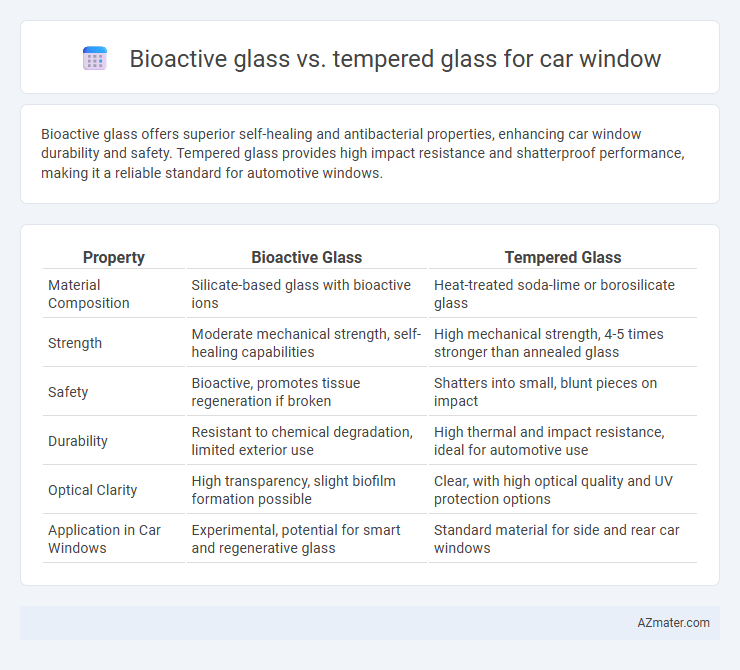
Bioactive glass offers superior self-healing and antibacterial properties, enhancing car window durability and safety. Tempered glass provides high impact resistance and shatterproof performance, making it a reliable standard for automotive windows.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioactive Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Silicate-based glass with bioactive ions | Heat-treated soda-lime or borosilicate glass |
| Strength | Moderate mechanical strength, self-healing capabilities | High mechanical strength, 4-5 times stronger than annealed glass |
| Safety | Bioactive, promotes tissue regeneration if broken | Shatters into small, blunt pieces on impact |
| Durability | Resistant to chemical degradation, limited exterior use | High thermal and impact resistance, ideal for automotive use |
| Optical Clarity | High transparency, slight biofilm formation possible | Clear, with high optical quality and UV protection options |
| Application in Car Windows | Experimental, potential for smart and regenerative glass | Standard material for side and rear car windows |
Introduction to Bioactive Glass and Tempered Glass
Bioactive glass is a specialized material known for its ability to bond with biological tissues, often used in medical applications, while tempered glass is commonly employed in car windows for its enhanced strength and safety features. Tempered glass undergoes a heat treatment process that increases its resistance to impact and causes it to shatter into small, blunt pieces upon breakage, minimizing injury risk. Bioactive glass offers potential automotive applications due to its unique surface properties, but tempered glass remains the standard choice for vehicle windows due to its proven durability and safety performance.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Bioactive glass, primarily composed of silica, calcium oxide, and phosphorus pentoxide, is engineered through a sol-gel or melt-quenching process that enables it to bond with biological tissues and release beneficial ions. Tempered glass, made from soda-lime silica glass, undergoes a thermal tempering process involving rapid heating and cooling to increase its strength and cause it to shatter into small, blunt pieces upon impact. The fundamental difference lies in bioactive glass's bioactive ion release and bonding capabilities versus tempered glass's mechanical reinforcement for safety in car windows.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Tempered glass exhibits superior mechanical strength due to its heat-treatment process, which increases resistance to impact and thermal stress, making it a common choice for car windows. Bioactive glass, although known for its chemical durability and bioactivity in medical applications, generally possesses lower mechanical strength compared to tempered glass, limiting its practical use in automotive windows. The durability of tempered glass under mechanical shocks and temperature fluctuations outperforms bioactive glass, ensuring enhanced safety and longevity in automotive environments.
Impact Resistance and Safety Features
Bioactive glass for car windows offers enhanced impact resistance by promoting self-healing properties that reduce micro-cracks, thereby increasing durability compared to tempered glass. Tempered glass, while strong and shattering into small, blunt pieces for safety, lacks the regenerative capabilities of bioactive glass, making it more susceptible to gradual damage over time. Safety features of bioactive glass include advanced crack prevention and improved structural integrity, potentially reducing replacement frequency and enhancing passenger protection during collisions.
Optical Clarity and Visibility Performance
Bioactive glass for car windows offers superior optical clarity due to its homogeneous composition and high light transmittance, reducing glare and enhancing visibility compared to tempered glass. Tempered glass, while strong and resistant to impacts, may have minor distortions and reduced optical clarity stemming from its heat-treatment process, which can affect driver visibility. Bioactive glass minimizes visual aberrations and provides clearer, more accurate views, crucial for safety and driver comfort in automotive applications.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Bioactive glass exhibits superior thermal stability compared to tempered glass due to its unique chemical composition, which allows it to withstand higher temperatures without deformation or thermal stress. Tempered glass, while strong and resistant to mechanical impact, may experience reduced heat resistance under extreme thermal conditions, leading to potential microfractures. For car windows, bioactive glass offers enhanced heat resistance, ensuring safer performance in high-temperature environments such as direct sunlight exposure or engine heat proximity.
Self-Healing and Bioactive Properties
Bioactive glass in car windows offers superior self-healing properties by promoting the natural regeneration of microcracks through ion exchange and hydroxyapatite formation, enhancing durability and reducing maintenance needs. Tempered glass, while known for its strength and safety, lacks bioactive components and does not possess self-repair capabilities, making it more prone to permanent damage from impacts. The integration of bioactive glass technology in automotive glazing represents a cutting-edge advancement, combining structural integrity with dynamic surface restoration.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Tempered glass remains the dominant choice for car windows due to its widespread availability and lower production costs, benefiting from established manufacturing processes and extensive supplier networks. Bioactive glass, while offering superior durability and potential self-healing properties, faces higher costs and limited availability because of specialized materials and complex fabrication techniques. Automotive manufacturers prioritize tempered glass for cost-efficiency and ease of procurement, though bioactive glass could see increased adoption as production technologies mature and economies of scale improve.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioactive glass promotes environmental sustainability by being composed of recyclable materials that can decompose naturally, reducing landfill waste compared to tempered glass, which involves energy-intensive manufacturing and limited recyclability. Tempered glass, while durable and safer upon breakage, has a higher carbon footprint due to high-temperature processing and often ends up in landfills because of recycling complexities. Choosing bioactive glass for car windows supports eco-friendly practices by minimizing resource consumption and enhancing the lifecycle through biodegradability and energy-efficient production methods.
Future Trends in Automotive Glass Technology
Bioactive glass in automotive windows offers self-healing properties and enhanced durability, positioning it as a groundbreaking alternative to traditional tempered glass. Future trends emphasize integrating bioactive materials to improve safety, reduce environmental impact, and enable smart functionalities such as self-cleaning and damage repair. Advances in nanotechnology and material science will drive the adoption of bioactive glass, revolutionizing automotive glass technology beyond the conventional tempered glass standards.
Infographic: Bioactive glass vs Tempered glass for Car window
 azmater.com
azmater.com