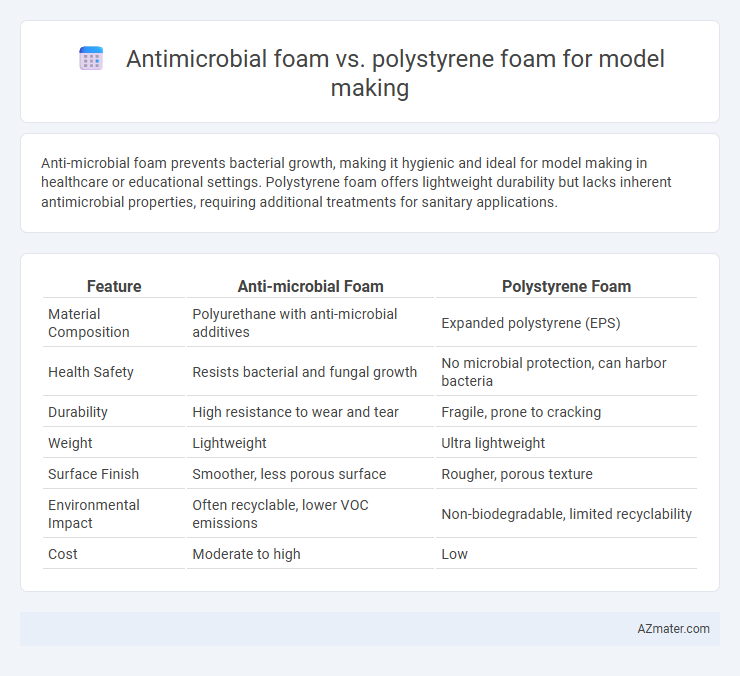
Anti-microbial foam prevents bacterial growth, making it hygienic and ideal for model making in healthcare or educational settings. Polystyrene foam offers lightweight durability but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, requiring additional treatments for sanitary applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-microbial Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyurethane with anti-microbial additives | Expanded polystyrene (EPS) |
| Health Safety | Resists bacterial and fungal growth | No microbial protection, can harbor bacteria |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and tear | Fragile, prone to cracking |
| Weight | Lightweight | Ultra lightweight |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, less porous surface | Rougher, porous texture |
| Environmental Impact | Often recyclable, lower VOC emissions | Non-biodegradable, limited recyclability |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low |
Introduction to Foam Materials in Model Making
Anti-microbial foam in model making offers enhanced resistance to bacterial growth, making it ideal for creating durable and hygienic prototypes, especially in medical or food-related applications. Polystyrene foam, known for lightweight and cost-effective properties, remains a popular choice for detailed and structurally stable models, often used in architectural and design mock-ups. Understanding the distinct characteristics of both foam types helps model makers select materials based on project requirements for durability, safety, and precision.
Overview of Polystyrene Foam Properties
Polystyrene foam is a lightweight, rigid material known for its excellent insulation properties, low moisture absorption, and ease of shaping, making it a popular choice for model making. Its high compressive strength and smooth surface allow for detailed sculpting and finishing, ideal for architectural prototypes and hobby projects. Compared to anti-microbial foam, polystyrene lacks inherent antimicrobial properties but offers superior structural stability and resistance to deformation under pressure.
What Is Anti-Microbial Foam?
Anti-microbial foam is engineered with additives that inhibit the growth of bacteria, mold, and fungi, making it ideal for hygienic and long-lasting model making applications. Unlike polystyrene foam, which is primarily valued for its lightweight and insulating properties, anti-microbial foam provides enhanced durability by reducing microbial degradation. This foam is especially useful in environments where models are exposed to moisture or require frequent handling, ensuring both structural integrity and cleanliness.
Durability Comparison: Anti-Microbial vs Polystyrene Foam
Anti-microbial foam offers superior durability compared to polystyrene foam due to its enhanced resistance to microbial growth, moisture, and environmental degradation. Polystyrene foam tends to degrade faster when exposed to UV light and physical stress, leading to brittleness and crumbling over time. The longevity of anti-microbial foam in model making ensures structural integrity and aesthetic preservation, especially in humid or contaminated environments.
Health and Safety Considerations
Anti-microbial foam offers significant health and safety benefits over polystyrene foam in model making by reducing the risk of microbial growth, which can lead to mold and bacterial contamination. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and easy to shape, tends to release harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and static charges that may pose respiratory hazards and increase fire risks during prolonged use. Selecting anti-microbial foam enhances workspace hygiene and minimizes exposure to toxic fumes, making it a safer choice for both hobbyists and professional model makers.
Workability and Ease of Shaping
Anti-microbial foam offers superior workability with a fine, consistent texture that allows precise cutting and detailed shaping ideal for intricate model making. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and affordable, tends to crumble and produce more dust during carving, making it less suitable for delicate or complex designs. The smooth surface of anti-microbial foam also facilitates easier painting and finishing, enhancing overall model quality and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Anti-microbial foam reduces bacterial growth but is often made from synthetic polymers, raising concerns about long-term environmental impact due to limited biodegradability. Polystyrene foam is widely used for model making but is non-biodegradable and contributes significantly to plastic pollution and landfill waste. Sustainable alternatives prioritize biodegradable, recycled, or bio-based materials to minimize ecological footprints in model construction.
Cost Analysis: Anti-Microbial vs Polystyrene Foam
Anti-microbial foam typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to polystyrene foam due to its specialized treatment that prevents bacterial growth. Polystyrene foam remains more cost-effective for large-scale model making, benefiting from widespread availability and lower manufacturing expenses. However, anti-microbial foam may reduce long-term costs by minimizing health risks and material degradation in environments requiring hygiene.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Anti-microbial foam offers superior hygiene and durability, making it ideal for model making in medical, food, and laboratory environments where contamination control is critical. Polystyrene foam excels in architectural and prototype models due to its lightweight, ease of shaping, and cost-effectiveness, especially for large-scale or detailed structural designs. For applications requiring frequent handling or exposure to moisture, anti-microbial foam provides enhanced resistance and longevity compared to standard polystyrene options.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Model Making Projects
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced hygiene and resistance to mold and bacteria, making it ideal for models needing long-term durability and frequent handling. Polystyrene foam provides lightweight, cost-effective, and easy-to-shape properties, preferred for quick prototypes and basic structural modeling. Selecting the right foam depends on project requirements for durability, hygiene, and detail precision in model making.
Infographic: Anti-microbial foam vs Polystyrene foam for Model making
 azmater.com
azmater.com