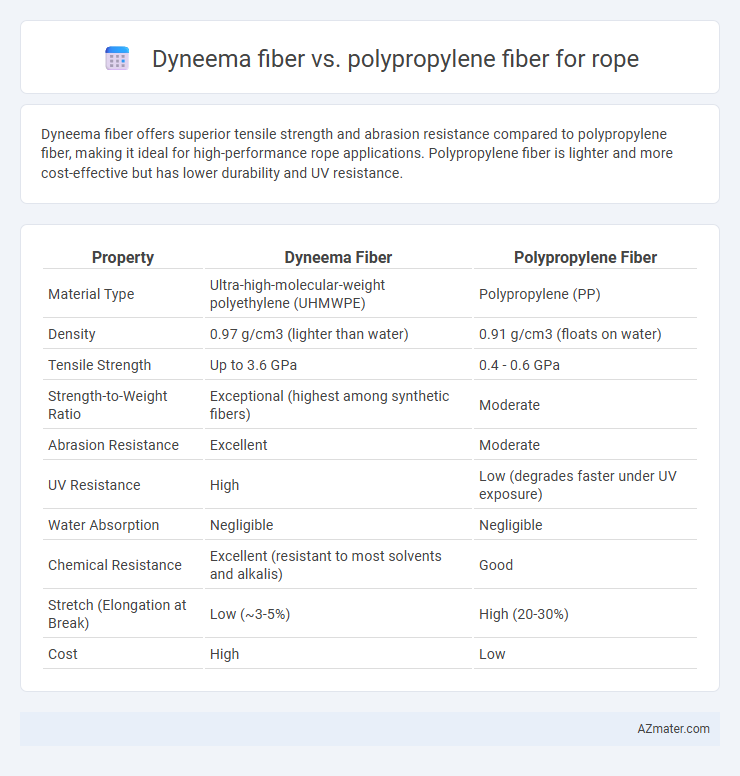
Dyneema fiber offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to polypropylene fiber, making it ideal for high-performance rope applications. Polypropylene fiber is lighter and more cost-effective but has lower durability and UV resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dyneema Fiber | Polypropylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) | Polypropylene (PP) |
| Density | 0.97 g/cm3 (lighter than water) | 0.91 g/cm3 (floats on water) |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3.6 GPa | 0.4 - 0.6 GPa |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Exceptional (highest among synthetic fibers) | Moderate |
| Abrasion Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| UV Resistance | High | Low (degrades faster under UV exposure) |
| Water Absorption | Negligible | Negligible |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (resistant to most solvents and alkalis) | Good |
| Stretch (Elongation at Break) | Low (~3-5%) | High (20-30%) |
| Cost | High | Low |
Introduction to Dyneema and Polypropylene Fibers
Dyneema fiber is an ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, offering superior tensile strength and cut resistance compared to traditional fibers. Polypropylene fiber, a thermoplastic polymer, is valued for its lightweight, low cost, and excellent resistance to moisture and chemical exposure but has lower tensile strength and UV stability than Dyneema. In rope applications, Dyneema provides enhanced durability and performance in demanding environments, whereas polypropylene is often chosen for economical, general-purpose uses where flexibility and water resistance are prioritized.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Dyneema fiber consists of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) produced through a gel-spinning process that aligns polymer chains for exceptional strength and lightweight properties. Polypropylene fiber is synthesized from polymerized propylene monomers using a melt-spinning method, resulting in a lightweight, chemical-resistant fiber with moderate tensile strength. The advanced gel-spinning technique of Dyneema enables superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to the simpler melt-spinning manufacturing process used for polypropylene fibers.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Dyneema fiber exhibits superior tensile strength, boasting up to 15 times the strength of steel by weight, making it significantly more robust than polypropylene fiber, which has lower breaking strength and is prone to stretching under load. Durability-wise, Dyneema resists UV degradation, moisture absorption, and chemical damage far better than polypropylene, which deteriorates faster when exposed to sunlight and harsh environmental conditions. For rope applications requiring exceptional strength and long-lasting performance, Dyneema is the optimal choice due to its high tensile strength and excellent resistance to wear and environmental factors.
Weight and Density Differences
Dyneema fiber has an exceptionally low density of about 0.97 g/cm3, making it one of the lightest high-performance fibers available, whereas polypropylene fiber has a density around 0.91 g/cm3, slightly lighter but with lower strength characteristics. Despite polypropylene's marginally lower density, Dyneema's superior strength-to-weight ratio allows ropes to be significantly lighter while carrying greater loads. This fundamental difference means Dyneema ropes provide enhanced performance in weight-sensitive applications compared to polypropylene counterparts.
Resistance to Abrasion and UV Exposure
Dyneema fiber exhibits exceptional resistance to abrasion, maintaining strength and integrity even under harsh, abrasive conditions, which makes it ideal for high-performance rope applications. In comparison, polypropylene fiber has moderate abrasion resistance but tends to degrade faster when exposed to rough surfaces. Dyneema also offers superior UV resistance, retaining its durability and reducing deterioration from prolonged sun exposure, whereas polypropylene fibers typically suffer significant weakening and discoloration under UV rays.
Water and Chemical Resistance
Dyneema fiber offers exceptional water resistance due to its hydrophobic properties, making it highly suitable for marine and wet environments where minimal water absorption is crucial. Polypropylene fiber is also inherently water-resistant and floats on water, providing buoyancy advantages but is less resistant to chemical degradation, especially from UV exposure and certain solvents. In chemical resistance, Dyneema outperforms polypropylene by withstanding a broader range of harsh chemicals and solvents, maintaining strength and durability in aggressive industrial conditions.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Dyneema fiber offers superior flexibility and exceptional handling characteristics compared to polypropylene fiber, making it ideal for ropes that require easy knotting and smooth manipulation. Its low stretch and high strength-to-weight ratio enhance performance in dynamic applications, while polypropylene tends to be stiffer and less resistant to abrasion. The enhanced flexibility and superior tactile feel of Dyneema fiber ropes provide better user control and durability in demanding marine or industrial environments.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Dyneema fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and durability, making it more expensive but highly cost-efficient over time for rope applications. Polypropylene fiber is cheaper and widely available, providing a budget-friendly option with moderate strength and less durability. For cost efficiency and immediate availability, polypropylene fibers dominate the market, while Dyneema fiber is preferred in high-performance, long-lasting rope solutions.
Common Applications for Ropes
Dyneema fiber ropes are widely used in high-performance marine, climbing, and industrial lifting applications due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to abrasion and UV light. Polypropylene fiber ropes are commonly found in boating, water sports, and general utility tasks because of their buoyancy, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Both fibers offer distinct advantages tailored to specific rope applications, making Dyneema ideal for demanding, safety-critical uses, while polypropylene suits lightweight, economical, and wet-environment needs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Needs
Dyneema fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, high tensile strength, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum durability and minimal weight, such as climbing ropes and marine uses. Polypropylene fiber is a cost-effective, lightweight, and water-resistant option suitable for general-purpose ropes, but it lacks the superior strength and UV resistance of Dyneema. Choosing the right fiber depends on your specific requirements for strength, durability, budget, and environmental exposure.
Infographic: Dyneema fiber vs Polypropylene fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com