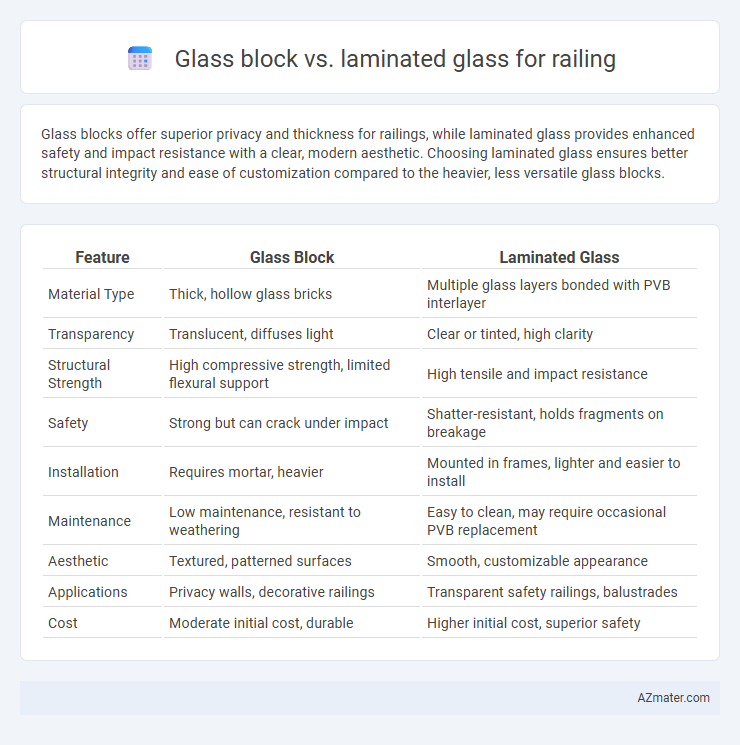
Glass blocks offer superior privacy and thickness for railings, while laminated glass provides enhanced safety and impact resistance with a clear, modern aesthetic. Choosing laminated glass ensures better structural integrity and ease of customization compared to the heavier, less versatile glass blocks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Block | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thick, hollow glass bricks | Multiple glass layers bonded with PVB interlayer |
| Transparency | Translucent, diffuses light | Clear or tinted, high clarity |
| Structural Strength | High compressive strength, limited flexural support | High tensile and impact resistance |
| Safety | Strong but can crack under impact | Shatter-resistant, holds fragments on breakage |
| Installation | Requires mortar, heavier | Mounted in frames, lighter and easier to install |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, resistant to weathering | Easy to clean, may require occasional PVB replacement |
| Aesthetic | Textured, patterned surfaces | Smooth, customizable appearance |
| Applications | Privacy walls, decorative railings | Transparent safety railings, balustrades |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, durable | Higher initial cost, superior safety |
Introduction to Glass Block and Laminated Glass
Glass block is a durable, translucent building material commonly used for railings, offering both structural support and privacy while allowing natural light to pass through. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing high impact resistance, enhanced safety, and superior clarity for railing applications. Both materials are valued in architectural designs for their strength, aesthetic appeal, and ability to meet safety standards in railing installations.
Key Differences Between Glass Block and Laminated Glass
Glass blocks are thick, solid units that provide high impact resistance and privacy, commonly used for outdoor railings requiring durability and minimal visibility. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of tempered glass with an interlayer, offering superior safety by holding shards together upon breakage and enhanced transparency for aesthetic appeal in railing applications. While glass blocks excel in structural strength and sound insulation, laminated glass is preferable for sleek designs and safety compliance in modern railing systems.
Structural Strength and Safety Considerations
Glass block offers exceptional compressive strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for creating rigid, load-bearing railings with enhanced safety. Laminated glass provides superior tensile strength and shatter-resistant properties due to its interlayer, ensuring that if broken, shards remain adhered to the film, reducing injury risk. For structural strength and safety, laminated glass railings are preferred in dynamic load scenarios, while glass blocks excel in fixed, high-load applications.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Versatility
Glass block provides a distinctive, textured aesthetic with a grid-like pattern that enhances privacy while allowing light diffusion, making it ideal for modern and industrial railing designs. Laminated glass offers superior design versatility with its clear, sleek surface that can be customized with tints, films, and patterns, providing both safety and an unobstructed view. The choice between glass block and laminated glass hinges on balancing artistic texture against transparent elegance to achieve the desired architectural impact.
Installation Process and Complexity
Glass blocks for railing require precise alignment and mortar application during installation, making the process labor-intensive and time-consuming, especially for curved or custom designs. Laminated glass panels offer a more straightforward installation, consisting of pre-cut panels secured with clamps or frames, reducing complexity and installation time. The structural support requirements differ, with laminated glass demanding robust framing systems to ensure safety and stability.
Maintenance and Durability
Glass block railings offer high durability due to their thick, solid construction, requiring minimal maintenance as they resist cracks and scratches effectively. Laminated glass railings provide enhanced safety with an interlayer that holds glass shards if broken, but they demand regular inspection to prevent delamination and edge damage caused by moisture. Maintenance for laminated glass involves cleaning with non-abrasive products and ensuring seal integrity, whereas glass blocks largely maintain their appearance with simple cleaning and occasional grout upkeep.
Privacy and Light Transmission
Glass block offers enhanced privacy due to its textured, opaque surface that diffuses light while obscuring direct visibility, making it ideal for railing applications where discretion is important. Laminated glass provides higher light transmission with clear, transparent panels but can be customized with frosted or tinted interlayers to improve privacy without significantly reducing natural light. Choosing between these materials depends on the balance desired between maintaining privacy and maximizing daylight in railing designs.
Cost Comparison: Glass Block vs. Laminated Glass
Glass block railings typically incur higher installation costs due to labor-intensive masonry work, with prices averaging between $30 to $50 per square foot, while laminated glass panels generally cost $25 to $35 per square foot but require specialized hardware and professional fitting. Maintenance and potential replacement expenses further influence overall costs; laminated glass, despite a higher initial investment in mounting systems, offers easier repairs compared to glass blocks, which may necessitate partial masonry reconstruction. Life-cycle cost analyses favor laminated glass for modern railing projects due to its balance of strength, clarity, and lower long-term upkeep expenses.
Suitable Applications for Railings
Glass block railings provide excellent structural strength and privacy, making them suitable for exterior balconies and stairwells where safety and opacity are priorities. Laminated glass railings offer superior impact resistance and clarity, ideal for modern terraces and pool enclosures requiring unobstructed views and enhanced safety. Both materials comply with building codes for railings but differ in aesthetics and application areas based on transparency and durability needs.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Project
Glass block offers durability and privacy with its thick, textured design ideal for decorative railings, while laminated glass provides superior strength and safety through its interlayer, making it suitable for clear, modern railings. Laminated glass excels in impact resistance and clarity, allowing unobstructed views and meeting stringent building codes for safety. Selecting the right option depends on project needs such as aesthetics, safety requirements, and maintenance preferences, with laminated glass favored for sleek designs and glass blocks for privacy and visual interest.
Infographic: Glass block vs Laminated glass for Railing
 azmater.com
azmater.com