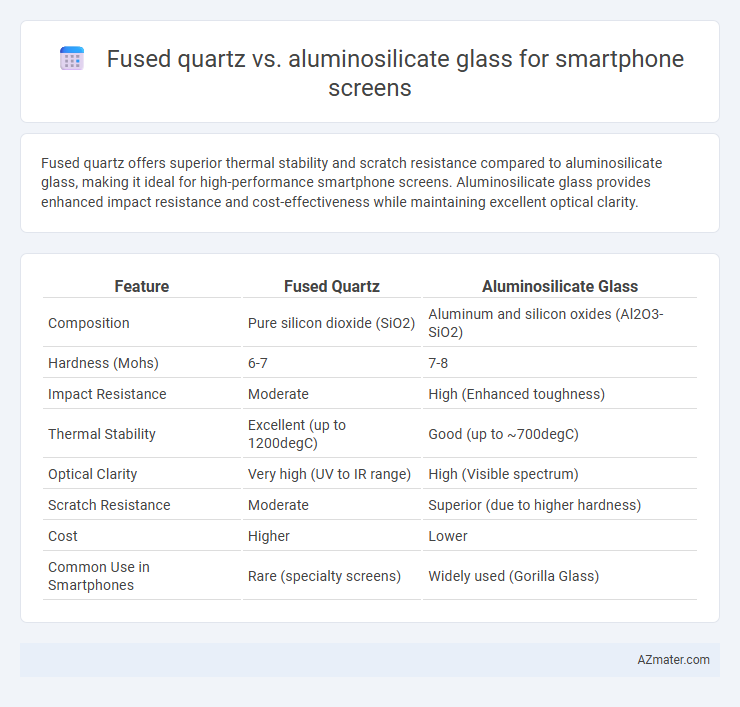
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and scratch resistance compared to aluminosilicate glass, making it ideal for high-performance smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass provides enhanced impact resistance and cost-effectiveness while maintaining excellent optical clarity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fused Quartz | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Aluminum and silicon oxides (Al2O3-SiO2) |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6-7 | 7-8 |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High (Enhanced toughness) |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent (up to 1200degC) | Good (up to ~700degC) |
| Optical Clarity | Very high (UV to IR range) | High (Visible spectrum) |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | Superior (due to higher hardness) |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Use in Smartphones | Rare (specialty screens) | Widely used (Gorilla Glass) |
Introduction to Fused Quartz and Aluminosilicate Glass
Fused quartz is a highly pure, non-crystalline form of silicon dioxide known for its exceptional thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and outstanding optical clarity, making it ideal for demanding applications such as smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass, composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, offers superior strength, scratch resistance, and damage tolerance, which enhances smartphone display durability under daily wear and impacts. Both materials serve critical roles in smartphone screen technology, balancing between optical performance and mechanical resilience.
Composition and Material Structure
Fused quartz, primarily composed of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2), exhibits an amorphous, non-crystalline structure that provides superior thermal stability and high optical clarity for smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass contains aluminum oxide (Al2O3) along with silicon dioxide, forming a denser, chemically strengthened network that enhances impact resistance and scratch durability. The distinct compositions and structural differences influence the performance characteristics, with fused quartz offering exceptional heat resistance and aluminosilicate glass delivering improved mechanical toughness in mobile device displays.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Fused quartz is produced by melting high-purity silica sand at temperatures exceeding 1700degC, resulting in a glass with exceptional thermal stability and minimal impurities, while aluminosilicate glass is manufactured through a melt-quench process involving alumina and silica compounds, followed by an ion-exchange strengthening stage to enhance toughness. The key manufacturing distinction lies in fused quartz's pure silica composition and slower cooling, yielding higher thermal resistance, versus aluminosilicate's engineered chemical composition and fast cooling enabling mass production with superior impact resistance. These differences affect overall cost, durability, and suitability for smartphone screen applications, with aluminosilicate glass dominating due to scalable production and effective scratch and impact resistance.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Fused quartz exhibits superior optical clarity and light transmission with a transmittance rate of approximately 92% across the visible spectrum, ensuring minimal distortion and exceptional transparency for smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass, while also offering high transparency with transmittance around 90%, combines durability with good optical performance but may introduce slightly more light scattering and reduced clarity under certain lighting conditions. For applications prioritizing maximum optical clarity and transparency, fused quartz remains the optimal choice despite its higher cost and manufacturing complexity.
Scratch and Crack Resistance
Fused quartz offers superior scratch resistance due to its high hardness and purity, making it highly durable against everyday abrasions. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone screens like Corning Gorilla Glass, combines excellent scratch resistance with enhanced crack resistance thanks to its chemically strengthened surface. While fused quartz provides unmatched scratch durability, aluminosilicate glass delivers a better balance of scratch and crack resistance for practical smartphone applications.
Durability Under Daily Usage
Fused quartz offers superior scratch resistance and extreme thermal stability, making it highly durable for smartphone screens under daily usage conditions. Aluminosilicate glass, widely used in popular smartphone brands, provides a balanced combination of toughness, impact resistance, and flexibility, enhancing durability against drops and impacts. While fused quartz excels in hardness, aluminosilicate glass is optimized for practical durability and cost-effectiveness in everyday smartphone use.
Thermal and Chemical Stability
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal stability with a high melting point around 1,650degC and minimal thermal expansion, making it highly resistant to temperature-induced deformation in smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass, while also thermally stable, typically has a lower melting point near 1,600degC and slightly higher thermal expansion but compensates with enhanced chemical durability against alkali attack. Both materials exhibit excellent chemical resistance, but fused quartz is superior in resisting hydrofluoric acid, whereas aluminosilicate glass provides better protection against scratching and mechanical impact.
Impact on Touch Sensitivity
Fused quartz exhibits superior transparency and excellent thermal stability, enhancing touch sensitivity by providing a smooth and consistent surface response. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone screens, offers higher strength and scratch resistance but may slightly reduce touch sensitivity due to its increased surface hardness. The balance between durability and touch responsiveness makes aluminosilicate glass the preferred choice for most touchscreen devices, despite fused quartz's advantage in signal clarity.
Cost and Availability for Manufacturers
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and scratch resistance but comes with higher material costs and limited mass production scalability, impacting overall manufacturing expenses. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone screens like Gorilla Glass, provides a cost-effective balance of strength, durability, and wide availability from multiple suppliers, enabling manufacturers to optimize production budgets. The abundant supply chain and lower raw material expense of aluminosilicate glass make it the preferred choice for large-scale smartphone screen manufacturing.
Future Trends in Smartphone Screen Materials
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal stability and scratch resistance, making it a potential candidate for next-generation smartphone screens that demand high durability and clarity. Aluminosilicate glass, favored for its superior toughness and impact resistance, remains the industry standard but faces ongoing enhancements to improve flexural strength and chemical durability. Future trends indicate a convergence toward hybrid materials and nano-engineered coatings that combine the hardness of fused quartz with the resilience of aluminosilicate glass to meet evolving consumer demands for ultra-thin, flexible, and shatterproof displays.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com