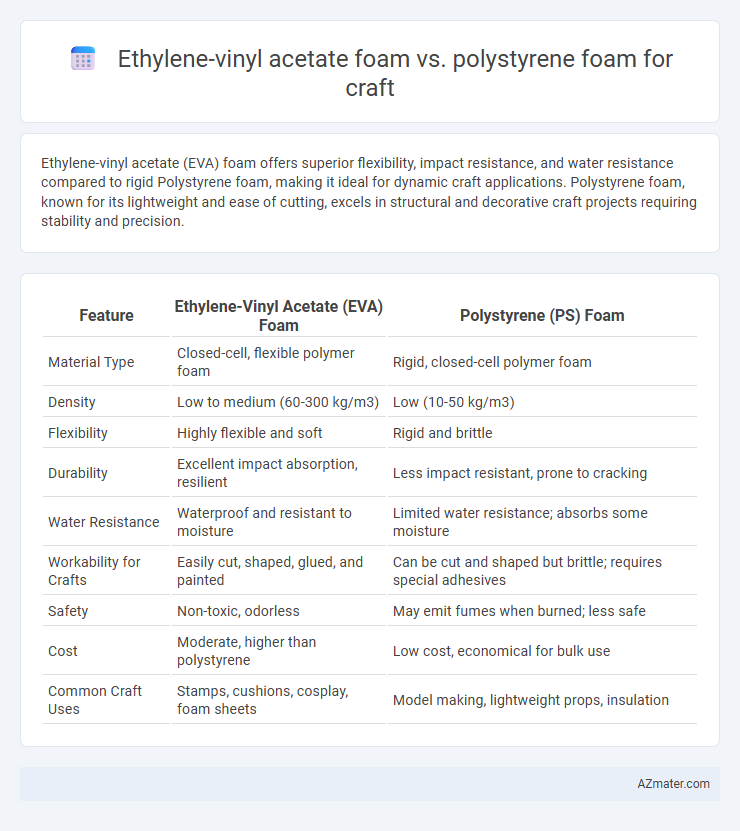
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior flexibility, impact resistance, and water resistance compared to rigid Polystyrene foam, making it ideal for dynamic craft applications. Polystyrene foam, known for its lightweight and ease of cutting, excels in structural and decorative craft projects requiring stability and precision.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam | Polystyrene (PS) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Closed-cell, flexible polymer foam | Rigid, closed-cell polymer foam |
| Density | Low to medium (60-300 kg/m3) | Low (10-50 kg/m3) |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and soft | Rigid and brittle |
| Durability | Excellent impact absorption, resilient | Less impact resistant, prone to cracking |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof and resistant to moisture | Limited water resistance; absorbs some moisture |
| Workability for Crafts | Easily cut, shaped, glued, and painted | Can be cut and shaped but brittle; requires special adhesives |
| Safety | Non-toxic, odorless | May emit fumes when burned; less safe |
| Cost | Moderate, higher than polystyrene | Low cost, economical for bulk use |
| Common Craft Uses | Stamps, cushions, cosplay, foam sheets | Model making, lightweight props, insulation |
Introduction to EVA Foam and Polystyrene Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers lightweight, flexible, and impact-resistant properties, making it ideal for detailed craft projects that require durability and comfort. Polystyrene foam, commonly known as Styrofoam, provides rigid, lightweight structure with excellent insulation but is more brittle and prone to breakage during intricate cutting or shaping. Choosing between EVA foam and polystyrene foam depends on the craft's need for flexibility versus structural stability, with EVA favored for wearable props and polystyrene preferred for static models and architectural mockups.
Material Composition and Properties
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam consists of a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate, providing a flexible, soft, and lightweight material with excellent shock absorption and durability, making it ideal for craft projects requiring cushioning and flexibility. Polystyrene foam, derived from styrene monomers, is rigid, lightweight, and offers high thermal insulation but lacks flexibility and has a brittle texture, which limits its use in crafts that demand pliability and impact resistance. EVA foam's closed-cell structure resists water and UV damage, while polystyrene foam is more prone to breaking down under environmental stress and is less resistant to solvents and adhesives commonly used in crafting.
Weight and Density Comparison
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam typically exhibits lower density values, ranging from 40 to 200 kg/m3, compared to polystyrene foam, which generally ranges from 15 to 80 kg/m3. EVA foam's lightweight structure offers flexibility and durability, making it suitable for crafts requiring cushioning and impact resistance. Polystyrene foam, while lighter at lower densities, is more rigid and less resilient under stress, influencing its selection in projects prioritizing structural support over softness.
Flexibility and Workability
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior flexibility compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for intricate craft designs requiring bending and shaping without cracking. EVA foam's soft texture and lightweight nature enhance workability, allowing easy cutting, gluing, and heat shaping. Polystyrene foam, while rigid and less flexible, provides sturdiness for structural projects but is more prone to breakage during detailed crafting tasks.
Cutting and Shaping Ease
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior flexibility and softness, making it easier to cut and shape smoothly with standard craft knives compared to rigid polystyrene foam. Polystyrene foam is prone to cracking and breaking during detailed cuts but holds its form well for structural craft projects. EVA foam's resilience and ability to withstand bending without snapping provide better versatility for intricate designs and wearable crafts.
Adhesion and Paint Compatibility
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior adhesion properties compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for crafts requiring strong bonding with various adhesives such as hot glue and contact cement. EVA foam exhibits excellent paint compatibility, allowing for smooth application of acrylic and spray paints without the risk of melting or damage. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight, is prone to dissolving or deforming under solvent-based paints and aggressive adhesives, limiting its use in intricate or durable craft projects.
Durability and Lifespan
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior durability and flexibility compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for crafts that require repeated bending or shaping without cracking. EVA foam resists moisture and UV damage better, ensuring a longer lifespan in various environmental conditions. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and inexpensive, tends to be more brittle and prone to deterioration over time, reducing its effectiveness for long-lasting craft projects.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is generally considered safer for craft use due to its non-toxic, non-irritant properties and low emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), posing minimal health risks during cutting and shaping. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and versatile, can release harmful styrene vapors when heated or burned, presenting toxicity concerns and potential respiratory irritation. Selecting EVA foam reduces exposure to hazardous chemicals, making it a preferred choice for craft projects requiring frequent handling and indoor use.
Applications in Craft Projects
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is ideal for craft projects requiring flexibility, durability, and ease of cutting, making it popular for costumes, model making, and foam stamps. Polystyrene foam excels in applications that demand lightweight, rigid structures such as architectural models, floral arrangements, and prop building due to its firm texture and ability to be easily shaped or painted. Both foams offer distinct advantages, with EVA foam better suited for tactile, wearable crafts and polystyrene favored for stiff, structural elements.
Cost and Accessibility
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam generally costs more than polystyrene foam due to its superior flexibility and durability, making it a preferred choice for high-quality crafts. Polystyrene foam is widely accessible and budget-friendly, often used for large-scale or disposable craft projects but lacks the resilience of EVA foam. Craft enthusiasts prioritize EVA foam when longevity and comfort are essential, while polystyrene foam caters to cost-effective and easily available options.
Infographic: Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam vs Polystyrene foam for Craft
 azmater.com
azmater.com