Urea-formaldehyde foam offers high rigidity and fire resistance but emits formaldehyde gas, posing health risks, while latex foam provides superior breathability, natural hypoallergenic properties, and better durability for mattress comfort. Choosing latex foam enhances sleep quality through its elastic support and moisture-wicking capabilities, making it a safer, eco-friendly alternative to urea-formaldehyde-based mattresses.
Table of Comparison
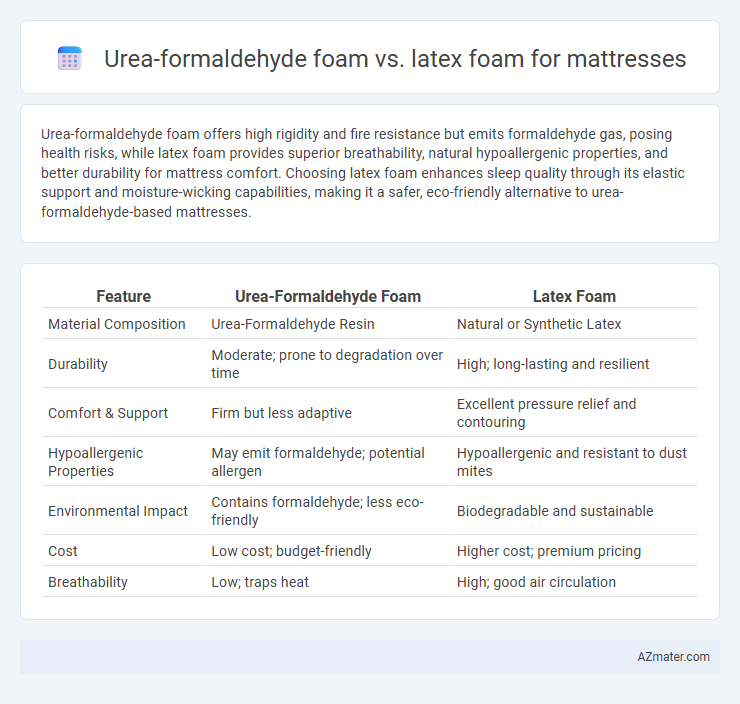
| Feature | Urea-Formaldehyde Foam | Latex Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Urea-Formaldehyde Resin | Natural or Synthetic Latex |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to degradation over time | High; long-lasting and resilient |
| Comfort & Support | Firm but less adaptive | Excellent pressure relief and contouring |
| Hypoallergenic Properties | May emit formaldehyde; potential allergen | Hypoallergenic and resistant to dust mites |
| Environmental Impact | Contains formaldehyde; less eco-friendly | Biodegradable and sustainable |
| Cost | Low cost; budget-friendly | Higher cost; premium pricing |
| Breathability | Low; traps heat | High; good air circulation |
Introduction to Mattress Foam Types
Urea-formaldehyde foam and latex foam represent two distinct mattress foam types with different compositions and performance characteristics. Urea-formaldehyde foam, a synthetic resin-based material, offers affordability and firm support but may emit formaldehyde gas during off-gassing, which raises health concerns. Latex foam, derived from natural or synthetic rubber, provides exceptional resilience, breathability, and hypoallergenic properties, making it a preferred choice for healthier and more durable mattresses.
What is Urea-Formaldehyde Foam?
Urea-formaldehyde foam is a rigid insulation material created by mixing urea, formaldehyde, and a foaming agent, widely used in construction but less common in mattresses due to its rigidity and potential off-gassing of formaldehyde. Unlike latex foam, which offers flexibility, breathability, and natural resistance to allergens, urea-formaldehyde foam is primarily valued for thermal insulation rather than comfort or durability in bedding. Mattress manufacturers prefer latex foam for its elasticity and hypoallergenic properties, while urea-formaldehyde foam remains unsuitable for sleep surfaces.
What is Latex Foam?
Latex foam is a resilient and natural material derived from the sap of rubber trees, known for its durability, breathability, and hypoallergenic properties. Unlike urea-formaldehyde foam, which is a synthetic material often associated with chemical emissions, latex foam offers a more eco-friendly and non-toxic sleep surface. Its inherent elasticity provides excellent pressure relief and support, making it a preferred choice for mattress comfort and longevity.
Chemical Composition and Manufacturing Process
Urea-formaldehyde foam is synthesized through a condensation reaction between urea and formaldehyde, resulting in a thermosetting polymer with rigid, cross-linked structures, whereas latex foam is derived from natural or synthetic latex rubber, primarily composed of polyisoprene chains undergoing vulcanization. The manufacturing of urea-formaldehyde foam involves emulsification and polymerization using catalysts to create a lightweight, rigid foam commonly used for insulation, while latex foam production employs the whipped-foam process or Dunlop and Talalay methods, incorporating aeration and vulcanization to produce flexible, resilient mattress foam. Chemical composition differences influence properties such as durability, elasticity, and hypoallergenic benefits, with latex foam favored for its natural origin and breathability, contrasting the more formaldehyde-emitting urea-formaldehyde foam.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Urea-formaldehyde foam mattresses provide firm support due to their rigid cell structure, offering excellent durability but limited contouring ability, which may reduce overall comfort for side sleepers. Latex foam mattresses excel in comfort by providing a responsive, pressure-relieving surface that adapts to body shape while maintaining consistent support, leading to better spinal alignment and reduced pressure points. The natural elasticity and breathability of latex foam further enhance comfort and temperature regulation compared to the denser, less breathable urea-formaldehyde foam.
Durability and Longevity
Urea-formaldehyde foam mattresses tend to have lower durability due to their brittleness and susceptibility to breaking down over time, resulting in a shorter lifespan. Latex foam mattresses offer superior longevity, maintaining shape and resilience for over a decade thanks to their natural elasticity and resistance to wear and tear. The inherent durability of latex foam makes it a preferred choice for consumers seeking long-lasting mattress performance.
Health and Safety Concerns
Urea-formaldehyde foam mattresses release formaldehyde gas, a known irritant and potential carcinogen, raising significant health concerns, especially for individuals with respiratory conditions or chemical sensitivities. Latex foam offers a safer alternative by naturally resisting dust mites and mold without emitting harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs), promoting better indoor air quality. Choosing latex foam reduces the risk of allergic reactions and long-term exposure to toxic chemicals commonly found in urea-formaldehyde foam products.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Urea-formaldehyde foam releases formaldehyde emissions, contributing to indoor air pollution and posing health risks, which negatively impacts environmental sustainability. Latex foam, especially natural or organic latex, is biodegradable, renewable, and has a lower carbon footprint due to its plant-based origins. Choosing latex foam over urea-formaldehyde foam supports eco-friendly mattress production and reduces harmful chemical exposure.
Cost Difference and Value for Money
Urea-formaldehyde foam mattresses typically cost less than latex foam mattresses due to cheaper raw materials and manufacturing processes. Latex foam offers superior durability, comfort, and hypoallergenic properties, providing better long-term value despite its higher upfront price. Consumers seeking cost-efficiency might prefer urea-formaldehyde foam, while those prioritizing longevity and health benefits often find latex foam to be a more valuable investment.
Which Foam is Best for Your Mattress?
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers high-density support and affordability but may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs), impacting indoor air quality. Latex foam provides superior breathability, durability, and hypoallergenic properties, making it ideal for those seeking natural and long-lasting comfort. For mattresses, latex foam is generally the best choice due to its balance of comfort, health benefits, and environmental safety.
Infographic: Urea-formaldehyde foam vs Latex foam for Mattress
 azmater.com
azmater.com