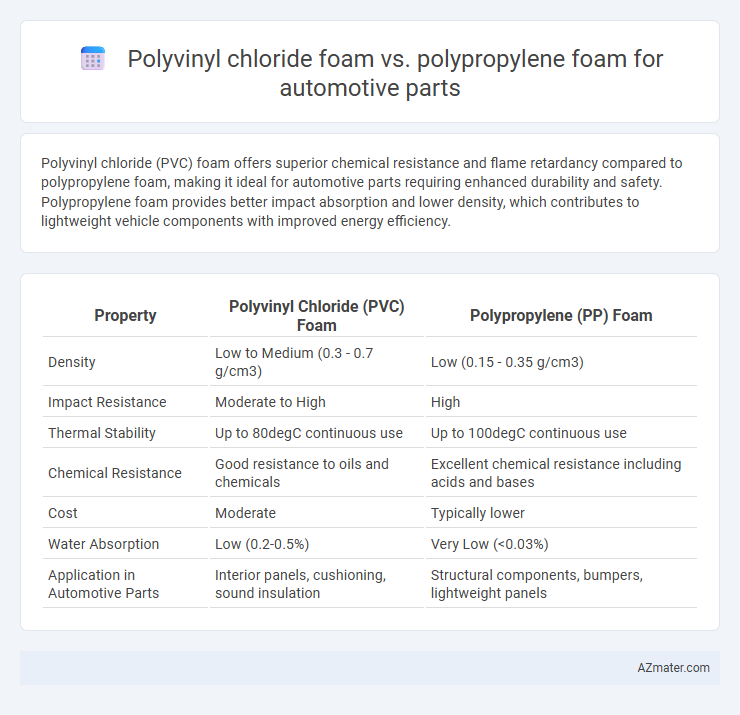
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior chemical resistance and flame retardancy compared to polypropylene foam, making it ideal for automotive parts requiring enhanced durability and safety. Polypropylene foam provides better impact absorption and lower density, which contributes to lightweight vehicle components with improved energy efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Polypropylene (PP) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to Medium (0.3 - 0.7 g/cm3) | Low (0.15 - 0.35 g/cm3) |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate to High | High |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 80degC continuous use | Up to 100degC continuous use |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and chemicals | Excellent chemical resistance including acids and bases |
| Cost | Moderate | Typically lower |
| Water Absorption | Low (0.2-0.5%) | Very Low (<0.03%) |
| Application in Automotive Parts | Interior panels, cushioning, sound insulation | Structural components, bumpers, lightweight panels |
Introduction to Automotive Foam Materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam and polypropylene (PP) foam are widely used automotive foam materials due to their lightweight and durable properties. PVC foam offers excellent flame retardancy and sound insulation, making it suitable for interior components like dashboards and door panels. Polypropylene foam, known for its higher impact resistance and chemical stability, is commonly used in under-the-hood applications and exterior parts requiring robust mechanical performance.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is widely used in automotive parts due to its excellent balance of rigidity, durability, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for interior components and decorative trims. It offers superior resistance to chemicals, moisture, and UV radiation compared to polypropylene foam, enhancing the longevity of automotive assemblies. PVC foam's closed-cell structure provides good thermal insulation and sound dampening, contributing to improved vehicle comfort and performance.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP) Foam
Polypropylene (PP) foam offers superior impact resistance and excellent chemical durability, making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. Its lightweight structure contributes to enhanced fuel efficiency while providing effective noise reduction and thermal insulation within vehicle interiors. Compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, PP foam exhibits better recyclability and environmental sustainability, aligning with industry demands for eco-friendly materials.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits higher tensile strength and better impact resistance compared to polypropylene (PP) foam, making it more suitable for automotive parts requiring durability under mechanical stress. PVC foam also offers superior dimensional stability and resistance to compression, enhancing its performance in structural applications. Polypropylene foam, while lighter and more flexible, generally provides lower stiffness and mechanical strength, limiting its use in high-load automotive components.
Weight and Density Analysis
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam typically has a higher density, ranging from 40 to 300 kg/m3, compared to polypropylene (PP) foam, which usually ranges between 20 and 100 kg/m3, making PP foam lighter for automotive parts where weight reduction is critical. The lower density of PP foam contributes to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions in vehicles by minimizing overall component weight. PVC foam offers higher rigidity and impact resistance, but its increased weight can negatively affect vehicle performance and fuel economy.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits superior chemical resistance against oils, acids, and solvents, making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. Polypropylene (PP) foam offers better thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 100degC, while PVC foam typically withstands slightly lower temperatures around 80degC. For automotive applications requiring a balance between chemical durability and thermal stability, selecting PVC foam ensures enhanced resistance to automotive fluids, whereas PP foam is preferable for components subjected to higher heat exposure.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam typically offers a lower material cost compared to polypropylene (PP) foam, making it a cost-effective option for automotive parts requiring moderate durability and vibration dampening. PVC foam exhibits easier processing with established manufacturing techniques such as extrusion and thermoforming, which reduces production time and tooling expenses. Polypropylene foam, while generally more expensive, provides superior chemical resistance and impact performance, but its processing demands higher temperatures and specialized equipment, increasing overall manufacturing costs.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam for automotive parts generates more environmental concerns due to the release of toxic chemicals such as dioxins during production and incineration, whereas polypropylene (PP) foam offers a lower environmental footprint with fewer harmful emissions. PP foam exhibits superior recyclability through mechanical recycling processes, facilitating reuse in automotive components, while PVC foam recycling is limited and often results in downcycling due to chlorine content. The selection of PP foam supports sustainable automotive manufacturing by reducing hazardous waste and promoting circular economy principles.
Typical Automotive Applications
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is extensively used in automotive parts for interior components such as door panels, dashboards, and headliners due to its excellent rigidity, sound insulation, and resistance to chemicals. Polypropylene (PP) foam is favored for automotive applications requiring lightweight and impact-resistant materials, including bumper cores, underbody protection, and energy absorption parts. Both foams enhance vehicle performance by improving durability and occupant comfort, with PVC foam excelling in structural applications and PP foam in cushioning and impact protection.
Key Factors in Material Selection
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers exceptional durability, chemical resistance, and good thermal insulation, making it suitable for automotive interior trims requiring rigidity and longevity. Polypropylene (PP) foam provides superior impact absorption, lightweight properties, and excellent fatigue resistance, ideal for energy-absorbing components such as door panels and bumpers. Critical factors in selecting these foams include mechanical strength, weight reduction priorities, thermal stability, and compatibility with automotive manufacturing processes.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Polypropylene foam for Automotive Part
 azmater.com
azmater.com