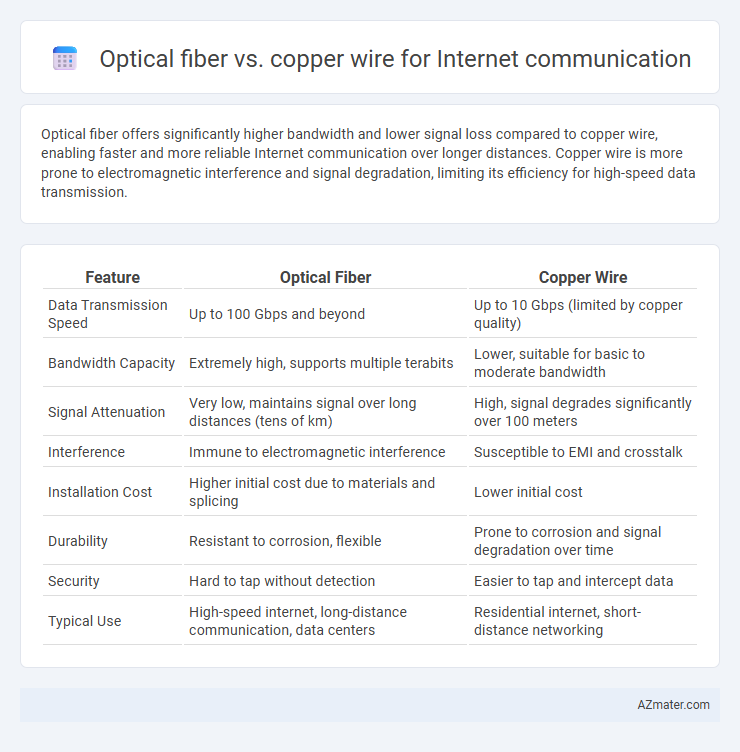
Optical fiber offers significantly higher bandwidth and lower signal loss compared to copper wire, enabling faster and more reliable Internet communication over longer distances. Copper wire is more prone to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation, limiting its efficiency for high-speed data transmission.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Optical Fiber | Copper Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transmission Speed | Up to 100 Gbps and beyond | Up to 10 Gbps (limited by copper quality) |
| Bandwidth Capacity | Extremely high, supports multiple terabits | Lower, suitable for basic to moderate bandwidth |
| Signal Attenuation | Very low, maintains signal over long distances (tens of km) | High, signal degrades significantly over 100 meters |
| Interference | Immune to electromagnetic interference | Susceptible to EMI and crosstalk |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial cost due to materials and splicing | Lower initial cost |
| Durability | Resistant to corrosion, flexible | Prone to corrosion and signal degradation over time |
| Security | Hard to tap without detection | Easier to tap and intercept data |
| Typical Use | High-speed internet, long-distance communication, data centers | Residential internet, short-distance networking |
Introduction to Internet Transmission Media
Optical fiber offers significantly higher bandwidth and faster data transmission speeds compared to copper wire, making it the preferred medium for modern Internet communication. Unlike copper wire, which uses electrical signals susceptible to interference and signal degradation over long distances, optical fiber relies on light signals that provide greater distance coverage with minimal loss. This superior performance enables optical fiber to support the growing demand for high-speed, reliable Internet connectivity in both residential and commercial networks.
Overview of Optical Fiber Technology
Optical fiber technology uses thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as pulses of light, enabling significantly higher bandwidth and faster Internet speeds compared to copper wire. Its immunity to electromagnetic interference and lower signal attenuation over long distances make it ideal for high-speed Internet communication. This technology supports future scalability with increasing data demands, surpassing the limitations of traditional copper wire infrastructure.
Fundamentals of Copper Wire Communication
Copper wire communication relies on electrical signals transmitted through metal conductors, primarily using twisted pair or coaxial cables to carry data. The fundamental limitations include higher susceptibility to electromagnetic interference and signal attenuation over long distances, resulting in reduced bandwidth and slower internet speeds compared to optical fiber. Despite these drawbacks, copper wires remain widely used due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation in existing infrastructure.
Speed and Bandwidth Comparison
Optical fiber provides significantly higher speed and bandwidth compared to copper wire, supporting data rates up to 100 Gbps and beyond, ideal for high-demand internet communication. Copper wire, typically using traditional Ethernet cables, offers speeds up to 1 Gbps with limited bandwidth capacity prone to electromagnetic interference. The advanced signaling and light transmission in optical fiber enable far greater data throughput, lower latency, and longer transmission distances without signal degradation.
Signal Quality and Data Integrity
Optical fiber provides superior signal quality and data integrity compared to copper wire due to its resistance to electromagnetic interference and low signal attenuation over long distances. Fiber optic cables maintain high bandwidth with minimal data loss, ensuring consistent and reliable internet communication. Copper wires, susceptible to interference and signal degradation, often result in lower data transmission speeds and increased error rates.
Distance and Transmission Limitations
Optical fiber allows data transmission over much longer distances than copper wire, often reaching tens of kilometers without significant signal loss, whereas copper wire typically loses signal quality beyond 100 meters. Fiber optic cables use light signals, which are immune to electromagnetic interference, enabling high-speed communication with minimal attenuation. Copper wire suffers from resistance and electromagnetic interference, limiting its bandwidth and effective transmission range for Internet communication.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Optical fiber installation requires specialized equipment and trained technicians to handle delicate glass fibers, whereas copper wire installation is generally more straightforward and compatible with existing infrastructure. Maintenance of optical fiber is less frequent due to its resistance to electromagnetic interference and corrosion, while copper wires often demand more regular checks and repairs because of susceptibility to environmental damage and signal degradation. Despite higher initial installation complexity, optical fiber offers lower long-term maintenance costs and improved durability compared to copper wire in internet communication networks.
Cost Analysis: Optical Fiber vs Copper Wire
Optical fiber offers higher data transmission speeds and greater bandwidth at a lower long-term maintenance cost compared to copper wire, despite having a higher initial installation expense. Copper wire typically incurs lower upfront costs but suffers from higher signal degradation and increased maintenance requirements, raising total expenses over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors optical fiber, especially for businesses and services requiring scalable, reliable, and high-speed internet connections.
Security and Interference Resistance
Optical fiber offers superior security compared to copper wire by transmitting data as light signals, making it nearly immune to electromagnetic interference and extremely difficult to tap without detection. Copper wire, however, is vulnerable to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation, which can compromise data integrity and enable easier unauthorized access. The inherent resistance of optical fiber to environmental noise and eavesdropping makes it the preferred medium for secure and reliable internet communication.
Future Trends in Internet Communication Technology
Optical fiber is poised to dominate future internet communication due to its unparalleled bandwidth capacity, low latency, and immunity to electromagnetic interference, supporting the explosive growth in 5G, IoT, and AI applications. Copper wire, limited by signal attenuation and slower speeds, faces obsolescence in high-demand environments but remains relevant for last-mile connectivity in legacy infrastructure. Advances in optical fiber technologies like coherent optics and space-division multiplexing further enhance transmission speeds and network scalability, driving the evolution of ultra-fast, reliable broadband networks worldwide.
Infographic: Optical fiber vs Copper wire for Internet communication
 azmater.com
azmater.com