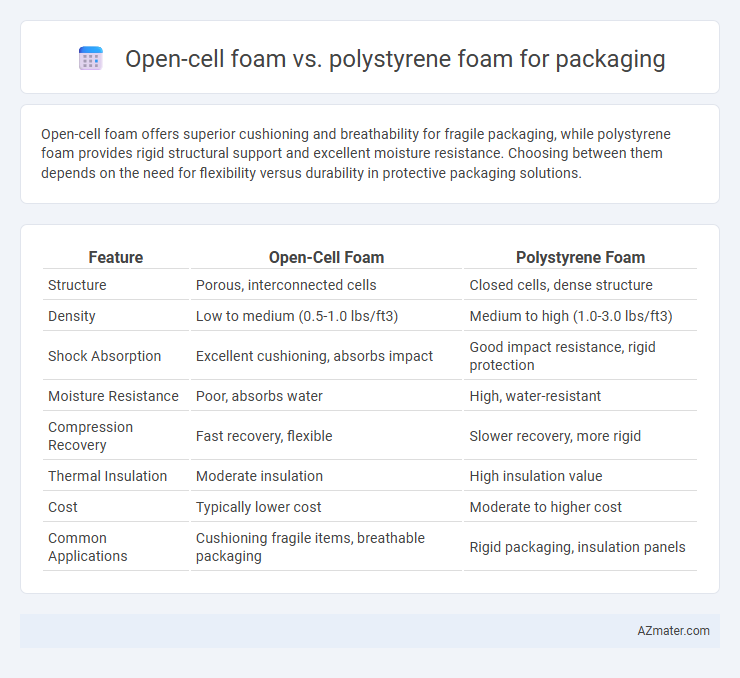
Open-cell foam offers superior cushioning and breathability for fragile packaging, while polystyrene foam provides rigid structural support and excellent moisture resistance. Choosing between them depends on the need for flexibility versus durability in protective packaging solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Open-Cell Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Porous, interconnected cells | Closed cells, dense structure |
| Density | Low to medium (0.5-1.0 lbs/ft3) | Medium to high (1.0-3.0 lbs/ft3) |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent cushioning, absorbs impact | Good impact resistance, rigid protection |
| Moisture Resistance | Poor, absorbs water | High, water-resistant |
| Compression Recovery | Fast recovery, flexible | Slower recovery, more rigid |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation | High insulation value |
| Cost | Typically lower cost | Moderate to higher cost |
| Common Applications | Cushioning fragile items, breathable packaging | Rigid packaging, insulation panels |
Introduction to Packaging Foams
Open-cell foam and polystyrene foam serve distinct roles in packaging due to their structural differences and performance characteristics. Open-cell foam, characterized by interconnected pores, offers superior cushioning and breathability, making it ideal for fragile items requiring shock absorption. Polystyrene foam, with its closed-cell structure, provides excellent rigidity, moisture resistance, and insulation, suitable for protecting heavier or temperature-sensitive products during shipping.
What is Open-Cell Foam?
Open-cell foam is a porous, flexible material characterized by interconnected cells that allow air to flow freely through its structure, providing excellent cushioning and shock absorption in packaging applications. This foam type is typically made from polyurethane and offers superior breathability and compressibility compared to closed-cell options like polystyrene foam. Open-cell foam is ideal for protecting delicate items by dispersing impact forces while being lightweight and environmentally friendly, making it a preferred choice for sustainable packaging solutions.
What is Polystyrene Foam?
Polystyrene foam, a lightweight and rigid material made from expanded polystyrene beads, is widely used in packaging for its excellent insulation and shock absorption properties. This closed-cell foam provides superior protection against impact and moisture, making it ideal for cushioning fragile items during shipping. Compared to open-cell foam, polystyrene foam offers greater structural strength and resistance to compression, ensuring products remain secure throughout transit.
Key Differences Between Open-Cell and Polystyrene Foam
Open-cell foam features a porous structure that offers excellent cushioning and breathability, making it ideal for packaging fragile items that require shock absorption and ventilation. Polystyrene foam, characterized by its closed-cell composition, provides rigid, lightweight protection with superior moisture resistance, often used for packaging electronics and food products. The key differences lie in density, compressive strength, and water absorption, impacting their suitability for various packaging applications.
Protection and Cushioning Performance
Open-cell foam offers superior cushioning by absorbing shocks through its porous structure, making it ideal for delicate or irregularly shaped items in packaging. Polystyrene foam provides excellent protection against compression and impacts due to its rigid, closed-cell composition, often used for heavy or brittle products requiring firm support. Choosing between these foams depends on balancing cushioning needs with structural protection based on the specific packaging requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Open-cell foam offers superior biodegradability and reduced environmental toxicity compared to polystyrene foam, which is notorious for its persistence in landfills and contribution to ocean pollution. The porous structure of open-cell foam allows for easier microbial decomposition, enhancing its sustainability profile in packaging applications. Polystyrene foam production relies heavily on non-renewable petroleum resources and generates significant greenhouse gas emissions, making it less eco-friendly than open-cell alternatives.
Cost Comparison: Open-Cell vs Polystyrene Foam
Open-cell foam typically offers a lower cost per cubic foot compared to polystyrene foam, making it a budget-friendly option for packaging applications requiring cushioning and impact absorption. Polystyrene foam, while slightly more expensive, provides superior rigidity and moisture resistance, which can reduce product damage and overall costs in transit. Evaluating total packaging expenses requires balancing upfront material costs against protection performance and potential product loss.
Common Packaging Applications
Open-cell foam offers superior cushioning and shock absorption, making it ideal for packaging fragile electronics and delicate instruments. Polystyrene foam, known for its rigidity and lightweight properties, excels in protecting heavy or bulky items such as appliances and automotive parts. Both materials enhance packaging efficiency by preventing damage during transport, but choice depends on the level of protection and product sensitivity required.
Customization and Versatility
Open-cell foam offers superior customization options with its flexible density and compressibility, making it ideal for delicate item protection and irregular shapes. Polystyrene foam provides rigidity and consistent cushioning, suitable for standard-shaped products requiring strong impact resistance but offers limited adaptability. The versatility of open-cell foam allows tailored cushioning solutions, whereas polystyrene excels in mass production with uniform protective properties.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Open-cell foam offers superior cushioning and flexibility, making it ideal for fragile items requiring shock absorption and breathability, while polystyrene foam excels in rigid support and moisture resistance for heavy or moisture-sensitive products. Selecting the right foam depends on factors such as product fragility, weight, environmental exposure, and cost efficiency. Careful evaluation of these parameters ensures optimal protection and cost-effectiveness in packaging applications.
Infographic: Open-cell foam vs Polystyrene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com