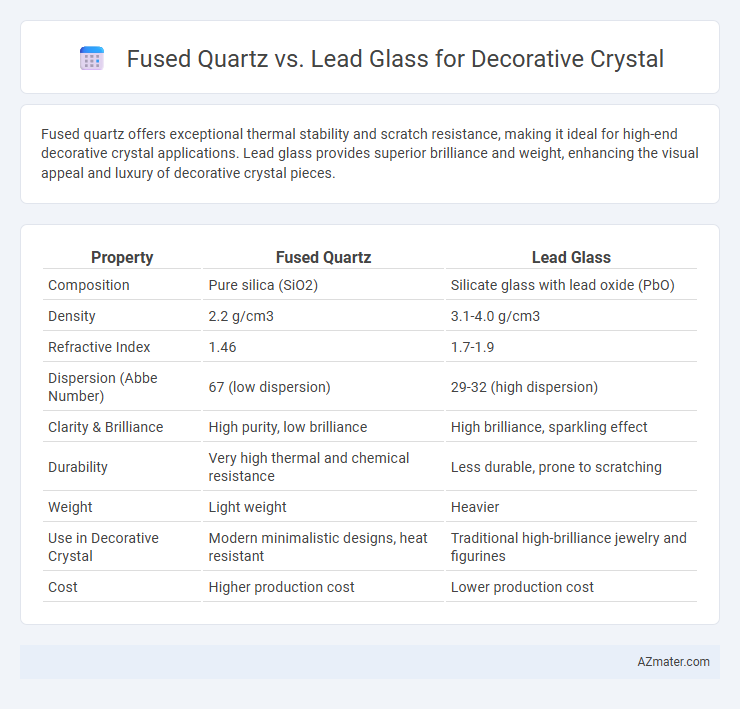
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal stability and scratch resistance, making it ideal for high-end decorative crystal applications. Lead glass provides superior brilliance and weight, enhancing the visual appeal and luxury of decorative crystal pieces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | Lead Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure silica (SiO2) | Silicate glass with lead oxide (PbO) |
| Density | 2.2 g/cm3 | 3.1-4.0 g/cm3 |
| Refractive Index | 1.46 | 1.7-1.9 |
| Dispersion (Abbe Number) | 67 (low dispersion) | 29-32 (high dispersion) |
| Clarity & Brilliance | High purity, low brilliance | High brilliance, sparkling effect |
| Durability | Very high thermal and chemical resistance | Less durable, prone to scratching |
| Weight | Light weight | Heavier |
| Use in Decorative Crystal | Modern minimalistic designs, heat resistant | Traditional high-brilliance jewelry and figurines |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
Introduction to Decorative Crystal Materials
Decorative crystal materials commonly include fused quartz and lead glass, each offering distinct optical and physical properties. Fused quartz is prized for its exceptional thermal stability, high purity, and resistance to scratching, making it ideal for precision crystal art and lighting applications. Lead glass, characterized by its higher refractive index and density, provides superior brilliance and clarity, creating striking visual effects in decorative crystal pieces.
What is Fused Quartz?
Fused quartz is a high-purity, non-crystalline silica glass known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and optical clarity, making it ideal for high-end decorative crystal applications. Compared to lead glass, which contains heavy metal oxides to enhance weight and brilliance but is less durable, fused quartz offers superior strength and resistance to discoloration over time. Its unmatched transparency and durability make fused quartz a premium choice for intricate, long-lasting decorative crystal designs.
Understanding Lead Glass
Lead glass, often referred to as lead crystal, contains at least 24% lead oxide, which enhances its refractive index and brilliance, making it highly desirable for decorative crystal applications. Its density and softness allow intricate cutting and engraving, creating sparkling effects unmatched by fused quartz. In contrast, fused quartz lacks lead oxide and is prized for its thermal resistance and durability but does not possess the same optical clarity or decorative appeal as lead glass.
Visual Differences: Clarity and Color
Fused quartz offers exceptional clarity with minimal color distortion, providing a pure, transparent appearance ideal for high-end decorative crystal. Lead glass typically exhibits a warmer tone with slight color tints due to its lead content, enhancing brilliance but reducing overall transparency compared to fused quartz. The visual distinction is marked by fused quartz's crisp, cool clarity versus lead glass's sparkling, warmer glow.
Light Refraction and Brilliance Comparison
Fused quartz exhibits a lower refractive index around 1.46, resulting in more subtle light dispersion and softer brilliance in decorative crystal applications. Lead glass contains a higher lead oxide content, increasing its refractive index to approximately 1.7-1.8, which significantly enhances light refraction and produces sharper, more vibrant sparkle. The pronounced difference in optical properties makes lead glass preferred for highly brilliant decorative crystals, while fused quartz offers durability with moderate brilliance.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Fused quartz exhibits exceptional durability and high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for decorative crystal applications requiring long-term strength and stability. Lead glass offers greater brilliance and weight but is more susceptible to scratches and breakage due to its lower hardness compared to fused quartz. When prioritizing durability and strength, fused quartz outperforms lead glass in maintaining structural integrity under mechanical and thermal stress.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Fused quartz offers superior safety for decorative crystal use due to its non-toxic composition and exceptional thermal resistance, reducing the risk of hazardous leaching or breakage under heat. Lead glass, while prized for brilliance and clarity, contains lead oxide, posing health risks through exposure and environmental hazards during disposal or recycling. Selecting fused quartz enhances environmental sustainability by minimizing heavy metal contamination, aligning with stricter regulations and eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Crafting Techniques and Workability
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for delicate, high-temperature crafting techniques like flame working and precision engraving in decorative crystal. Lead glass, known for its high refractive index and ease of cutting and polishing, provides greater malleability for intricate shaping and detailed faceting often required in traditional crystal craftwork. Workability differences influence tooling choices and finishing processes, with fused quartz demanding specialized equipment for grinding, while lead glass allows faster production through standard cutting and polishing methods.
Cost Factors: Fused Quartz vs Lead Glass
Fused quartz commands a higher price due to its superior thermal resistance, durability, and optical clarity, making it ideal for premium decorative crystal applications. Lead glass, being less expensive, offers excellent brilliance and weight at a fraction of the cost but lacks the high-temperature stability of fused quartz. Cost considerations often favor lead glass for large-scale or budget-sensitive projects, while fused quartz is preferred where performance justifies the investment.
Choosing the Right Material for Decorative Crystals
Fused quartz offers exceptional clarity, high thermal resistance, and durability, making it ideal for premium decorative crystals that require longevity and minimal discoloration. Lead glass excels in brilliance and refractive index, providing a sparkling effect preferred for luxury aesthetics but may be less durable and prone to lead content concerns. Selecting the right material depends on prioritizing optical brilliance versus material strength and safety requirements in decorative crystal applications.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs Lead glass for Decorative crystal
 azmater.com
azmater.com