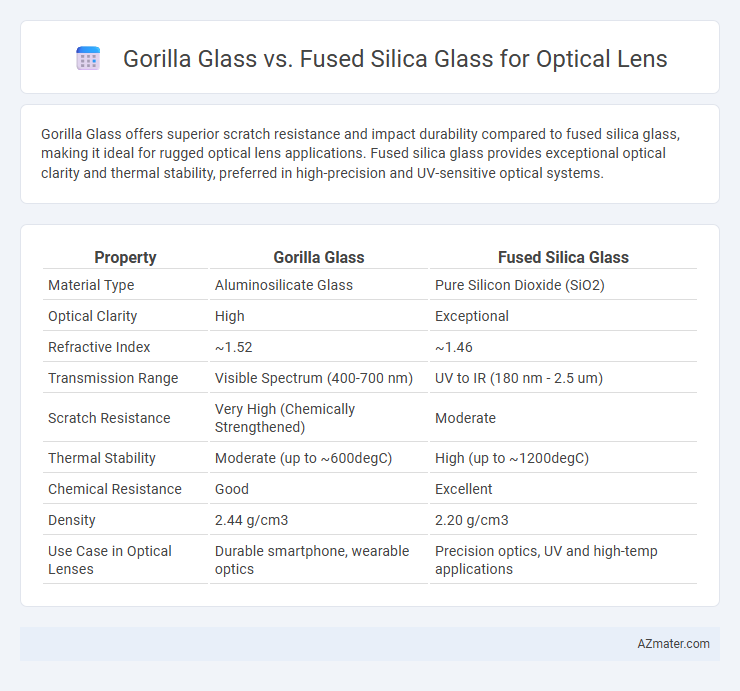
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and impact durability compared to fused silica glass, making it ideal for rugged optical lens applications. Fused silica glass provides exceptional optical clarity and thermal stability, preferred in high-precision and UV-sensitive optical systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gorilla Glass | Fused Silica Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Aluminosilicate Glass | Pure Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) |
| Optical Clarity | High | Exceptional |
| Refractive Index | ~1.52 | ~1.46 |
| Transmission Range | Visible Spectrum (400-700 nm) | UV to IR (180 nm - 2.5 um) |
| Scratch Resistance | Very High (Chemically Strengthened) | Moderate |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate (up to ~600degC) | High (up to ~1200degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Density | 2.44 g/cm3 | 2.20 g/cm3 |
| Use Case in Optical Lenses | Durable smartphone, wearable optics | Precision optics, UV and high-temp applications |
Introduction to Gorilla Glass and Fused Silica Glass
Gorilla Glass, a chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glass developed by Corning, offers high scratch resistance and durability, making it ideal for optical lenses in devices requiring impact protection. Fused silica glass, composed of high-purity silicon dioxide, provides exceptional optical clarity and thermal stability, essential for precision lenses in scientific and industrial applications. Comparing their properties highlights Gorilla Glass's toughness versus fused silica's superior optical performance and thermal resistance.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Gorilla Glass, primarily composed of alkali-aluminosilicate, undergoes a chemical strengthening process through ion exchange, resulting in high scratch resistance and durability for optical lenses. Fused silica glass consists of nearly pure silicon dioxide (SiO2), manufactured via fusion of high-purity quartz sand at extremely high temperatures, yielding exceptional thermal stability and optical clarity. The manufacturing of Gorilla Glass involves precise thermal treatment and ion-exchange baths, whereas fused silica lenses require controlled melting and annealing processes to maintain their low thermal expansion and high transparency.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Gorilla Glass offers high optical clarity with transmission rates exceeding 90%, making it suitable for applications requiring sharp image reproduction and minimal light distortion. Fused silica glass outperforms Gorilla Glass in light transmission, boasting over 92% transmission across a broad wavelength range, including UV and visible spectra, ensuring superior clarity and color fidelity in optical lenses. The inherent low dispersion and excellent surface quality of fused silica result in less chromatic aberration compared to Gorilla Glass, enhancing precision in high-performance optical systems.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Gorilla Glass exhibits superior mechanical strength with high resistance to scratches and impacts, making it ideal for optical lenses requiring durability under harsh conditions. Fused silica glass offers exceptional thermal stability and chemical durability but has lower resistance to mechanical shocks compared to Gorilla Glass. For applications demanding robust mechanical performance, Gorilla Glass provides enhanced durability, while fused silica excels in environments requiring minimal thermal expansion and high optical clarity.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance compared to fused silica glass due to its chemically strengthened surface, making it highly durable for optical lenses in everyday use. However, fused silica glass excels in impact resistance because of its inherent structural toughness and ability to withstand thermal shock, which is crucial in high-precision optical applications. Selecting between Gorilla Glass and fused silica depends on balancing the need for scratch durability versus impact resilience in specific optical environments.
Thermal Stability and Expansion
Gorilla Glass offers moderate thermal stability with a thermal expansion coefficient around 8.1 x 10^-6 /degC, suitable for devices exposed to varying temperatures but prone to slight deformation under high heat. Fused silica glass excels in thermal stability due to its ultra-low thermal expansion coefficient of approximately 0.5 x 10^-6 /degC, making it ideal for optical lenses requiring precision and minimal dimensional change under extreme temperature variations. The superior thermal expansion properties of fused silica ensure consistent optical performance and reduced thermal stress compared to Gorilla Glass in high-temperature applications.
Cost and Availability
Gorilla Glass offers a cost-effective solution for optical lenses due to its mass production and widespread availability, making it suitable for consumer electronics. Fused silica glass, while more expensive, provides superior optical clarity and thermal stability, but its limited production scale restricts availability. Manufacturers balance cost and performance needs when selecting between Gorilla Glass and fused silica for optical applications.
Applications in Optical Lenses
Gorilla Glass offers high scratch resistance and durability, making it ideal for smartphone cameras and compact optical devices where lightweight and impact resistance are critical. Fused silica glass provides superior optical clarity and thermal stability, suited for high-precision lenses in microscopy, laser systems, and UV optics. Applications demanding extreme optical performance and minimal distortion often favor fused silica despite higher costs, while Gorilla Glass fits consumer electronics prioritizing toughness and cost-efficiency.
Environmental and Chemical Resistance
Gorilla Glass exhibits superior chemical resistance due to its aluminosilicate composition, providing enhanced durability against environmental factors such as acid rain and alkaline exposure compared to fused silica glass. While fused silica glass offers exceptional thermal stability and resistance to UV radiation, it is more prone to chemical attack by hydrofluoric acid and strong alkalis. The enhanced toughness and scratch resistance of Gorilla Glass contribute to longer-lasting optical lenses in outdoor and harsh chemical environments.
Choosing the Right Glass for Optical Lenses
Gorilla Glass offers high durability and scratch resistance, making it ideal for rugged environments where lens longevity is crucial. Fused silica glass excels in optical clarity and thermal stability, providing superior performance for precision lenses requiring minimal distortion and high transmission across UV to IR spectra. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing mechanical toughness and optical quality requirements, with Gorilla Glass favored for impact resistance and fused silica preferred for advanced imaging applications.
Infographic: Gorilla glass vs Fused silica glass for Optical lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com