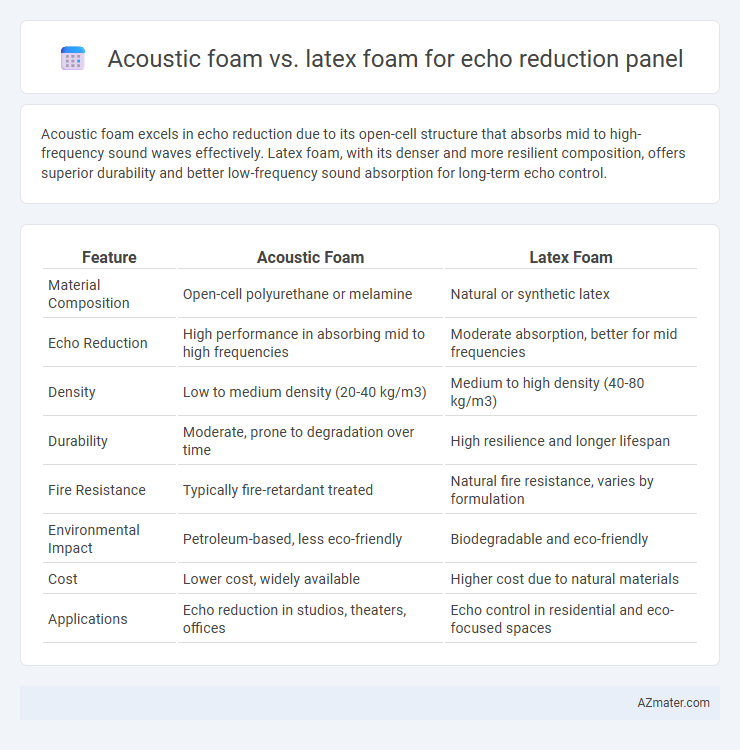
Acoustic foam excels in echo reduction due to its open-cell structure that absorbs mid to high-frequency sound waves effectively. Latex foam, with its denser and more resilient composition, offers superior durability and better low-frequency sound absorption for long-term echo control.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acoustic Foam | Latex Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Open-cell polyurethane or melamine | Natural or synthetic latex |
| Echo Reduction | High performance in absorbing mid to high frequencies | Moderate absorption, better for mid frequencies |
| Density | Low to medium density (20-40 kg/m3) | Medium to high density (40-80 kg/m3) |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to degradation over time | High resilience and longer lifespan |
| Fire Resistance | Typically fire-retardant treated | Natural fire resistance, varies by formulation |
| Environmental Impact | Petroleum-based, less eco-friendly | Biodegradable and eco-friendly |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to natural materials |
| Applications | Echo reduction in studios, theaters, offices | Echo control in residential and eco-focused spaces |
Introduction to Echo Reduction Panels
Echo reduction panels designed with acoustic foam are highly effective due to their open-cell structure that absorbs high-frequency sound waves, reducing reverberation in rooms. Latex foam panels offer enhanced versatility by combining sound absorption with durability and natural resistance to mold and mildew, making them suitable for a variety of environments. Both materials contribute significantly to improving sound clarity and minimizing echo, with acoustic foam excelling in professional studio settings and latex foam favored for eco-friendly or residential applications.
Understanding Acoustic Foam: Composition and Properties
Acoustic foam, composed primarily of open-cell polyurethane, is designed to absorb sound waves by converting acoustical energy into heat, making it effective for reducing echoes and reverberations in indoor spaces. Its porous structure traps sound waves, particularly in mid to high frequency ranges, thus minimizing sound reflections and improving overall audio clarity. In contrast to latex foam, which is denser and often used for cushioning, acoustic foam's lightweight and rigid properties specifically target sound diffusion and absorption, enhancing its performance in echo reduction panels.
Latex Foam Explained: Features and Structure
Latex foam features an open-cell structure that provides excellent sound absorption by trapping and dispersing sound waves, making it highly effective for echo reduction panels. Unlike acoustic foam, latex foam offers superior durability, natural resistance to mold and dust mites, and a softer, more flexible texture that enhances comfort and longevity. Its eco-friendly composition and breathability contribute to maintaining optimal acoustic performance over time in various environments.
Sound Absorption Efficiency: Acoustic vs Latex Foam
Acoustic foam typically offers superior sound absorption efficiency due to its open-cell structure that effectively traps airborne sound waves, reducing echo and reverberation. Latex foam, while providing some degree of sound dampening, generally performs better in vibration isolation and impact noise reduction rather than high-frequency echo absorption. The porous nature and density of acoustic foam make it a preferred material for echo reduction panels in professional audio environments.
Durability and Longevity: Which Foam Lasts Longer?
Acoustic foam typically offers excellent sound absorption but tends to degrade faster due to exposure to UV light and humidity, reducing its lifespan to around 3-5 years. Latex foam, made from natural or synthetic rubber, provides superior durability and resistance to environmental factors, often maintaining its structural integrity and acoustic properties for over a decade. Choosing latex foam for echo reduction panels ensures longer-lasting performance with lower maintenance compared to traditional acoustic foam options.
Installation and Maintenance Comparison
Acoustic foam panels are lightweight and easy to install using spray adhesive or double-sided tape, making them ideal for quick mounting and repositioning without damage. Latex foam requires more precise installation, often necessitating professional adhesives or mechanical fasteners due to its denser structure and higher flexibility. Acoustic foam demands minimal maintenance, primarily occasional dusting, while latex foam benefits from more frequent cleaning to prevent degradation from dust and oils, ensuring long-term echo reduction performance.
Health and Safety Considerations
Acoustic foam is typically made from polyurethane and may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that require proper ventilation during installation to minimize respiratory irritation. Latex foam, made from natural or synthetic latex, is generally hypoallergenic and resistant to mold and mildew, reducing the risk of allergens and microbial growth in echo reduction panels. Both materials should be assessed for flame retardancy and toxicity levels to ensure compliance with health and safety regulations in enclosed spaces.
Cost-Effectiveness and Budget Factors
Acoustic foam typically offers a more cost-effective solution for echo reduction panels due to its lower price point and availability in various densities and thicknesses that suit budget constraints. Latex foam, while more expensive, provides superior durability and natural sound absorption properties, which may reduce replacement frequency and long-term costs. Budget considerations favor acoustic foam for short-term projects, whereas latex foam's higher initial investment may deliver better value in professional or high-performance acoustic treatments.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Acoustic foam is typically made from petroleum-based polyurethane, which poses environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradable nature and reliance on fossil fuels, whereas latex foam is derived from natural rubber, offering a more sustainable and biodegradable option for echo reduction panels. Latex foam's renewable sourcing and lower environmental impact make it a preferred choice for eco-conscious applications, contributing to reduced carbon footprint and waste. Selecting latex foam enhances sustainability in soundproofing by combining effective acoustic performance with renewable material benefits.
Choosing the Right Foam for Optimal Echo Reduction
Acoustic foam is specifically engineered with open-cell structures that absorb mid to high-frequency sounds, making it ideal for echo reduction in recording studios and home theaters. Latex foam, although denser and more durable, primarily provides comfort and support rather than targeted sound absorption, resulting in less effective echo control. Selecting acoustic foam with the appropriate thickness and density ensures optimal echo reduction by minimizing sound reflections and enhancing room acoustics.
Infographic: Acoustic foam vs Latex foam for Echo reduction panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com