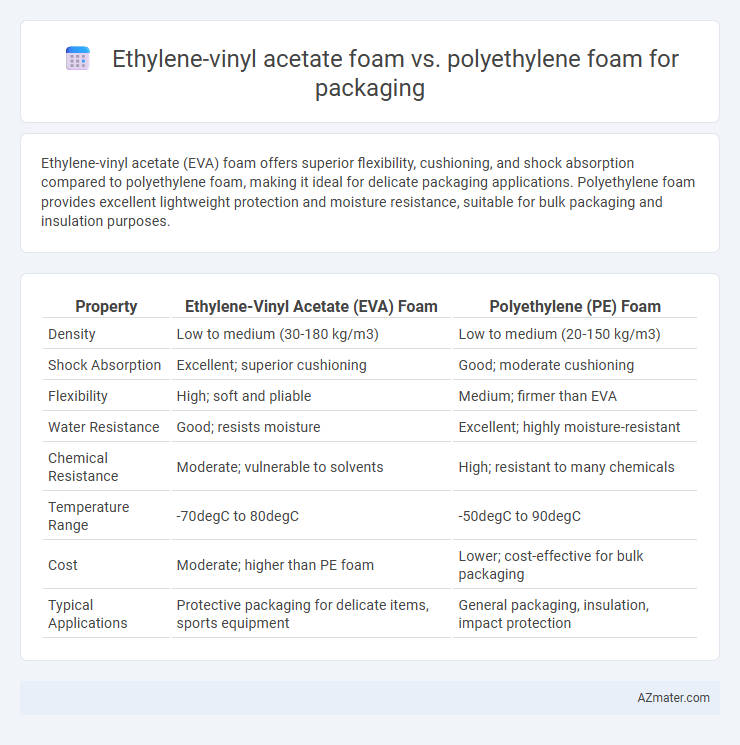
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior flexibility, cushioning, and shock absorption compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for delicate packaging applications. Polyethylene foam provides excellent lightweight protection and moisture resistance, suitable for bulk packaging and insulation purposes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam | Polyethylene (PE) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to medium (30-180 kg/m3) | Low to medium (20-150 kg/m3) |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent; superior cushioning | Good; moderate cushioning |
| Flexibility | High; soft and pliable | Medium; firmer than EVA |
| Water Resistance | Good; resists moisture | Excellent; highly moisture-resistant |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate; vulnerable to solvents | High; resistant to many chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -70degC to 80degC | -50degC to 90degC |
| Cost | Moderate; higher than PE foam | Lower; cost-effective for bulk packaging |
| Typical Applications | Protective packaging for delicate items, sports equipment | General packaging, insulation, impact protection |
Introduction to EVA and PE Foams in Packaging
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam and polyethylene (PE) foam are widely used materials in packaging due to their unique cushioning and protective properties. EVA foam offers excellent elasticity, shock absorption, and resistance to UV radiation, making it ideal for delicate or outdoor-sensitive products. PE foam provides lightweight, closed-cell structure with superior moisture resistance and thermal insulation, commonly used for heavy-duty shipping and impact protection.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam consists of a copolymer blend of ethylene and vinyl acetate units that create a flexible, elastic matrix with moderate polarity, enhancing adhesion and cushioning properties. Polyethylene (PE) foam is composed primarily of long chains of the ethylene monomer, resulting in a nonpolar, chemically inert structure with closed-cell morphology that provides excellent moisture resistance and compression recovery. The incorporation of vinyl acetate in EVA foam introduces polar functional groups, increasing flexibility and impact absorption compared to the more rigid, nonpolar, and hydrophobic nature of PE foam used in packaging applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to polyethylene (PE) foam, making it ideal for cushioning delicate items. EVA foam typically exhibits higher tensile strength and better resilience under compression, maintaining shape after repeated stress. Polyethylene foam, on the other hand, has a lower density and excellent moisture resistance, providing lightweight, water-repellent packaging protection but less durability under heavy loads.
Cushioning and Shock Absorption Performance
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits superior cushioning and shock absorption performance compared to polyethylene (PE) foam due to its greater elasticity and resilience, making it ideal for packaging fragile items. EVA foam maintains its shape and absorbs impact more effectively under repeated stress, ensuring enhanced protection during transportation. In contrast, PE foam offers moderate cushioning but tends to compress permanently over time, reducing its shock absorption capabilities in high-impact packaging applications.
Durability and Longevity in Packaging Applications
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior durability and longevity compared to polyethylene (PE) foam in packaging applications due to its higher resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and mechanical stress. EVA foam maintains cushioning and structural integrity over extended periods, making it ideal for protecting sensitive and heavy products during long-term storage and transit. Polyethylene foam, while cost-effective and lightweight, tends to degrade faster under environmental exposure, reducing its effectiveness in providing consistent protective performance over time.
Customization and Versatility in Packaging Design
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior customization with the ability to be easily molded into various shapes and densities, making it ideal for protective packaging that requires precise fit and impact absorption. Polyethylene (PE) foam provides excellent versatility due to its closed-cell structure, which offers resistance to moisture and chemicals, suitable for diverse packaging designs from cushioning fragile electronics to insulation materials. Both EVA and PE foams support customization in packaging design, but EVA excels in flexibility and softness, while PE foam is preferred for durability and resistance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is less environmentally friendly compared to polyethylene (PE) foam due to its lower biodegradability and more complex recycling process, resulting in limited end-of-life options. Polyethylene foam is widely recyclable through established municipal and industrial recycling streams, contributing to reduced landfill waste and lower carbon footprint in packaging applications. The choice of PE foam supports sustainable packaging initiatives by enhancing circular economy practices and minimizing environmental impact.
Cost Analysis: EVA Foam vs PE Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam typically costs more than polyethylene (PE) foam due to its enhanced cushioning properties and better flexibility, making it preferred for premium packaging. PE foam remains the more economical choice for bulk packaging applications, offering adequate protection at a lower price point. When performing cost analysis, consider that EVA's superior impact resistance and durability may reduce damage-related expenses, potentially offsetting the initial higher material cost.
Typical Packaging Applications and Industry Use Cases
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is widely used in packaging applications requiring flexibility and impact absorption, such as protective cushioning for electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods. Polyethylene (PE) foam specializes in moisture resistance and chemical inertness, making it ideal for industrial packaging, automotive parts, and food packaging. Both foams provide excellent shock absorption, but EVA foam's higher durability suits long-term storage, while PE foam's lightweight properties optimize shipping efficiency.
Choosing the Right Foam for Optimal Packaging Solutions
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior flexibility, cushioning, and resistance to UV radiation, making it ideal for packaging delicate electronic components and fragile goods requiring impact absorption. Polyethylene foam excels in chemical resistance, moisture barrier properties, and lightweight durability, suitable for industrial packaging and outdoor shipments exposed to varying environmental conditions. Selecting the right foam depends on product sensitivity, environmental exposure, and required compressive strength to ensure optimal protection and cost efficiency in packaging solutions.
Infographic: Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com