Polypropylene foam offers higher chemical resistance and temperature tolerance compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for packaging sensitive electronics. Polyethylene foam excels in cushioning and impact absorption, providing superior protection for fragile items during shipping.
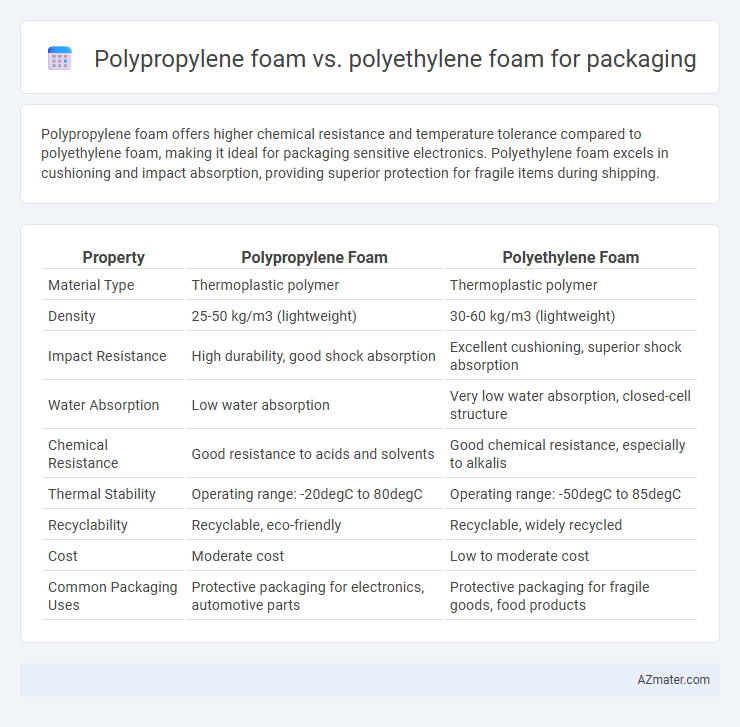
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | 25-50 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 30-60 kg/m3 (lightweight) |
| Impact Resistance | High durability, good shock absorption | Excellent cushioning, superior shock absorption |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Very low water absorption, closed-cell structure |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and solvents | Good chemical resistance, especially to alkalis |
| Thermal Stability | Operating range: -20degC to 80degC | Operating range: -50degC to 85degC |
| Recyclability | Recyclable, eco-friendly | Recyclable, widely recycled |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Low to moderate cost |
| Common Packaging Uses | Protective packaging for electronics, automotive parts | Protective packaging for fragile goods, food products |
Introduction to Foam Materials in Packaging
Polypropylene foam offers higher tensile strength and better chemical resistance compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for durable packaging solutions. Polyethylene foam provides excellent cushioning and impact absorption due to its closed-cell structure, suitable for protecting fragile items. Both foams are lightweight, but polyethylene foam is often preferred for shock absorption while polypropylene foam excels in thermal insulation and rigidity.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP) Foam
Polypropylene (PP) foam is a lightweight, durable material known for its excellent impact resistance and thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for protective packaging applications. Its closed-cell structure provides superior stiffness and resilience compared to polyethylene foam, enhancing cushioning performance while maintaining form under pressure. PP foam also offers enhanced chemical resistance and recyclability, positioning it as a sustainable alternative in the packaging industry.
Overview of Polyethylene (PE) Foam
Polyethylene (PE) foam is a closed-cell, lightweight material known for its excellent cushioning and shock absorption properties, making it ideal for protective packaging. It exhibits superior resistance to moisture, chemicals, and impact compared to polypropylene foam, enhancing product safety during transportation and storage. PE foam's flexibility and easy machinability allow for customized packaging solutions tailored to various industrial and consumer applications.
Key Differences in Material Properties
Polypropylene foam offers higher rigidity and better heat resistance compared to polyethylene foam, making it suitable for packaging fragile or temperature-sensitive items. Polyethylene foam excels in flexibility and impact absorption, providing superior cushioning for delicate goods during transit. Both materials feature excellent moisture resistance, but polypropylene foam's enhanced chemical stability ensures greater durability in harsh environments.
Protective Qualities: Shock Absorption and Cushioning
Polypropylene foam offers superior shock absorption due to its higher compressive strength and resilience, making it ideal for packaging fragile items requiring robust protection from impacts. Polyethylene foam provides excellent cushioning with its closed-cell structure, effectively absorbing vibrations and preventing surface damage through soft, flexible support. Both materials excel in protective packaging, but polypropylene foam is preferable for heavy-duty applications, while polyethylene foam suits lightweight, delicate contents.
Weight and Density Comparison
Polypropylene foam exhibits a lower density range of about 15-50 kg/m3 compared to polyethylene foam, which typically ranges from 20-100 kg/m3, making polypropylene foam significantly lighter for packaging applications. The reduced weight of polypropylene foam enhances shipping efficiency and lowers transportation costs while maintaining cushioning properties. Polyethylene foam's higher density offers increased durability and impact resistance but adds to the overall package weight.
Durability and Chemical Resistance
Polypropylene foam exhibits superior durability compared to polyethylene foam, offering enhanced resistance to impact, compression, and fatigue, which makes it ideal for protecting heavy or delicate items during transit. Polypropylene foam also boasts excellent chemical resistance, effectively withstanding exposure to solvents, oils, and acids, whereas polyethylene foam has moderate resistance but can degrade when exposed to strong chemicals over time. These properties make polypropylene foam a preferred choice for packaging applications that require prolonged protection and exposure to harsh environmental conditions.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene foam offers superior recyclability compared to polyethylene foam due to its higher melting point and resistance to chemical breakdown, allowing it to be processed multiple times without significant loss of quality. Polyethylene foam, while widely used for cushioning and impact protection, typically has a lower recycling rate and often ends up in landfills, contributing to environmental pollution. Both materials are lightweight and provide excellent shock absorption, but polypropylene foam's enhanced recyclability makes it a more environmentally sustainable option for packaging applications.
Cost Considerations for Packaging Applications
Polyethylene foam generally offers a lower cost solution compared to polypropylene foam for packaging applications due to its widespread availability and simpler manufacturing process. Polypropylene foam provides enhanced durability and chemical resistance, which can justify higher costs in packaging fragile or sensitive items. Choosing between the two depends on balancing budget constraints with the specific protective qualities required for the packaged product.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Polypropylene foam offers superior rigidity and chemical resistance, making it ideal for packaging delicate electronics and automotive parts, while polyethylene foam excels in shock absorption and flexibility, perfect for cushioning fragile items and food packaging. Consider the weight, durability, and environmental resistance requirements of your product to determine the appropriate foam type. Polypropylene suits applications needing long-term protection, whereas polyethylene is better for lightweight, impact-resistant packaging solutions.
Infographic: Polypropylene foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com