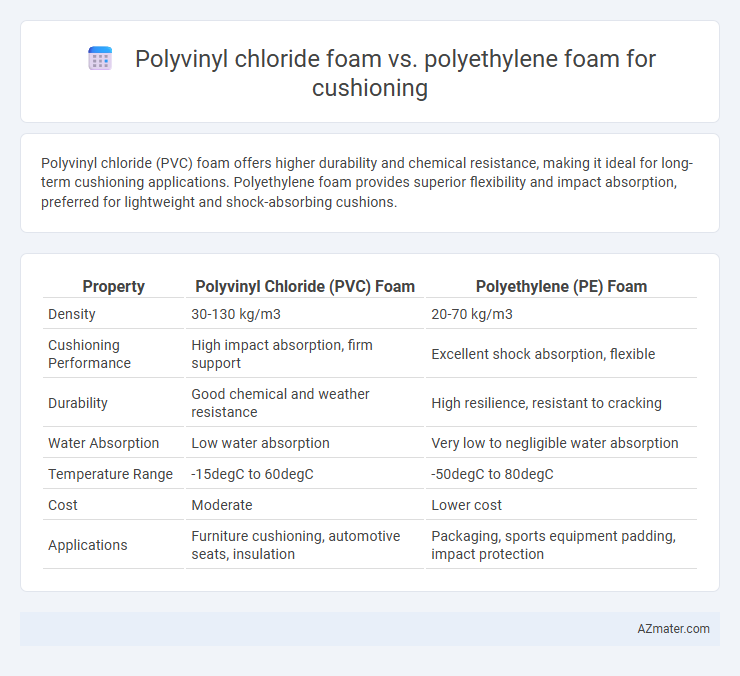
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers higher durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for long-term cushioning applications. Polyethylene foam provides superior flexibility and impact absorption, preferred for lightweight and shock-absorbing cushions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Polyethylene (PE) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 30-130 kg/m3 | 20-70 kg/m3 |
| Cushioning Performance | High impact absorption, firm support | Excellent shock absorption, flexible |
| Durability | Good chemical and weather resistance | High resilience, resistant to cracking |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Very low to negligible water absorption |
| Temperature Range | -15degC to 60degC | -50degC to 80degC |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower cost |
| Applications | Furniture cushioning, automotive seats, insulation | Packaging, sports equipment padding, impact protection |
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam and Polyethylene (PE) Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a closed-cell, rigid foam with excellent chemical resistance, high durability, and superior compression strength, making it ideal for cushioning applications requiring long-lasting support and structural integrity. Polyethylene (PE) foam is a lightweight, flexible, open- or closed-cell foam known for its shock absorption, low water absorption, and high resilience, commonly used in packaging and protective cushioning. Both foams provide cushioning benefits, but PVC foam offers more rigidity and durability, whereas PE foam delivers enhanced flexibility and impact absorption.
Chemical Composition and Structural Differences
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam consists of polymerized vinyl chloride units, characterized by a rigid, closed-cell structure that provides excellent chemical resistance and durability for cushioning applications. Polyethylene (PE) foam, made from polymerized ethylene molecules, features a softer, flexible open or closed-cell structure offering superior shock absorption and cushioning comfort. The chemical composition of PVC results in higher stiffness and resistance to solvents, while PE's aliphatic hydrocarbon backbone grants enhanced elasticity and moisture resistance in cushioning uses.
Cushioning Performance: Impact Absorption and Support
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior impact absorption due to its closed-cell structure, providing excellent cushioning and long-term support in high-pressure environments. Polyethylene (PE) foam is lighter and more flexible but generally demonstrates lower impact resistance and support retention under sustained loads. For applications demanding durable cushioning and enhanced shock absorption, PVC foam outperforms PE foam by maintaining shape and resilience over extended use.
Durability and Longevity in Cushioning Applications
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior durability and longevity in cushioning applications due to its high chemical resistance, enhanced structural integrity, and excellent resistance to wear and tear compared to polyethylene (PE) foam. PE foam provides good cushioning with excellent shock absorption but tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV light and chemicals, reducing its effective lifespan. PVC foam's density and closed-cell structure ensure greater resilience and sustained performance in demanding environments, making it the preferred choice for long-term cushioning needs.
Weight and Flexibility Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is generally denser and heavier than polyethylene (PE) foam, making PE foam a preferred choice for applications requiring lightweight cushioning. PE foam exhibits superior flexibility and resilience due to its closed-cell structure, which offers enhanced shock absorption and compression recovery compared to the stiffer PVC foam. The weight-to-flexibility ratio of PE foam makes it ideal for dynamic cushioning in sports and packaging, whereas PVC foam is suited for more rigid, supportive cushioning needs.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior chemical resistance compared to polyethylene (PE) foam, making it ideal for cushioning applications exposed to solvents, oils, and acids. PVC foam also exhibits excellent moisture resistance, preventing water absorption and maintaining cushioning performance in damp conditions. In contrast, polyethylene foam, while providing good cushioning, tends to absorb more moisture and has limited resistance to harsh chemicals, reducing its effectiveness in corrosive or wet environments.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers moderate thermal insulation with a closed-cell structure that reduces heat transfer, making it suitable for applications requiring both cushioning and temperature resistance. Polyethylene (PE) foam provides superior thermal insulation due to its low thermal conductivity and high closed-cell content, effectively minimizing heat flow and maintaining temperature stability. For cushioning purposes where thermal insulation is critical, polyethylene foam generally outperforms PVC foam in maintaining consistent temperature control.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam and polyethylene (PE) foam differ significantly in environmental impact and recyclability, with PE foam generally offering a more eco-friendly profile due to its lower toxicity and better degradability. PVC foam contains chlorine, which can release harmful dioxins during production and incineration, making it more challenging to recycle and dispose of safely. PE foam, being a polyolefin, is easier to recycle through established recovery streams and tends to have a lower environmental footprint in cushioning applications.
Cost Analysis for Cushioning Solutions
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam generally offers a higher cost compared to polyethylene (PE) foam due to its superior durability, chemical resistance, and fire retardant properties, making it suitable for premium cushioning applications. Polyethylene foam provides a more budget-friendly cushioning solution with excellent impact absorption and lighter weight, ideal for cost-sensitive projects requiring moderate protection. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including material longevity and maintenance, highlights that PVC foam can reduce long-term expenses despite the initial higher investment, whereas PE foam is preferred for short-term or disposable cushioning needs.
Best Use Cases: PVC vs PE Foam in Cushioning
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam excels in applications requiring high durability, chemical resistance, and structural support, making it ideal for automotive seating and heavy-duty cushioning. Polyethylene (PE) foam offers superior shock absorption and lightweight properties, suitable for packaging delicate electronics, sports equipment padding, and protective cushioning in shipping. Choosing between PVC and PE foam depends on balancing factors like load-bearing requirements, environmental exposure, and flexibility needs in cushioning applications.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Polyethylene foam for Cushioning
 azmater.com
azmater.com