Electrochromic glass for tabletops offers dynamic light control and UV protection, enhancing privacy and reducing glare. Annealed glass provides basic strength and clarity but lacks the adaptive tinting features of electrochromic technology.
Table of Comparison
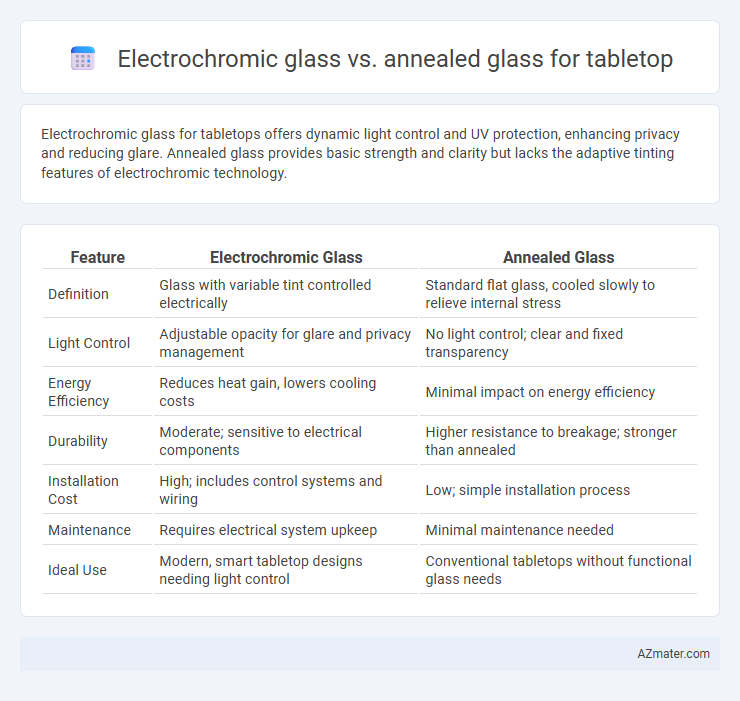
| Feature | Electrochromic Glass | Annealed Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass with variable tint controlled electrically | Standard flat glass, cooled slowly to relieve internal stress |
| Light Control | Adjustable opacity for glare and privacy management | No light control; clear and fixed transparency |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces heat gain, lowers cooling costs | Minimal impact on energy efficiency |
| Durability | Moderate; sensitive to electrical components | Higher resistance to breakage; stronger than annealed |
| Installation Cost | High; includes control systems and wiring | Low; simple installation process |
| Maintenance | Requires electrical system upkeep | Minimal maintenance needed |
| Ideal Use | Modern, smart tabletop designs needing light control | Conventional tabletops without functional glass needs |
Introduction to Electrochromic and Annealed Glass
Electrochromic glass, featuring dynamic tinting technology, adjusts transparency levels through an applied electrical voltage, offering customizable light control and privacy ideal for tabletops. Annealed glass, a standard float glass cooled slowly to relieve internal stresses, provides basic transparency with enhanced durability but lacks adjustable opacity. This contrast highlights electrochromic glass's advanced functionality versus annealed glass's traditional fixed clarity in tabletop applications.
How Electrochromic Glass Works
Electrochromic glass functions by applying a low voltage to a conductive coating, causing ions and electrons to move between layers, which changes the glass from transparent to tinted. This dynamic light modulation enables precise control of glare and privacy on tabletops without the need for physical shades. Unlike annealed glass, which is static and untreated, electrochromic glass offers energy-efficient adaptability and enhanced user interaction through its smart glazing technology.
Properties of Annealed Glass
Annealed glass is known for its smooth surface, clarity, and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for tabletops where aesthetics are essential. It is produced by slowly cooling molten glass to relieve internal stresses, resulting in a glass that is strong but can shatter into sharp shards when broken. Unlike electrochromic glass, annealed glass lacks the ability to change tint or opacity, offering a static transparency ideal for straightforward, elegant tabletop designs.
Visual Appearance and Aesthetics Comparison
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic tinting capabilities, allowing users to adjust transparency and light transmission, enhancing both privacy and aesthetic versatility for tabletops. Annealed glass provides a consistent clarity and smooth surface finish, emphasizing simplicity and classic elegance without light modulation. The dynamic visual adaptability of electrochromic glass makes it ideal for modern, multifunctional spaces, while annealed glass suits traditional designs requiring stable, clear visibility.
Durability and Strength Differences
Electrochromic glass offers enhanced durability through its multilayer construction and integrated electronic components, providing resistance to scratches and impact compared to standard annealed glass. Annealed glass, while common and cost-effective for tabletops, lacks the strengthened structural integrity of electrochromic glass, making it more prone to breakage and chips under stress. The smart functionality of electrochromic glass does not compromise its strength, combining aesthetic adaptability with improved toughness ideal for high-use furniture surfaces.
Light Control and Privacy Features
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control by adjusting transparency levels electronically, providing customizable privacy and glare reduction for tabletops. Annealed glass remains static, allowing no variation in light transmission, which limits its effectiveness in managing privacy and sunlight exposure. Electrochromic glass enhances user comfort with on-demand opacity, while annealed glass prioritizes durability without adaptive light or privacy capabilities.
Energy Efficiency and Thermal Performance
Electrochromic glass offers superior energy efficiency by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and reducing cooling loads through its ability to tint on demand, unlike annealed glass which remains static and allows greater heat transfer. Thermal performance of electrochromic glass surpasses annealed glass by minimizing infrared radiation penetration, thus enhancing insulation and maintaining consistent indoor temperatures. This adaptive glazing technology significantly lowers energy consumption for heating and cooling in tabletop applications, delivering a sustainable and comfortable environment.
Safety Considerations for Tabletop Use
Electrochromic glass offers enhanced safety for tabletops due to its ability to dynamically adjust transparency, reducing glare and minimizing eye strain. Its laminated structure typically includes multiple layers, providing increased resistance to shattering compared to single-pane annealed glass, which can break into sharp, dangerous shards upon impact. For tabletop use, electrochromic glass ensures smarter safety with both impact resilience and adaptive light control, whereas annealed glass, though cost-effective, poses higher risks of injury in case of breakage.
Cost Analysis: Electrochromic vs Annealed Glass
Electrochromic glass commands a higher upfront cost due to advanced smart technology that enables dynamic tinting, significantly increasing material and installation expenses compared to annealed glass. Annealed glass is economically advantageous, offering lower production and replacement costs but lacks the multifunctional benefits of electrochromic variants. Long-term cost considerations include energy savings and privacy control with electrochromic glass, which can offset the initial investment over time.
Best Use Cases for Tabletop Applications
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control and privacy, making it ideal for conference tables and adaptable workspaces where variable transparency enhances functionality. Annealed glass provides cost-effective durability and clarity, suited for lightweight, static tabletop applications such as dining or office desks. Selecting between electrochromic and annealed glass depends on whether adjustable opacity or traditional strength and affordability best meet the tabletop's intended use.
Infographic: Electrochromic glass vs Annealed glass for Tabletop
 azmater.com
azmater.com