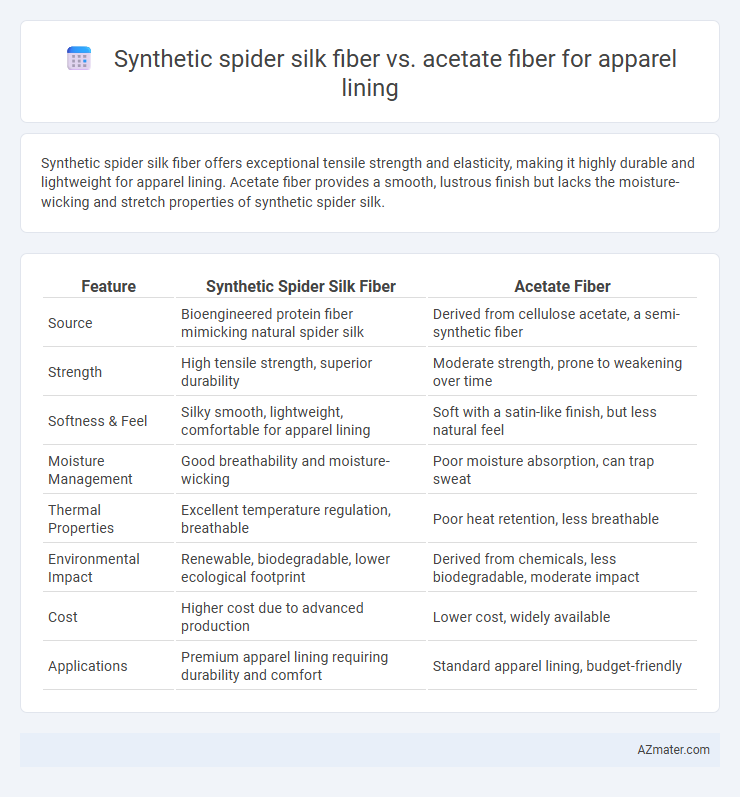
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it highly durable and lightweight for apparel lining. Acetate fiber provides a smooth, lustrous finish but lacks the moisture-wicking and stretch properties of synthetic spider silk.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Spider Silk Fiber | Acetate Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bioengineered protein fiber mimicking natural spider silk | Derived from cellulose acetate, a semi-synthetic fiber |
| Strength | High tensile strength, superior durability | Moderate strength, prone to weakening over time |
| Softness & Feel | Silky smooth, lightweight, comfortable for apparel lining | Soft with a satin-like finish, but less natural feel |
| Moisture Management | Good breathability and moisture-wicking | Poor moisture absorption, can trap sweat |
| Thermal Properties | Excellent temperature regulation, breathable | Poor heat retention, less breathable |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable, lower ecological footprint | Derived from chemicals, less biodegradable, moderate impact |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced production | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Premium apparel lining requiring durability and comfort | Standard apparel lining, budget-friendly |
Introduction to Apparel Lining Materials
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers exceptional strength, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties, making it a cutting-edge option for apparel linings that enhance comfort and durability. Acetate fiber, derived from cellulose acetate, provides a smooth, lustrous finish with excellent drape and breathability, commonly used in lining fabrics for its affordability and aesthetic appeal. Both materials serve distinct functions in apparel lining, with synthetic spider silk excelling in performance and acetate favored for its traditional, elegant texture.
Overview of Synthetic Spider Silk Fiber
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, surpassing traditional acetate fiber commonly used in apparel lining. This biomimetic material offers superior moisture-wicking and thermal regulation properties, enhancing garment comfort and durability. Its lightweight, biodegradable composition positions synthetic spider silk as a sustainable alternative in high-performance fashion applications.
Understanding Acetate Fiber in Apparel
Acetate fiber, derived from cellulose acetate, is widely used in apparel lining due to its smooth texture, excellent drape, and ability to mimic the feel of silk while being more affordable. It offers good moisture absorption and a lustrous finish, enhancing comfort and aesthetic appeal in garment interiors. Compared to synthetic spider silk fibers, acetate is less durable and has a lower tensile strength, but its cost-effectiveness and ease of dyeing make it a popular choice for lining in various clothing applications.
Fiber Structure and Composition Comparison
Synthetic spider silk fiber features a hierarchical protein-based structure with beta-sheet nanocrystals that provide exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, closely mimicking natural spider silk. In contrast, acetate fiber is a cellulose acetate derivative composed of esterified cellulose chains, offering smoothness and a crisp hand but lacking the robust molecular alignment and mechanical performance of synthetic spider silk. The proteinaceous composition of synthetic spider silk enables superior moisture-wicking, durability, and lightweight properties compared to the thermoplastic nature of acetate fibers used in apparel linings.
Comfort, Softness, and Skin Sensation
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers exceptional comfort and softness, mimicking natural silk's smooth texture while being lightweight and breathable, which enhances skin sensation during wear. Acetate fiber provides a silky finish and moderate softness but tends to trap heat and moisture, potentially causing discomfort and a less breathable feel against the skin. For apparel lining, synthetic spider silk is superior in creating a luxurious, gentle, and cool sensation, making it ideal for sensitive skin and extended wear.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits superior moisture management and breathability compared to acetate fiber, effectively wicking sweat away from the skin and enabling rapid evaporation. The advanced nanostructure of synthetic spider silk allows enhanced airflow and temperature regulation, reducing discomfort and humidity buildup inside garments. In contrast, acetate fiber tends to retain moisture and offers lower breathability, making it less ideal for apparel lining in active or warm conditions.
Durability and Strength in Daily Wear
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits superior durability and tensile strength compared to acetate fiber, making it highly suitable for apparel lining subjected to daily wear. Its exceptional resistance to stretching and abrasion ensures prolonged fabric integrity, while acetate fibers tend to weaken and degrade faster under similar conditions. The advanced molecular structure of synthetic spider silk provides enhanced elasticity and resilience, contributing to longer-lasting performance in garments.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior biodegradability and lower carbon emissions during production compared to acetate fiber, which relies on cellulose acetate derived through intensive chemical processes. The sustainable nature of synthetic spider silk is enhanced by its renewable bioengineered proteins, reducing reliance on petrochemical inputs and minimizing toxic waste. Conversely, acetate fiber's environmental impact includes high water consumption and challenges in recyclability, making synthetic spider silk a more eco-friendly choice for apparel lining applications.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Synthetic spider silk fiber commands a higher production cost due to complex biotechnological processes and limited large-scale manufacturing facilities, whereas acetate fiber benefits from established, cost-effective acetate production methods with widespread industrial availability. Market availability of synthetic spider silk remains constrained, primarily accessible through niche suppliers and premium apparel brands, contrasting with the broad, global distribution network of acetate fibers commonly used in apparel linings. Cost analysis highlights synthetic spider silk's premium pricing driven by innovation and material performance, while acetate fiber presents an economical choice with consistent supply for mass-market applications.
Future Trends in Lining Material Innovations
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength, biodegradability, and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional acetate fiber, making it a promising candidate for next-generation apparel lining. Innovations in bioengineered fibers are driving the shift towards sustainable, high-performance materials that enhance comfort and durability in garments. Future trends emphasize eco-friendly production processes and advanced functional attributes, positioning synthetic spider silk fiber as a key material in the evolution of apparel linings.
Infographic: Synthetic spider silk fiber vs Acetate fiber for Apparel lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com