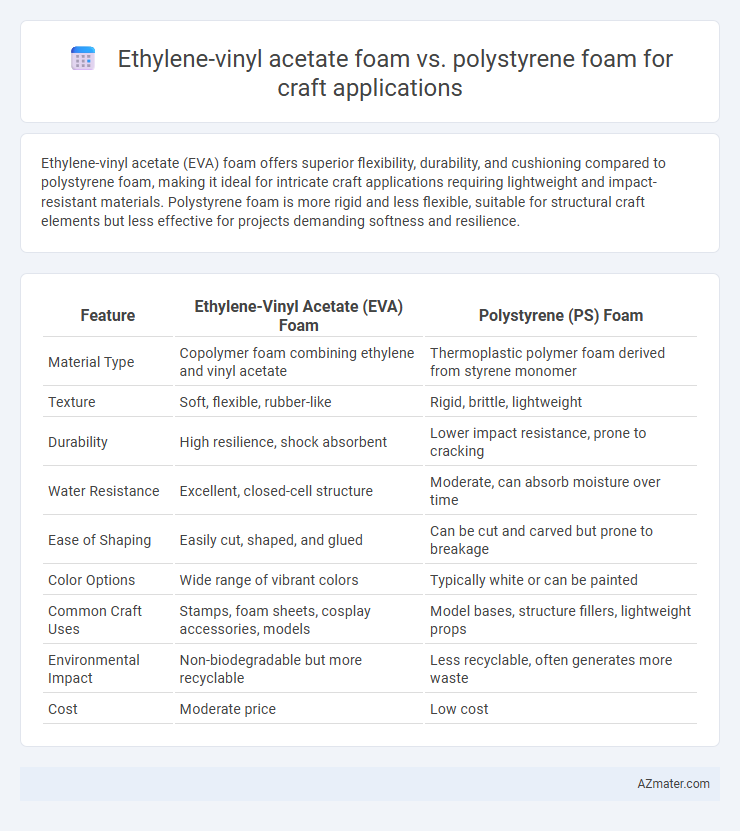
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior flexibility, durability, and cushioning compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for intricate craft applications requiring lightweight and impact-resistant materials. Polystyrene foam is more rigid and less flexible, suitable for structural craft elements but less effective for projects demanding softness and resilience.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam | Polystyrene (PS) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Copolymer foam combining ethylene and vinyl acetate | Thermoplastic polymer foam derived from styrene monomer |
| Texture | Soft, flexible, rubber-like | Rigid, brittle, lightweight |
| Durability | High resilience, shock absorbent | Lower impact resistance, prone to cracking |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, closed-cell structure | Moderate, can absorb moisture over time |
| Ease of Shaping | Easily cut, shaped, and glued | Can be cut and carved but prone to breakage |
| Color Options | Wide range of vibrant colors | Typically white or can be painted |
| Common Craft Uses | Stamps, foam sheets, cosplay accessories, models | Model bases, structure fillers, lightweight props |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable but more recyclable | Less recyclable, often generates more waste |
| Cost | Moderate price | Low cost |
Introduction to Craft Foam Materials
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam and polystyrene foam are both popular materials used in craft applications due to their unique properties. EVA foam offers excellent flexibility, durability, and a soft texture, making it ideal for wearable crafts and detailed shaping. Polystyrene foam, characterized by its lightweight and rigid structure, is preferred for model building and sculpting projects that require a sturdy base.
Overview of Ethylene-vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior flexibility, durability, and shock absorption compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for craft applications requiring softness and resilience. Its closed-cell structure ensures water resistance and excellent cushioning, while its ease of cutting and shaping facilitates intricate designs and detailed projects. EVA foam's non-toxic, lightweight, and color-retentive properties provide significant advantages over the more rigid and brittle polystyrene foam in artistic and functional crafts.
Overview of Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam is a lightweight, rigid material commonly used in craft applications due to its excellent insulation properties and ease of cutting and shaping. Its closed-cell structure provides strong resistance to moisture, making it ideal for projects requiring durability and water resistance. Compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate foam, polystyrene foam offers higher compressive strength but is less flexible and more brittle, influencing its suitability for specific crafting needs.
Physical Properties Comparison
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits superior flexibility, cushioning, and impact resistance compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for craft applications requiring durable and pliable material. Polystyrene foam offers higher rigidity and excellent thermal insulation but lacks the resilience and softness of EVA foam, limiting its use where flexibility is critical. The density of EVA foam typically ranges from 70 to 300 kg/m3, whereas polystyrene foam density varies widely but is generally lower, contributing to EVA's enhanced shock absorption and tensile strength in crafting projects.
Ease of Cutting and Shaping
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior ease of cutting and shaping compared to polystyrene foam due to its pliable, flexible structure that resists cracking and crumbling. EVA foam can be smoothly sculpted with scissors, craft knives, or heat tools, making it ideal for detailed craft projects requiring intricate designs. Polystyrene foam, while rigid and lightweight, tends to produce rough edges and can easily break or chip during cutting, posing challenges for precise shaping in crafting applications.
Adhesion and Compatibility with Glues
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits superior adhesion properties and is highly compatible with various craft glues, including hot glue, contact cement, and PVA adhesives, ensuring strong, flexible bonds suitable for diverse craft projects. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and easy to shape, often requires specialized adhesives like foam-safe glues or solvent-based products to prevent surface damage and achieve effective bonding. EVA foam's flexibility and resilience enhance glue compatibility, reducing the risk of cracking or detachment compared to the more brittle polystyrene foam used in crafting.
Paintability and Finishing Options
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior paintability compared to polystyrene foam due to its closed-cell structure, which allows for smooth surface finishing without excessive absorption or paint blistering. Polystyrene foam tends to require specialized primers and sealants to prevent solvent damage and ensure proper adhesion of paints, making finishing more labor-intensive. EVA foam's flexibility and resistance to cracking provide a wider range of finishing options, including airbrushing, screen printing, and coatings, ideal for detailed craft applications.
Durability and Flexibility in Crafts
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for craft applications requiring repeated bending and shaping without breaking. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and rigid, tends to be brittle and prone to cracking under stress, limiting its durability in dynamic or flexible craft projects. EVA foam's resilience and cushioning properties provide enhanced longevity and versatility compared to the more fragile nature of polystyrene foam in craft usage.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior safety in craft applications due to its non-toxic, flexible, and hypoallergenic properties, reducing risks of skin irritation and chemical exposure compared to polystyrene foam. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, releases toxic styrene compounds during manufacturing and disposal, posing environmental hazards and contributing to persistent plastic pollution. EVA foam is more environmentally friendly, being recyclable and less prone to releasing harmful microplastics, making it a safer sustainable choice for crafts.
Choosing the Best Foam for Your Craft Project
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior flexibility, durability, and ease of cutting, making it ideal for detailed craft projects requiring a soft, resilient material. Polystyrene foam, known for its rigid structure and lightweight nature, provides excellent insulation and is better suited for static, structural crafts that need firm support. Choosing the best foam depends on the project's needs: EVA excels in wearable or flexible designs, while polystyrene supports sturdy, three-dimensional models.
Infographic: Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam vs Polystyrene foam for Craft application
 azmater.com
azmater.com