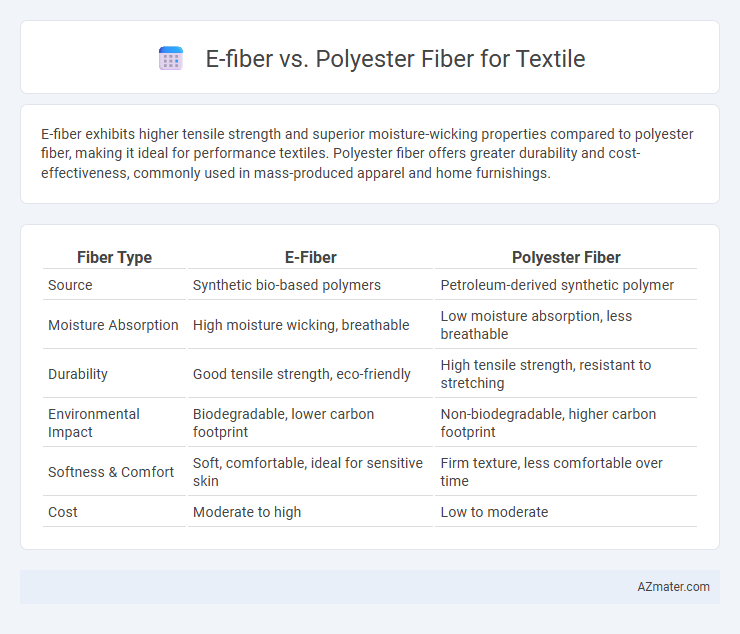
E-fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and superior moisture-wicking properties compared to polyester fiber, making it ideal for performance textiles. Polyester fiber offers greater durability and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in mass-produced apparel and home furnishings.
Table of Comparison
| Fiber Type | E-Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Synthetic bio-based polymers | Petroleum-derived synthetic polymer |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture wicking, breathable | Low moisture absorption, less breathable |
| Durability | Good tensile strength, eco-friendly | High tensile strength, resistant to stretching |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Softness & Comfort | Soft, comfortable, ideal for sensitive skin | Firm texture, less comfortable over time |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to E-Fiber and Polyester Fiber
E-fiber, also known as E-glass fiber, is a type of glass fiber widely used in textile applications due to its high tensile strength, excellent thermal resistance, and non-conductive properties. Polyester fiber, a synthetic polymer derived from petroleum, is renowned for its durability, resistance to shrinking and stretching, and quick-drying capabilities, making it ideal for fabric production. Both fibers serve distinct roles in textiles, with E-fiber primarily enhancing structural integrity and fire resistance, while polyester fiber offers flexibility and moisture-wicking performance.
Material Composition and Production Processes
E-fiber, made primarily from cellulose derived from wood pulp, offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative to petroleum-based polyester fiber synthesized through polymerization of purified terephthalic acid and monoethylene glycol. The production of E-fiber involves a closed-loop process utilizing solvent spinning technology that minimizes environmental impact, whereas polyester fiber manufacturing relies on energy-intensive melt spinning with significant greenhouse gas emissions. Material composition differences affect their physical properties, with E-fiber known for moisture absorption and softness, contrasting with polyester's durability, hydrophobicity, and resistance to shrinking and stretching.
Physical Properties Comparison
E-fiber offers superior tensile strength and higher modulus compared to polyester fiber, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced durability and rigidity. Additionally, E-fiber exhibits excellent thermal stability and lower elongation at break, whereas polyester fibers provide more elasticity and moisture resistance. The density of E-fiber is lower than polyester, contributing to lighter textiles with comparable strength characteristics.
Durability and Strength Analysis
E-fiber, composed of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, exhibits superior tensile strength and exceptional durability compared to traditional polyester fiber, making it ideal for high-performance textile applications. Polyester fibers offer good mechanical properties and abrasion resistance but generally fall short of the strength-to-weight ratio and impact resistance provided by E-fiber. In contexts requiring sustained load-bearing capacity and prolonged wear resistance, E-fiber outperforms polyester, ensuring enhanced longevity and structural integrity in technical and industrial fabrics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
E-fiber, derived from wood pulp or recycled materials, offers a significantly lower carbon footprint and greater biodegradability compared to polyester fiber, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. Polyester production releases higher greenhouse gases and depends heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to microplastic pollution in water bodies. E-fiber's renewable sourcing and enhanced recyclability position it as a more sustainable option within the textile industry aiming to reduce environmental impact.
Comfort and Aesthetic Differences
E-fiber, derived from renewable cellulose sources, offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to polyester fiber, enhancing comfort in textile applications. Polyester fiber, known for its durability and wrinkle resistance, provides a smoother, shinier finish that maintains fabric shape and color intensity. The natural texture of E-fiber lends a softer, more matte aesthetic ideal for casual and eco-friendly fashion, while polyester supports vibrant, high-gloss designs favored in performance and activewear.
Applications in the Textile Industry
E-fiber, known for its superior tensile strength and lightweight properties, is increasingly favored in high-performance textile applications such as technical fabrics, sportswear, and industrial textiles. Polyester fiber remains widely used in apparel, upholstery, and home textiles due to its durability, resistance to wrinkles, and cost-effectiveness. The choice between E-fiber and polyester fiber in textile production depends on required performance characteristics, with E-fiber excelling in specialized markets demanding enhanced strength and flexibility.
Cost and Market Availability
E-fiber offers a competitive cost advantage over polyester fiber due to lower raw material expenses and energy-efficient production processes. Polyester fiber dominates the textile market with widespread availability, established supply chains, and extensive manufacturing capacity. Market preference tends to favor polyester fiber for its consistent quality and versatility, while E-fiber is gaining traction in cost-sensitive applications.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
E-fiber's eco-friendly attributes and superior moisture-wicking properties are increasingly favored by environmentally conscious consumers in the textile market. Polyester fiber remains popular for its durability, cost-effectiveness, and easy care, appealing to budget-driven buyers and performance-focused applications. Current consumer trends indicate a growing demand for sustainable materials, with E-fiber gaining traction in athleisure and activewear segments due to its natural origin and biodegradability.
Future Prospects and Innovations
E-fiber, derived from renewable sources, offers significant environmental advantages over traditional polyester fiber, which is petroleum-based and less sustainable. Innovations in E-fiber focus on enhancing biodegradability and improving mechanical properties to compete with polyester's durability and cost-effectiveness. Future prospects emphasize integrating E-fiber into high-performance textile applications through advanced bioengineering and hybrid fiber technologies.
Infographic: E-fiber vs Polyester fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com