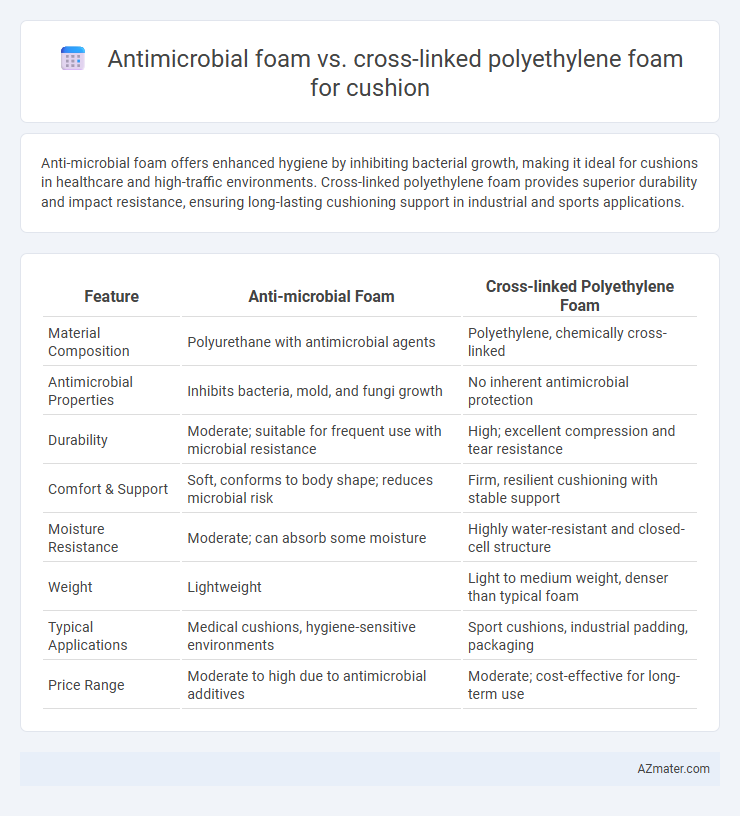
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced hygiene by inhibiting bacterial growth, making it ideal for cushions in healthcare and high-traffic environments. Cross-linked polyethylene foam provides superior durability and impact resistance, ensuring long-lasting cushioning support in industrial and sports applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-microbial Foam | Cross-linked Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyurethane with antimicrobial agents | Polyethylene, chemically cross-linked |
| Antimicrobial Properties | Inhibits bacteria, mold, and fungi growth | No inherent antimicrobial protection |
| Durability | Moderate; suitable for frequent use with microbial resistance | High; excellent compression and tear resistance |
| Comfort & Support | Soft, conforms to body shape; reduces microbial risk | Firm, resilient cushioning with stable support |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate; can absorb some moisture | Highly water-resistant and closed-cell structure |
| Weight | Lightweight | Light to medium weight, denser than typical foam |
| Typical Applications | Medical cushions, hygiene-sensitive environments | Sport cushions, industrial padding, packaging |
| Price Range | Moderate to high due to antimicrobial additives | Moderate; cost-effective for long-term use |
Introduction to Cushion Materials
Anti-microbial foam incorporates agents that inhibit bacterial growth, enhancing hygiene and durability in cushion materials. Cross-linked polyethylene foam offers superior resilience, shock absorption, and water resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting comfort and structural support. Both foams serve specific purposes, with anti-microbial foam prioritizing cleanliness and cross-linked polyethylene foam focusing on mechanical performance in cushion applications.
Overview of Anti-Microbial Foam
Anti-microbial foam incorporates specialized agents that inhibit bacteria, mold, and odor-causing microbes, enhancing hygiene and durability in cushions. This foam type is engineered to resist microbial growth, making it ideal for healthcare, hospitality, and environments requiring stringent sanitation. Compared to cross-linked polyethylene foam, which offers superior resilience and structural support, anti-microbial foam prioritizes cleanliness and user safety in prolonged use.
What is Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) Foam?
Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) foam is a durable, closed-cell material known for its excellent cushioning properties, resistance to compression, and high thermal insulation. Unlike anti-microbial foam, XLPE foam offers superior resilience and moisture resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting cushions in environments prone to dehydration or frequent use. Its cross-linked structure enhances durability and prevents microbial growth, providing a hygienic and comfortable cushioning solution.
Key Differences in Composition
Anti-microbial foam incorporates biocidal agents such as silver ions or zinc compounds, providing inherent resistance to bacteria, mold, and fungi, whereas cross-linked polyethylene foam is a chemically cross-linked polymer structure primarily focused on durability and cushioning properties. The anti-microbial foam's composition allows it to inhibit microbial growth, which is absent in the hydrophobic, closed-cell structure of cross-linked polyethylene foam that emphasizes water resistance and mechanical strength. Each foam's distinct chemical makeup influences its suitability for hygiene-critical environments versus robust, impact-absorbing applications in cushions.
Anti-Microbial Properties: Efficacy and Benefits
Anti-microbial foam exhibits superior efficacy in inhibiting bacterial growth and fungal contamination compared to cross-linked polyethylene foam, which lacks inherent antimicrobial properties. The embedded antimicrobial agents in the foam provide long-lasting protection, reducing odor, allergens, and potential infections in cushion applications. This makes anti-microbial foam particularly beneficial in healthcare settings or environments requiring high hygiene standards.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced resistance to microbial growth, contributing to prolonged hygiene and material integrity in cushion applications. Cross-linked polyethylene foam provides superior durability due to its closed-cell structure, making it highly resistant to compression set, moisture, and wear over extended use. When comparing longevity, cross-linked polyethylene foam typically outperforms anti-microbial foam in maintaining shape and support under constant pressure, while anti-microbial variants excel in environments requiring strict sanitation and reduced microbial degradation.
Comfort and Support Levels
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced hygiene by inhibiting bacterial growth while providing medium to high comfort levels with good support for pressure relief. Cross-linked polyethylene foam delivers firmer support with higher durability and maintains consistent cushioning, ideal for long-term use with moderate comfort. Both foams balance comfort and support differently, with antimicrobial foams prioritizing hygiene and softness, while cross-linked polyethylene excels in structural resilience and firmness.
Safety and Hypoallergenic Considerations
Anti-microbial foam in cushions offers enhanced protection against bacteria, mold, and allergens, significantly reducing risks of skin irritation and respiratory issues for sensitive users. Cross-linked polyethylene foam maintains a stable, closed-cell structure that resists moisture absorption and microbial growth but may lack the inherent anti-microbial properties necessary for demanding hypoallergenic environments. For safety and hypoallergenic applications, anti-microbial foam provides superior protection by actively inhibiting pathogen presence, whereas cross-linked polyethylene foam primarily relies on its physical barrier properties.
Applications and Suitability in Cushioning
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced hygiene by inhibiting microbial growth, making it ideal for cushioning in healthcare, fitness, and food industry applications where cleanliness and odor control are critical. Cross-linked polyethylene foam provides superior durability, impact absorption, and water resistance, suitable for heavy-use cushioning in industrial, automotive, and outdoor environments. Choosing between these foams depends on the specific requirements of microbial resistance versus mechanical performance and environmental exposure.
Cost-Effectiveness and Sustainability
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced hygiene benefits and durability, reducing the need for frequent replacement and cleaning, which translates to long-term cost-effectiveness in cushion applications. Cross-linked polyethylene foam is recognized for its superior resilience and recyclability, contributing to sustainability by supporting circular material usage and minimizing environmental impact. Balancing initial investment, lifespan, and eco-friendliness, both foam types provide cost-effective solutions with distinct advantages for sustainable cushion manufacturing.
Infographic: Anti-microbial foam vs Cross-linked polyethylene foam for Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com