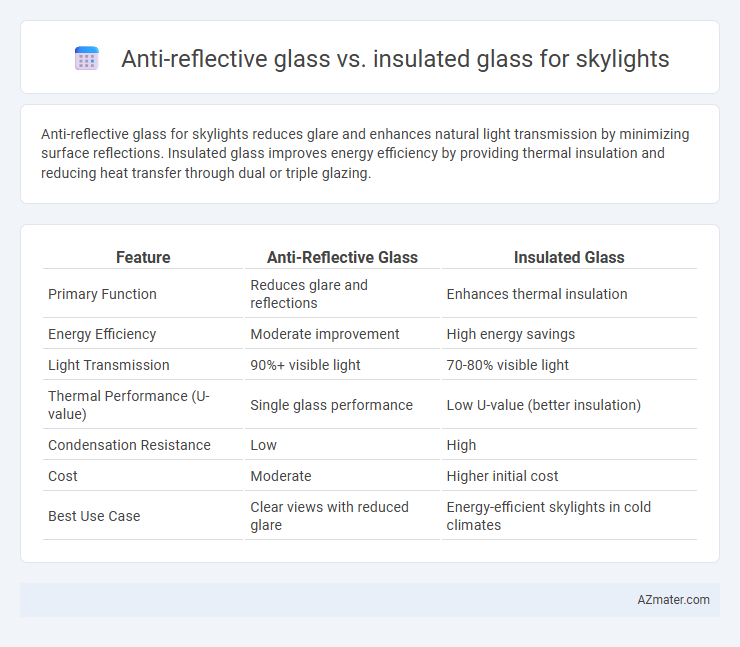
Anti-reflective glass for skylights reduces glare and enhances natural light transmission by minimizing surface reflections. Insulated glass improves energy efficiency by providing thermal insulation and reducing heat transfer through dual or triple glazing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-Reflective Glass | Insulated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reduces glare and reflections | Enhances thermal insulation |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate improvement | High energy savings |
| Light Transmission | 90%+ visible light | 70-80% visible light |
| Thermal Performance (U-value) | Single glass performance | Low U-value (better insulation) |
| Condensation Resistance | Low | High |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher initial cost |
| Best Use Case | Clear views with reduced glare | Energy-efficient skylights in cold climates |
Introduction to Skylight Glass Options
Skylight glass options primarily include anti-reflective glass and insulated glass, each enhancing natural light differently while addressing energy efficiency. Anti-reflective glass minimizes glare and improves transparency, making it ideal for maximizing daylight without compromising visual clarity. Insulated glass, composed of multiple panes with air or gas filling, optimizes thermal performance by reducing heat transfer and increasing energy savings in skylight installations.
What is Anti-Reflective Glass?
Anti-reflective glass is engineered with specialized coatings that minimize light reflection, enhancing natural daylight transmission through skylights while reducing glare. This glass type improves visual clarity and energy efficiency by allowing more sunlight to pass through without compromising insulation. Compared to insulated glass, which primarily focuses on thermal performance through multiple panes and air gaps, anti-reflective glass optimizes light quality and comfort within interior spaces.
What is Insulated Glass?
Insulated glass for skylights consists of two or more glass panes separated by a sealed air or gas-filled space, enhancing thermal performance and energy efficiency. This design minimizes heat transfer, reduces condensation, and improves sound insulation compared to single-pane or anti-reflective glass. Insulated glass is ideal for skylights in climates requiring temperature regulation and increased comfort without compromising natural light intake.
Light Transmission Comparison
Anti-reflective glass for skylights offers superior light transmission, typically allowing up to 98% of natural light to pass through by minimizing surface reflections. Insulated glass, composed of multiple layers with air or gas fills, generally transmits around 70-80% of light due to internal reflections and the thickness of the panes. Selecting anti-reflective glass enhances daylighting efficiency in skylights, while insulated glass prioritizes thermal performance with a slight compromise in light transmission.
Energy Efficiency: Anti-Reflective vs Insulated Glass
Insulated glass provides superior energy efficiency for skylights by minimizing heat transfer through its double or triple-pane construction with inert gas fills, reducing heating and cooling costs significantly. Anti-reflective glass enhances light transmission by reducing glare and improving daylight penetration but does not offer substantial insulation benefits. Combining insulated glass with anti-reflective coatings can optimize both energy efficiency and natural lighting in skylight installations.
Glare Reduction in Skylights
Anti-reflective glass significantly reduces glare in skylights by minimizing light reflection, enhancing natural daylight without causing visual discomfort. Insulated glass, while primarily designed for thermal efficiency, also contributes to glare control by providing multiple layers that diffuse and soften incoming light. Selecting anti-reflective glass for skylights ensures superior glare reduction, improving indoor comfort and visibility, especially in spaces with high sun exposure.
Thermal Performance and Comfort
Anti-reflective glass for skylights enhances natural light transmission while reducing glare, improving visual comfort but offering limited thermal insulation. Insulated glass units (IGUs) consist of multiple panes separated by gas-filled spaces, significantly reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency and indoor comfort. Combining anti-reflective coatings with insulated glass optimizes both daylight clarity and thermal performance, balancing comfort and energy savings.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Anti-reflective glass for skylights offers enhanced light transmission and reduces glare but may require more frequent cleaning to maintain clarity due to its special coatings. Insulated glass, composed of multiple panes with a gas-filled gap, provides superior durability by resisting thermal stress and minimizing condensation, reducing maintenance needs over time. When prioritizing longevity and minimal upkeep, insulated glass generally outperforms anti-reflective options in long-term skylight applications.
Cost Differences and Budget Implications
Anti-reflective glass for skylights generally carries a higher upfront cost due to specialized coatings that reduce glare and improve light transmission, enhancing energy efficiency and indoor comfort. Insulated glass, often double or triple-glazed, tends to be more cost-effective initially while providing superior thermal insulation, reducing heating and cooling expenses over time. Budget considerations should weigh the initial investment against long-term energy savings, with insulated glass offering better value for colder climates and anti-reflective glass appealing for maximizing natural light in bright environments.
Which Glass Type is Best for Your Skylight?
Anti-reflective glass reduces glare and enhances natural light transmission, making it ideal for skylights in areas where maximizing daylight is crucial. Insulated glass offers superior thermal performance by minimizing heat loss and condensation, which is essential for energy efficiency and comfort in varying climates. Choosing the best glass depends on your priorities: anti-reflective glass for optimal light clarity, or insulated glass for enhanced insulation and energy savings.
Infographic: Anti-reflective glass vs Insulated glass for Skylight
 azmater.com
azmater.com