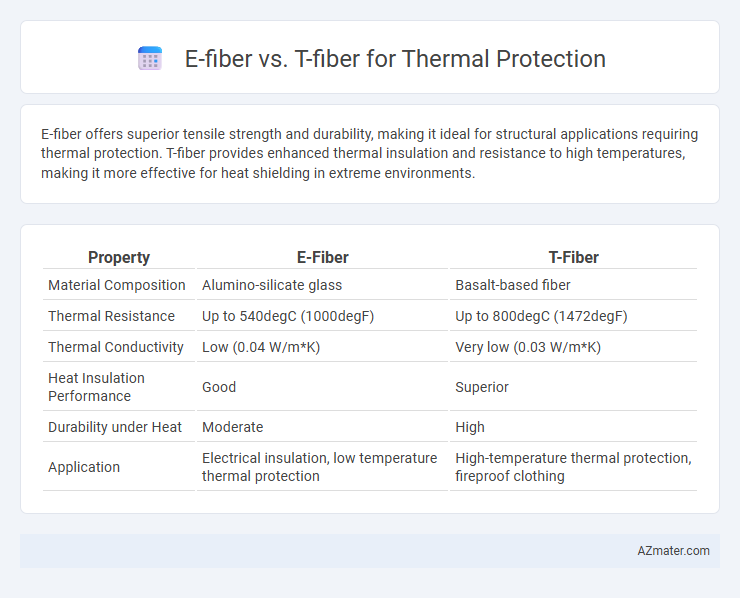
E-fiber offers superior tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for structural applications requiring thermal protection. T-fiber provides enhanced thermal insulation and resistance to high temperatures, making it more effective for heat shielding in extreme environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber | T-Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Alumino-silicate glass | Basalt-based fiber |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 540degC (1000degF) | Up to 800degC (1472degF) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.04 W/m*K) | Very low (0.03 W/m*K) |
| Heat Insulation Performance | Good | Superior |
| Durability under Heat | Moderate | High |
| Application | Electrical insulation, low temperature thermal protection | High-temperature thermal protection, fireproof clothing |
Introduction to Thermal Protection Systems
E-fiber and T-fiber are critical materials in Thermal Protection Systems (TPS) designed to shield spacecraft from extreme aerodynamic heating during re-entry. E-fibers, known for their high tensile strength and resistance to thermal degradation, provide structural reinforcement while maintaining thermal insulation. T-fibers offer superior thermal stability and char formation, enhancing ablative properties essential for dissipating intense heat flux in TPS applications.
Overview of E-Fiber and T-Fiber Materials
E-fiber and T-fiber are specialized glass fibers utilized in thermal protection systems due to their distinct material properties. E-fiber, known as electrical grade glass fiber, offers excellent electrical insulation and moderate thermal resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring electrical and thermal protection. T-fiber, or high-temperature-resistant glass fiber, exhibits superior thermal stability and strength at elevated temperatures, ideal for extreme heat shielding and insulation in aerospace and industrial environments.
Key Properties of E-Fiber for Heat Resistance
E-fiber, also known as E-glass fiber, exhibits superior heat resistance with a melting point around 825degC, making it suitable for thermal protection applications requiring moderate temperature endurance. Its composition, primarily silica and alumina, enhances thermal stability while maintaining excellent tensile strength and electrical insulation properties. These key features provide E-fiber with the ability to withstand prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures without significant degradation.
Unique Characteristics of T-Fiber in Thermal Applications
T-fiber offers superior thermal resistance compared to E-fiber, withstanding temperatures exceeding 1000degC, making it ideal for extreme thermal protection applications. Its unique composition ensures low heat conductivity and enhanced structural integrity under prolonged heat exposure. This makes T-fiber a preferred choice in aerospace, automotive, and firefighting gear requiring reliable insulation and durability.
Thermal Conductivity: E-Fiber vs. T-Fiber
E-fiber exhibits a higher thermal conductivity compared to T-fiber, making it less effective for insulation applications. T-fiber's lower thermal conductivity enhances its thermal protection capabilities by better resisting heat flow and maintaining temperature stability. This makes T-fiber a preferred choice in environments requiring superior thermal insulation performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
E-fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength with high tensile modulus and excellent tensile strength, making it highly effective for thermal protection in demanding environments. T-fiber, while providing adequate thermal resistance, typically shows lower mechanical durability and is more susceptible to degradation under prolonged thermal stress. For applications requiring long-term durability and mechanical resilience, E-fiber is generally preferred over T-fiber in thermal protection systems.
Cost-Effectiveness in Thermal Protection Usage
E-fibers offer a lower cost alternative to T-fibers, making them a more cost-effective choice for large-scale thermal protection applications where budget constraints are critical. While T-fibers provide superior thermal resistance and higher melting points, their production and raw material costs are significantly higher compared to E-fibers. Selecting E-fibers balances thermal protection performance and affordability, especially in environments with moderate heat exposure.
Industry Applications for E-Fiber and T-Fiber
E-fiber and T-fiber materials offer distinct advantages in thermal protection across various industries. E-fiber, known for its high tensile strength and electrical insulation, is widely used in aerospace and automotive sectors to protect components from heat and electrical interference. T-fiber, with superior thermal resistance and flexibility, is preferred in industrial manufacturing and chemical processing for insulation of high-temperature equipment and machinery.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
E-fibers offer lower environmental impact due to their energy-efficient production and recyclability compared to traditional T-fibers, which often rely on energy-intensive manufacturing processes and non-biodegradable materials. The use of E-fibers in thermal protection contributes to sustainability through reduced carbon emissions and enhanced material lifecycle management. In contrast, T-fibers typically generate more waste and pose greater challenges in end-of-life disposal, making E-fiber solutions preferable for eco-conscious thermal protection applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Thermal Protection
Selecting the appropriate fiber for thermal protection depends on specific application requirements, such as temperature resistance, mechanical strength, and environmental exposure. E-fibers offer cost-effective insulation with moderate heat resistance up to approximately 1200degF (650degC), suitable for less demanding conditions, while T-fibers provide superior thermal stability and chemical resistance beyond 1800degF (980degC), ideal for high-performance or industrial settings. Evaluating factors like operating temperature, durability, and budget ensures optimal thermal protection by matching the fiber type to the intended use.
Infographic: E-fiber vs T-fiber for Thermal Protection
 azmater.com
azmater.com