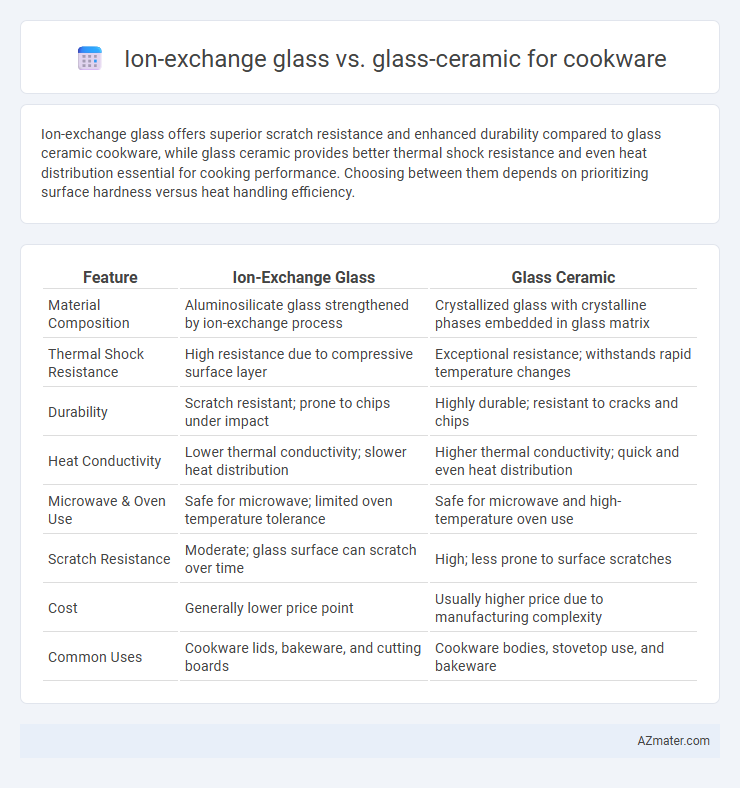
Ion-exchange glass offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced durability compared to glass ceramic cookware, while glass ceramic provides better thermal shock resistance and even heat distribution essential for cooking performance. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing surface hardness versus heat handling efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ion-Exchange Glass | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Aluminosilicate glass strengthened by ion-exchange process | Crystallized glass with crystalline phases embedded in glass matrix |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High resistance due to compressive surface layer | Exceptional resistance; withstands rapid temperature changes |
| Durability | Scratch resistant; prone to chips under impact | Highly durable; resistant to cracks and chips |
| Heat Conductivity | Lower thermal conductivity; slower heat distribution | Higher thermal conductivity; quick and even heat distribution |
| Microwave & Oven Use | Safe for microwave; limited oven temperature tolerance | Safe for microwave and high-temperature oven use |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate; glass surface can scratch over time | High; less prone to surface scratches |
| Cost | Generally lower price point | Usually higher price due to manufacturing complexity |
| Common Uses | Cookware lids, bakeware, and cutting boards | Cookware bodies, stovetop use, and bakeware |
Introduction: Ion-Exchange Glass vs Glass Ceramic Cookware
Ion-exchange glass cookware offers enhanced strength and scratch resistance due to a chemical strengthening process replacing smaller ions with larger ones, improving durability for daily use. Glass ceramic cookware provides superior thermal shock resistance and even heat distribution, making it ideal for stovetop cooking and oven use. Understanding the material properties helps consumers choose between the toughness of ion-exchange glass and the heat performance of glass ceramic cookware.
Material Composition: Ion-Exchange Glass Explained
Ion-exchange glass for cookware undergoes a chemical strengthening process where smaller sodium ions in the glass are replaced by larger potassium ions, enhancing surface compressive stress and improving durability. This material composition results in exceptional resistance to thermal shock and scratches, making it ideal for glass cookware exposed to rapid temperature changes. In contrast, glass ceramic cookware consists of crystalline structures embedded in glass, offering superior heat resistance and even heat distribution but lacks the ion-exchange strengthening benefits found in ion-exchange glass.
Glass Ceramic: Structure and Properties
Glass ceramic cookware features a unique microcrystalline structure formed through controlled crystallization of glass, providing exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock. Its low thermal expansion coefficient ensures even heat distribution and durability under rapid temperature changes, making it ideal for stovetop and oven use. Additionally, glass ceramic surfaces are non-porous and chemically inert, offering superior stain resistance and easy maintenance compared to ion-exchange glass cookware.
Thermal Shock Resistance: A Comparative Analysis
Ion-exchange glass offers moderate thermal shock resistance by strengthening the surface through a chemical process that replaces smaller ions with larger ones, reducing susceptibility to cracking under rapid temperature changes. Glass ceramic, engineered with a crystalline structure embedded in a glass matrix, provides superior thermal shock resistance due to its low thermal expansion coefficient, allowing it to withstand sudden temperature shifts without fracturing. For cookware applications, glass ceramic materials are preferred for their durability against thermal stress, ensuring longer-lasting performance compared to ion-exchange glass.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Ion-exchange glass cookware offers enhanced durability through a chemical strengthening process that compresses the surface layer, making it more resistant to cracks and chips compared to standard glass. Glass ceramic cookware excels in scratch resistance due to its crystalline structure, providing superior thermal stability and robustness under high-temperature cooking conditions. While ion-exchange glass improves surface hardness, glass ceramic's inherent toughness and resistance to abrasion make it more suitable for long-term durability in demanding kitchen environments.
Heat Distribution and Cooking Performance
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced heat resistance and uniform heat distribution due to its chemically strengthened surface, making it suitable for steady cooking at moderate temperatures. Glass ceramic cookware excels in thermal shock resistance and provides rapid, even heat distribution, which improves cooking performance by preventing hotspots and ensuring consistent food texture. The superior heat retention and durability of glass ceramics generally result in better overall cooking performance compared to ion-exchange glass.
Safety Features: Handling and Breakage
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced safety features through a chemical strengthening process that increases its resistance to breakage and chipping, making it more durable during handling and everyday use. Glass ceramic cookware combines thermal shock resistance with mechanical strength, allowing it to withstand sudden temperature changes without cracking, which significantly reduces the risk of breakage during cooking. Both materials prioritize safety, but ion-exchange glass focuses on surface toughness while glass ceramics deliver superior resistance to thermal stress and impact.
Design Versatility and Aesthetics
Ion-exchange glass offers sleek, glossy surfaces with vibrant color options, enhancing modern kitchen aesthetics and permitting custom shapes due to its malleability during manufacturing. Glass-ceramic cookware provides a matte or satin finish with a more consistent texture, showcasing minimalist and timeless designs well-suited for traditional and contemporary kitchens. The design versatility of ion-exchange glass excels in creating bold, eye-catching pieces, whereas glass-ceramic prioritizes subtle elegance and durability with heat-resistant patterns.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Ion-exchange glass cookware typically offers a lower price point and is widely available in most retail and online markets due to its simpler manufacturing process and mass production. Glass ceramic cookware, though generally more expensive, tends to be less commonly stocked and found primarily in specialty kitchenware stores, reflecting its higher durability and thermal shock resistance. Market availability of glass ceramic is limited compared to ion-exchange glass, impacting overall cost accessibility for consumers.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cookware Material
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced scratch resistance and durability due to its chemically strengthened surface, making it ideal for everyday use in cookware. Glass ceramic cookware excels in thermal shock resistance and even heat distribution, suitable for high-temperature cooking and stovetop applications. Selecting the right cookware material depends on your cooking style: prioritize ion-exchange glass for durability and ease of maintenance, or opt for glass ceramic when superior heat performance and thermal stability are essential.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs Glass ceramic for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com