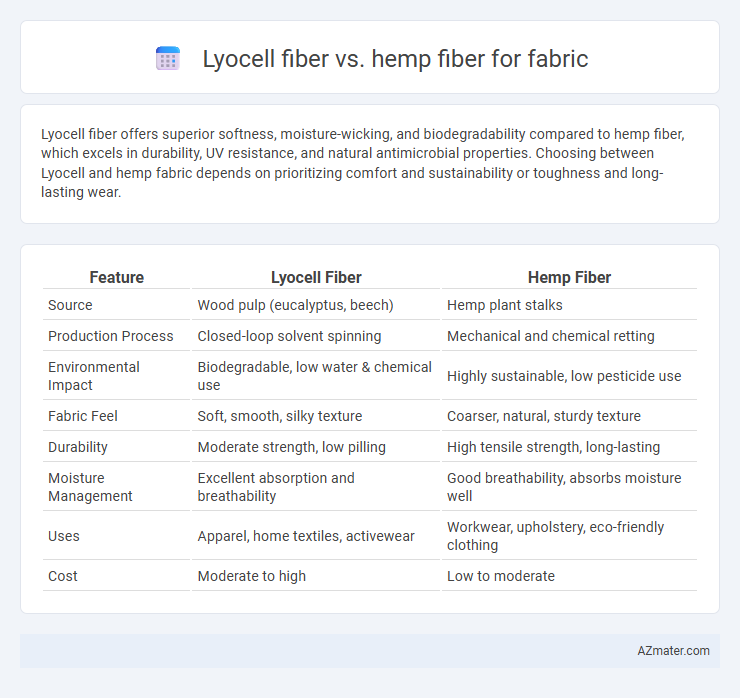
Lyocell fiber offers superior softness, moisture-wicking, and biodegradability compared to hemp fiber, which excels in durability, UV resistance, and natural antimicrobial properties. Choosing between Lyocell and hemp fabric depends on prioritizing comfort and sustainability or toughness and long-lasting wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lyocell Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Wood pulp (eucalyptus, beech) | Hemp plant stalks |
| Production Process | Closed-loop solvent spinning | Mechanical and chemical retting |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low water & chemical use | Highly sustainable, low pesticide use |
| Fabric Feel | Soft, smooth, silky texture | Coarser, natural, sturdy texture |
| Durability | Moderate strength, low pilling | High tensile strength, long-lasting |
| Moisture Management | Excellent absorption and breathability | Good breathability, absorbs moisture well |
| Uses | Apparel, home textiles, activewear | Workwear, upholstery, eco-friendly clothing |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Lyocell and Hemp Fibers
Lyocell fiber is a sustainable, biodegradable fabric made from wood pulp using an eco-friendly solvent spinning process, known for its softness, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties. Hemp fiber, derived from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, is highly durable, resistant to UV rays, and requires minimal water and pesticides, making it an eco-conscious choice for textiles. Both fibers offer environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional fabrics, with Lyocell excelling in comfort and Hemp in durability and environmental impact.
Source and Sustainability of Lyocell vs Hemp
Lyocell fiber is derived from sustainably managed eucalyptus wood pulp processed via a closed-loop system that recycles water and solvents, minimizing environmental impact. Hemp fiber originates from the hemp plant, which requires minimal pesticides and water, rapidly grows, and naturally replenishes soil nutrients, making it highly eco-friendly. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives to conventional textiles, with Lyocell emphasizing resource-efficient production and Hemp prioritizing regenerative agriculture.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Lyocell fiber is produced through a closed-loop solvent spinning process using wood pulp, minimizing environmental impact and recycling over 99% of the solvent. In contrast, hemp fiber extraction involves retting, decortication, and mechanical processing, requiring water and energy but yielding strong, coarse fibers. Lyocell manufacturing offers higher consistency and softness for fabric applications, while hemp processing is more labor-intensive but results in durable, breathable fabrics.
Environmental Impact: Lyocell vs Hemp
Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably managed eucalyptus wood pulp, utilizes a closed-loop production process that recycles water and solvents, significantly reducing environmental pollution compared to conventional textiles. Hemp fiber, grown as a fast-renewing crop with minimal pesticide and water requirements, naturally enhances soil health through nitrogen fixation and carbon sequestration, offering superior ecological benefits. Both fibers present eco-friendly alternatives, but hemp's lower agricultural input and regeneration capacity give it a distinct advantage in reducing the fabric industry's environmental footprint.
Fiber Properties and Texture Differences
Lyocell fiber is known for its exceptional softness, smooth texture, and high moisture absorbency due to its cellulose-based composition derived from wood pulp, making it ideal for comfortable, breathable fabrics. Hemp fiber offers superior durability, coarser texture, and excellent resistance to UV light and mold, with natural antimicrobial properties that enhance fabric longevity and sustainability. While Lyocell provides a silky, lightweight feel, hemp delivers a more textured, rugged fabric suited for heavy-duty applications and eco-friendly textiles.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Lyocell fiber offers superior breathability due to its smooth, porous structure that enhances airflow and promotes rapid moisture evaporation, making it ideal for moisture management in activewear. Hemp fiber, while breathable, has a coarser texture that provides moderate moisture-wicking capabilities and durability, suitable for everyday apparel. Lyocell excels in softness and moisture absorption, whereas hemp is favored for its antimicrobial properties and environmental sustainability.
Durability and Longevity
Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, offers excellent durability due to its strong cellulose structure, making it resistant to wear and tear over time. Hemp fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength and abrasion resistance, surpasses many natural fibers in longevity, maintaining fabric integrity through repeated use and washing. Both fibers provide long-lasting fabric solutions, with hemp generally favored for rugged durability and Lyocell prized for its combination of strength and softness.
Comfort and Skin Sensitivity
Lyocell fiber offers exceptional softness and breathability, making it highly comfortable for sensitive skin and reducing irritation risks. Hemp fiber is naturally hypoallergenic and antimicrobial, providing durability and moisture-wicking properties suitable for those prone to skin sensitivities. Both fibers enhance comfort, but Lyocell's smooth texture is often preferred for direct skin contact, while hemp excels in durability and natural freshness.
Applications in Fashion and Textiles
Lyocell fiber offers exceptional softness, moisture-wicking, and drape, making it ideal for high-end fashion garments, activewear, and sustainable luxury textiles. Hemp fiber provides superior durability, breathability, and natural antimicrobial properties, favored for eco-friendly casual wear, bags, and home textiles. Both fibers contribute to sustainable fashion, with Lyocell excelling in comfort and elegance, while hemp emphasizes ruggedness and environmental resilience.
Cost and Market Availability
Lyocell fiber generally costs more than hemp fiber due to its complex production process involving solvent spinning and sustainable wood pulp sourcing. Hemp fiber is more affordable, benefiting from easier cultivation and less intensive processing, which lowers manufacturing expenses. Market availability favors Lyocell for eco-friendly, high-performance textiles in fashion and activewear, while hemp has a strong presence in durable fabrics, upholstery, and niche organic markets.
Infographic: Lyocell fiber vs Hemp fiber for Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com