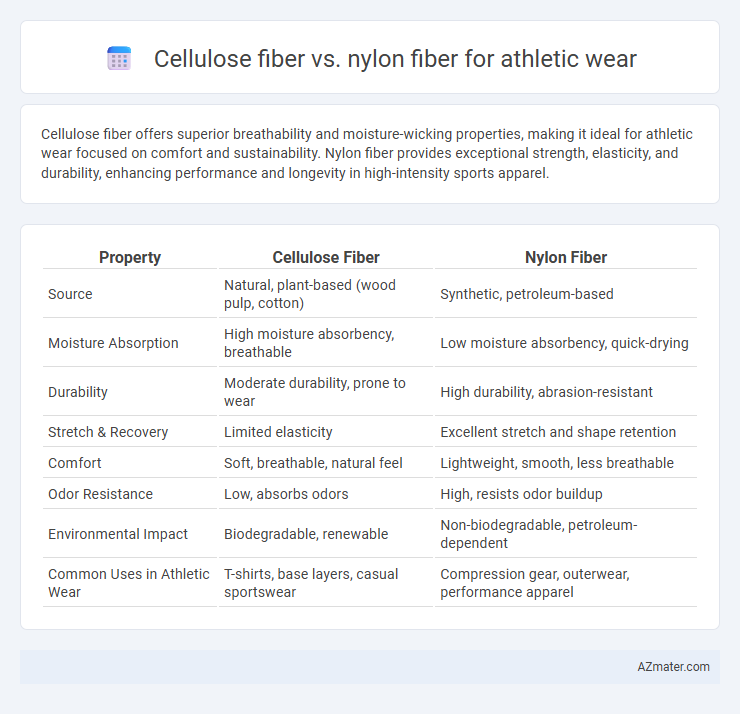
Cellulose fiber offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for athletic wear focused on comfort and sustainability. Nylon fiber provides exceptional strength, elasticity, and durability, enhancing performance and longevity in high-intensity sports apparel.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellulose Fiber | Nylon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, plant-based (wood pulp, cotton) | Synthetic, petroleum-based |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture absorbency, breathable | Low moisture absorbency, quick-drying |
| Durability | Moderate durability, prone to wear | High durability, abrasion-resistant |
| Stretch & Recovery | Limited elasticity | Excellent stretch and shape retention |
| Comfort | Soft, breathable, natural feel | Lightweight, smooth, less breathable |
| Odor Resistance | Low, absorbs odors | High, resists odor buildup |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-dependent |
| Common Uses in Athletic Wear | T-shirts, base layers, casual sportswear | Compression gear, outerwear, performance apparel |
Introduction to Cellulose and Nylon Fibers
Cellulose fibers, derived from natural plant sources such as cotton and bamboo, offer breathability and moisture-wicking properties ideal for athletic wear. Nylon fibers, synthetic polymers created through polymerization of hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid, provide high strength, elasticity, and durability under rigorous physical activity. Both fibers balance comfort and performance, with cellulose enhancing natural airflow and nylon delivering resilience and quick-drying capabilities for optimal athletic performance.
Composition and Structure of Cellulose Fiber
Cellulose fiber, derived from plant-based polymers like cotton and rayon, consists primarily of glucose units linked by b-1,4-glycosidic bonds, forming a linear, crystalline structure that enhances moisture absorbency and breathability in athletic wear. Nylon fiber, a synthetic polyamide, features repeating units connected by amide bonds, resulting in a highly resilient, elastic, and abrasion-resistant structure suitable for durability and stretch. The natural hydrophilic and biodegradable composition of cellulose contrasts with the hydrophobic, petroleum-based makeup of nylon, influencing moisture management and sustainability in sports apparel.
Chemical and Physical Properties of Nylon Fiber
Nylon fiber, a synthetic polymer composed mainly of polyamides, exhibits high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and superior elasticity compared to cellulose fibers such as cotton or rayon. Its moisture-wicking properties and low water absorption enhance breathability and quick-drying capabilities, making it ideal for athletic wear. Chemically, nylon's hydrophobic nature and crystalline structure contribute to durability and resistance to mildew and UV degradation, outperforming cellulose fibers in demanding sports environments.
Breathability: Cellulose vs Nylon in Athletic Wear
Cellulose fibers, derived from plant materials like cotton and bamboo, offer superior breathability due to their natural moisture-wicking and air-permeable properties, making them ideal for athletic wear that prioritizes comfort and sweat management. Nylon fibers, synthetic in origin, exhibit less breathability but provide higher durability and quick-drying capabilities, which are advantageous for high-intensity sports requiring lightweight and resilient fabrics. Choosing between cellulose and nylon fibers for athletic wear depends on balancing breathability needs against performance requirements like durability and moisture control.
Moisture Management and Sweat Wicking Performance
Cellulose fibers such as lyocell and bamboo excel in moisture management due to their hydrophilic properties, absorbing and releasing sweat rapidly to keep skin dry during athletic activities. Nylon fibers offer superior sweat-wicking performance by quickly transporting moisture away from the body to the fabric surface for faster evaporation, enhancing comfort and reducing chafing. The combination of cellulose's natural breathability and nylon's efficient drying makes them complementary choices in high-performance athletic wear.
Comfort and Skin Sensitivity: Comparing Both Fibers
Cellulose fiber, derived from natural sources like cotton or bamboo, offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort and reducing skin irritation during athletic activities. Nylon fiber, a synthetic material, provides excellent durability and elasticity but can trap heat and cause sweating, potentially leading to discomfort and skin sensitivity in some individuals. Athletes with sensitive skin often prefer cellulose fibers for their softness and hypoallergenic qualities, while nylon may be favored for high-performance wear requiring stretch and resilience.
Durability and Longevity in Activewear Applications
Cellulose fiber, derived from natural sources like cotton and viscose, offers breathability and moisture absorption but generally lacks the high durability required for intense athletic wear. Nylon fiber, a synthetic polymer, excels in tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and longevity, making it highly suitable for activewear subjected to frequent stretching and wear. The superior resilience and quick-drying properties of nylon fibers contribute to extended garment lifespan and consistent performance in rigorous physical activities.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Cellulose fibers, derived from renewable sources like wood pulp and cotton, offer superior biodegradability and lower carbon footprints compared to petroleum-based nylon fibers. Nylon production consumes significant non-renewable resources, releases nitrous oxide--a potent greenhouse gas--and is not readily biodegradable, contributing to long-term environmental pollution. Choosing cellulose-based fibers for athletic wear supports sustainable manufacturing practices and reduces microplastic pollution in aquatic ecosystems.
Cost and Accessibility for Manufacturers and Consumers
Cellulose fiber, derived from natural sources like wood pulp, offers a cost-effective and widely accessible option for athletic wear manufacturers due to its renewable supply and lower raw material expenses compared to synthetic Nylon fiber. Nylon fiber, though more expensive with higher production costs linked to petrochemical processes, provides superior durability and elasticity that justify its price for high-performance sports apparel. Consumers benefit from cellulose fiber apparel through affordability and eco-friendliness, while Nylon garments tend to be pricier but preferred for their strength and moisture-wicking properties.
Which Fiber is Better for Athletic Wear: Final Verdict
Cellulose fiber offers superior moisture absorption and breathability, making it ideal for athletes seeking natural comfort and sweat management. Nylon fiber excels in durability, elasticity, and quick-drying properties, providing enhanced performance and long-lasting wear during intense physical activities. For athletic wear, nylon fiber is generally better due to its strength, resilience, and ability to maintain shape under stress while cellulose fiber suits those prioritizing natural feel and eco-friendliness.
Infographic: Cellulose fiber vs Nylon fiber for Athletic wear
 azmater.com
azmater.com