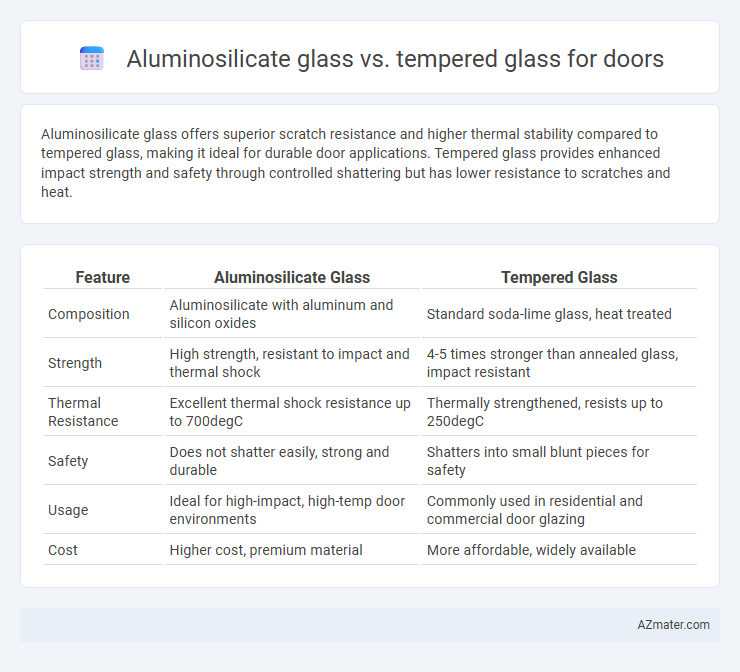
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior scratch resistance and higher thermal stability compared to tempered glass, making it ideal for durable door applications. Tempered glass provides enhanced impact strength and safety through controlled shattering but has lower resistance to scratches and heat.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aluminosilicate Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminosilicate with aluminum and silicon oxides | Standard soda-lime glass, heat treated |
| Strength | High strength, resistant to impact and thermal shock | 4-5 times stronger than annealed glass, impact resistant |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent thermal shock resistance up to 700degC | Thermally strengthened, resists up to 250degC |
| Safety | Does not shatter easily, strong and durable | Shatters into small blunt pieces for safety |
| Usage | Ideal for high-impact, high-temp door environments | Commonly used in residential and commercial door glazing |
| Cost | Higher cost, premium material | More affordable, widely available |
Introduction to Aluminosilicate and Tempered Glass
Aluminosilicate glass, known for its high strength and thermal resistance, is engineered by adding aluminum oxide to silicon dioxide, making it suitable for doors requiring durability and heat tolerance. Tempered glass undergoes a controlled thermal or chemical treatment process to increase its strength compared to ordinary glass, offering enhanced safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon breakage. Both types of glass serve distinct purposes in door construction, with aluminosilicate glass excelling in high-performance applications and tempered glass providing reliable impact resistance and safety compliance.
Key Differences Between Aluminosilicate and Tempered Glass
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal and chemical resistance compared to tempered glass, making it ideal for environments with extreme temperature fluctuations or exposure to corrosive substances. Tempered glass is mechanically strengthened through rapid heating and cooling, resulting in increased impact resistance but lower thermal tolerance than aluminosilicate glass. While tempered glass shatters into small, safer pieces upon breakage, aluminosilicate glass maintains structural integrity longer, reducing the risk of sudden failure in door applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass boasts exceptional strength and durability due to its chemical composition, offering superior resistance to impact, scratching, and thermal stress compared to tempered glass. Tempered glass undergoes a heat-treatment process that enhances its strength by creating compressive surface layers but remains more prone to shattering under extreme force or sharp impact. The enhanced fracture resistance and lower thermal expansion coefficient of aluminosilicate glass make it a preferred choice for doors requiring long-lasting durability and safety performance.
Safety Features: Aluminosilicate vs Tempered Glass
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior impact resistance and enhanced shatterproof properties compared to tempered glass, reducing the risk of injury during accidental breakage. Tempered glass, while strong and capable of breaking into small blunt pieces, can still shatter under extreme force, posing potential hazards. The inherent chemical durability and thermal stability of aluminosilicate glass make it a safer choice for door applications requiring maximum protection against impacts and thermal stress.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior scratch resistance compared to tempered glass due to its chemically strengthened surface, making it ideal for high-traffic door applications. Tempered glass provides excellent impact resistance by undergoing a thermal treatment that increases its strength and causes it to shatter into small, safer pieces upon breakage. In scenarios requiring both durability and safety, the enhanced scratch resistance of aluminosilicate glass combined with the impact resilience of tempered glass must be carefully evaluated based on specific door usage conditions.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal stability compared to tempered glass, maintaining structural integrity under rapid temperature changes up to 700degC, making it ideal for high-heat environments in door applications. Tempered glass, while stronger in impact resistance due to its heat-treatment process, typically withstands temperatures only up to 250degC before losing its structural properties. The enhanced thermal shock resistance of aluminosilicate glass ensures better performance and safety in doors exposed to extreme or fluctuating temperatures.
Aesthetic Options and Customization
Aluminosilicate glass offers a sleek, modern look with a smooth, clear finish that complements minimalist and contemporary door designs, allowing for various tints and coatings to enhance aesthetics. Tempered glass provides versatile options including frosted, patterned, or tinted surfaces, enabling homeowners to customize privacy and style to fit traditional or modern interiors. Both glass types support customization in size and shape, but aluminosilicate glass excels in clarity and subtle color options, while tempered glass is preferred for intricate decorative textures and enhanced safety features.
Cost Analysis: Aluminosilicate vs Tempered Glass for Doors
Aluminosilicate glass costs significantly more than tempered glass due to its enhanced durability and heat resistance, often used in high-performance or specialty door applications. Tempered glass offers a more budget-friendly option with sufficient strength and safety features for standard residential and commercial doors. Choosing between the two depends on weighing upfront material costs against long-term performance and maintenance benefits.
Installation Considerations for Door Applications
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for door installations in high-heat or corrosive environments, while tempered glass provides enhanced strength and safety through controlled thermal processing. Installation of aluminosilicate glass requires careful handling due to its brittleness but allows for thinner panels without compromising performance, whereas tempered glass installation demands precise sizing and edge finishing to prevent stress fractures during fitting. Choosing between the two depends on required durability, safety standards, and environmental conditions, with aluminosilicate glass benefiting applications needing heat resistance and tempered glass preferred for impact resistance.
Choosing the Best Glass Type for Your Door Needs
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for doors exposed to extreme temperatures or requiring enhanced safety features. Tempered glass provides high impact strength and shatters into small, blunt pieces, improving security and preventing injury, which is essential for areas with high traffic or risk of breakage. Selecting the best glass type depends on factors such as thermal exposure, safety requirements, and environmental conditions surrounding the door.
Infographic: Aluminosilicate glass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com