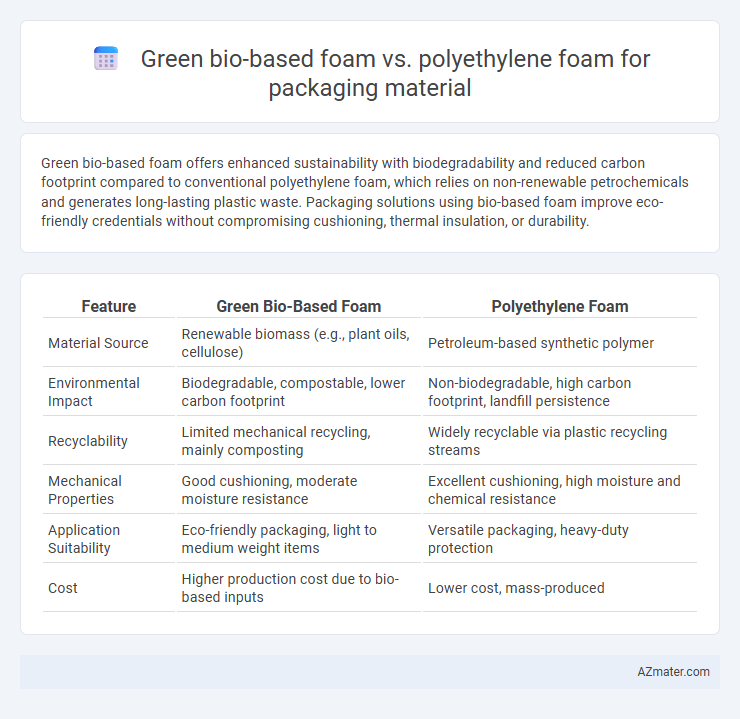
Green bio-based foam offers enhanced sustainability with biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint compared to conventional polyethylene foam, which relies on non-renewable petrochemicals and generates long-lasting plastic waste. Packaging solutions using bio-based foam improve eco-friendly credentials without compromising cushioning, thermal insulation, or durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Bio-Based Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable biomass (e.g., plant oils, cellulose) | Petroleum-based synthetic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, high carbon footprint, landfill persistence |
| Recyclability | Limited mechanical recycling, mainly composting | Widely recyclable via plastic recycling streams |
| Mechanical Properties | Good cushioning, moderate moisture resistance | Excellent cushioning, high moisture and chemical resistance |
| Application Suitability | Eco-friendly packaging, light to medium weight items | Versatile packaging, heavy-duty protection |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to bio-based inputs | Lower cost, mass-produced |
Introduction to Packaging Foams: Green Bio-Based vs Polyethylene
Green bio-based foams, derived from renewable resources like plant oils and starches, offer sustainable alternatives to conventional polyethylene foam, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. These eco-friendly foams provide comparable cushioning, thermal insulation, and impact resistance while significantly reducing carbon footprint and waste accumulation. Advances in green polymer chemistry enable tailored bio-foam properties suitable for diverse packaging applications, highlighting their growing role in sustainable supply chains.
Defining Green Bio-Based Foam: Composition and Benefits
Green bio-based foam is primarily made from renewable resources such as plant starches, cellulose, or polylactic acid (PLA), which significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels compared to polyethylene foam. It offers enhanced biodegradability and lower carbon footprint, making it an eco-friendly alternative for packaging materials. The foam's lightweight structure provides effective cushioning while supporting sustainability goals in packaging applications.
Understanding Polyethylene Foam: Structure and Usage
Polyethylene foam consists of closed-cell structures that provide excellent cushioning, water resistance, and durability, making it a preferred choice for protective packaging. Its lightweight and flexible properties allow it to absorb shocks effectively, safeguarding fragile items during transit. Commonly used in electronics, automotive parts, and consumer goods packaging, polyethylene foam ensures impact resistance and long-lasting performance.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Sustainability
Green bio-based foam offers superior biodegradability compared to polyethylene foam, breaking down naturally in composting environments within months. Its production relies on renewable resources such as plant-based materials, significantly reducing carbon footprint and dependence on fossil fuels. Conversely, polyethylene foam is derived from non-renewable petroleum, persists in landfills for centuries, and contributes to long-term environmental pollution.
Performance Comparison: Cushioning and Protection
Green bio-based foam offers superior cushioning and impact absorption due to its natural cellular structure, enhancing product protection during transit. Polyethylene foam provides excellent resilience and water resistance, making it effective for shock isolation but less biodegradable. The eco-friendly composition of bio-based foam aligns with sustainability goals while maintaining competitive protective performance in packaging applications.
Cost Analysis: Production and Market Prices
Green bio-based foam typically incurs higher production costs than polyethylene foam due to the expense of raw bio-based materials and less established manufacturing processes. Market prices for green bio-based foam remain elevated given limited scale production and premium demand for sustainable packaging solutions. Polyethylene foam benefits from mass production efficiencies and abundant petrochemical feedstocks, offering lower market prices and widespread availability.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Green bio-based foams often meet stringent environmental regulations such as USDA BioPreferred and European EN 13432 compostability standards, ensuring eco-friendly packaging solutions. Polyethylene foam, while widely accepted for its protective qualities, requires compliance with FDA food-contact regulations and REACH chemical safety standards to guarantee safety. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and ASTM D6400 for compostability further distinguish green bio-based foams in sustainable packaging compliance.
Consumer Perceptions and Industry Trends
Green bio-based foam, derived from renewable resources such as plant starches and algae, is increasingly favored by consumers for its eco-friendly properties and biodegradability, aligning with the growing demand for sustainable packaging. Polyethylene foam, valued for its durability, cushioning, and moisture resistance, remains dominant in industries requiring robust protection but faces criticism for its environmental impact and difficulty in recycling. Industry trends reveal a shift towards hybrid solutions combining bio-based materials with polyethylene to balance performance with sustainability, driven by regulatory pressures and consumer preferences for green alternatives.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Materials
Green bio-based foam faces challenges such as higher production costs, limited mechanical strength, and inconsistent performance under varying environmental conditions compared to polyethylene foam. Polyethylene foam exhibits excellent durability and moisture resistance but struggles with environmental issues, including low biodegradability and dependency on fossil fuels. Both materials are limited by processing complexities and recycling constraints, impacting their widespread adoption in sustainable packaging solutions.
Future Outlook: Innovations in Sustainable Packaging Foams
Green bio-based foam is rapidly advancing with innovations that enhance biodegradability and reduce carbon footprint in packaging applications. Researchers are developing novel plant-based polymers and mycelium composites that offer comparable cushioning and durability to traditional polyethylene foam. Future packaging solutions will likely integrate smart bio-foams with improved recyclability, supporting circular economy goals and meeting stricter environmental regulations globally.
Infographic: Green bio-based foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging material
 azmater.com
azmater.com