated glass provides enhanced safety and sound insulation for doors by bonding multiple glass layers with a plastic interlayer, while annealed glass is basic, offering less impact resistance and no shatter protection. Choosing laminated glass for doors improves security and durability in high-traffic or vulnerable areas.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Annealed Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more glass layers bonded with interlayer (PVB/SGP) | Single solid glass sheet, slowly cooled |
| Safety | Shards stick to interlayer, reduces injury risk | Breaks into large sharp shards, higher injury risk |
| Security | Enhanced intrusion resistance | Lower security, easier to break |
| Sound Insulation | Improved noise reduction | Minimal soundproofing |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% UV rays | Limited UV protection |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
| Application | Ideal for safety doors, high-traffic areas | Suitable for interior doors with less safety demand |
Introduction to Laminated and Annealed Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, enhancing safety by preventing shattering upon impact, making it ideal for door applications requiring security and noise reduction. Annealed glass is standard float glass cooled slowly to relieve internal stresses, offering basic durability but shatters into sharp shards when broken, posing safety risks for doors. Choosing between laminated and annealed glass depends on safety needs, impact resistance, and noise insulation requirements for door installations.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety and sound insulation for doors. Annealed glass undergoes controlled slow cooling during manufacturing to reduce internal stresses but remains a single solid sheet without interlayers. The lamination process involves heat and pressure to fuse layers, whereas annealed glass is simply cooled gradually after forming to improve durability but lacks the composite structure of laminated glass.
Key Differences Between Laminated and Annealed Glass
Laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety by holding shards together upon breakage, making it ideal for door applications requiring security and noise reduction. Annealed glass is a single pane that has been slowly cooled to relieve internal stresses, offering basic strength but shattering into large, sharp pieces which pose safety risks in door installations. The key differences lie in laminated glass's superior impact resistance and safety features compared to annealed glass's vulnerability to breakage and limited protective qualities.
Safety Features and Impact Resistance
Laminated glass offers superior safety features compared to annealed glass due to its multi-layer construction, which includes a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that holds the glass shards together upon impact, preventing sharp fragments from causing injury. Impact resistance of laminated glass is significantly higher, making it ideal for doors in areas prone to forced entry or severe weather, as it can absorb and dissipate energy without shattering. Annealed glass, while less expensive, lacks this interlayer and shatters into large, dangerous shards, posing higher risks in safety-critical door applications.
Security and Break-In Protection
Laminated glass offers superior security and break-in protection for doors due to its multi-layered construction, which holds the glass together even when shattered, making forced entry significantly more difficult. Annealed glass, while affordable and clear, lacks the reinforced bonding and easily breaks into large, sharp shards that can be exploited during break-ins. Choosing laminated glass enhances safety by delaying intrusion attempts and reducing the risk of injury from broken glass.
Sound Insulation Capabilities
Laminated glass offers superior sound insulation for doors due to its interlayer that dampens noise vibrations, significantly reducing sound transmission compared to annealed glass. Annealed glass lacks this specialized interlayer, making it less effective at blocking external noise and vibrations. Choosing laminated glass enhances acoustic comfort, especially in noisy environments or locations requiring better soundproofing.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection
Laminated glass for doors provides superior energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer and improving insulation due to its multiple layers bonded with an interlayer, which also blocks up to 99% of harmful UV rays, preventing interior fading and damage. Annealed glass, being a single layer without additional coatings or interlayers, offers minimal UV protection and lower thermal performance, leading to higher energy costs and less effective insulation. Choosing laminated glass over annealed glass enhances thermal comfort while protecting interior furnishings from UV deterioration and reduces reliance on heating and cooling systems.
Design Versatility and Aesthetic Options
Laminated glass offers superior design versatility for doors through customizable interlayers that can incorporate colors, patterns, and textures, enhancing both aesthetic appeal and privacy. Annealed glass provides a clearer, more traditional look but lacks the ability to embed decorative elements, limiting creative design options. For projects prioritizing unique visual effects and enhanced safety, laminated glass is the preferred choice.
Cost Comparison: Laminated vs Annealed Glass for Doors
Laminated glass for doors generally costs 30-50% more than annealed glass due to its multi-layer construction involving a polymer interlayer that enhances safety and sound insulation. Annealed glass remains the most budget-friendly option, but it lacks the impact resistance and security features of laminated glass, which can reduce long-term replacement and repair expenses. Investing in laminated glass can lead to cost savings by minimizing damage risks and improving energy efficiency, justifying the higher initial expense compared to annealed glass.
Choosing the Right Glass Type for Your Door
Laminated glass offers enhanced security and safety for doors due to its interlayer that holds shards in place upon impact, making it ideal for high-traffic or exterior doors. Annealed glass, being standard and more cost-effective, provides clarity and basic protection but shatters into large, sharp pieces when broken, reducing its suitability for safety-critical applications. When choosing the right glass type for your door, prioritize laminated glass for superior durability and safety, while annealed glass suits interior or less vulnerable locations where budget is a primary concern.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Annealed glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com