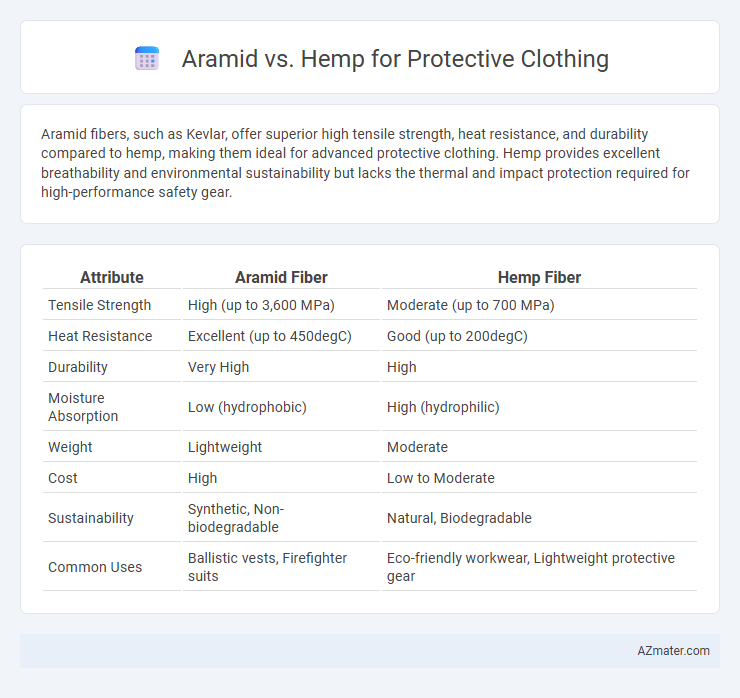
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior high tensile strength, heat resistance, and durability compared to hemp, making them ideal for advanced protective clothing. Hemp provides excellent breathability and environmental sustainability but lacks the thermal and impact protection required for high-performance safety gear.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Aramid Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 3,600 MPa) | Moderate (up to 700 MPa) |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent (up to 450degC) | Good (up to 200degC) |
| Durability | Very High | High |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (hydrophobic) | High (hydrophilic) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate |
| Cost | High | Low to Moderate |
| Sustainability | Synthetic, Non-biodegradable | Natural, Biodegradable |
| Common Uses | Ballistic vests, Firefighter suits | Eco-friendly workwear, Lightweight protective gear |
Introduction to Aramid and Hemp Fibers
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Twaron, are synthetic fibers known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, heat resistance, and high tensile strength, making them ideal for advanced protective clothing. Hemp fibers, derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, offer natural durability, breathability, and antimicrobial properties, providing an eco-friendly alternative in protective textiles. Both fibers serve distinct roles in safety gear, with aramid fibers excelling in impact and cut resistance, while hemp contributes to comfort and sustainability.
Material Composition and Origin
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, are synthetic polymers made from aromatic polyamides, offering exceptional tensile strength, heat resistance, and durability ideal for protective clothing in high-risk environments. Hemp is a natural fiber derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, known for its biodegradability, breathability, and moderate tensile strength, often blended with other fibers for increased protective properties. The synthetic origin of aramid fibers provides superior thermal and abrasion resistance, while hemp's plant-based composition supports sustainable and eco-friendly textile production.
Mechanical Strength: Aramid vs Hemp
Aramid fibers exhibit superior mechanical strength with tensile strength up to 3,600 MPa, making them ideal for high-performance protective clothing against impacts and abrasions. Hemp fibers, while renewable and sustainable, have tensile strengths around 550 MPa, which limits their application in heavy-duty protective gear. The significant difference in tensile strength and durability positions aramid as the preferred material for critical mechanical protection, whereas hemp serves better in lightweight, eco-friendly garments.
Thermal and Flame Resistance
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer superior thermal and flame resistance compared to hemp, withstanding temperatures up to 370degC without melting or igniting. Hemp provides natural breathability and moderate heat resistance but lacks the high-performance flame retardant properties essential for protective clothing. Aramid's inherent flame resistance and stability under sustained heat exposure make it the preferred choice for firefighter suits and industrial protective gear.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior heat resistance and durability but tend to be less breathable and stiffer compared to hemp, affecting overall comfort during prolonged use. Hemp fabric provides excellent moisture-wicking and breathability, enhancing wearability in warm conditions while offering natural antimicrobial properties. Protective clothing that combines aramid's high-performance strength with hemp's softness and ventilation can optimize comfort and extended wearability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer high durability and strength but involve energy-intensive production processes and non-biodegradable synthetic chemicals, leading to significant environmental footprints. Hemp fibers are renewable, biodegradable, and require minimal water and pesticides, making them an eco-friendly alternative for protective clothing with a lower carbon footprint. Choosing hemp over aramid reduces long-term environmental impact through sustainable cultivation and end-of-life biodegradability.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are significantly more expensive than hemp due to their complex manufacturing process and high-performance properties, making them a premium choice for protective clothing with superior cut and heat resistance. Hemp offers a more cost-effective and sustainable alternative, widely available in natural fiber markets, but lacks the same level of protective performance as aramid materials. Market availability favors aramid in specialized safety and military sectors, while hemp is increasingly popular in eco-friendly and budget-conscious consumer segments seeking moderate protection.
Applications in Protective Clothing
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer exceptional heat resistance, high tensile strength, and cut resistance, making them ideal for applications in firefighter gear, ballistic vests, and industrial protective clothing. Hemp fibers provide natural biodegradability, moisture-wicking properties, and moderate durability, often used in eco-friendly protective workwear and gloves that require breathability and comfort. Selecting between aramid and hemp depends on the required balance of protection level, environmental sustainability, and specific use-case scenarios in protective apparel.
Maintenance and Longevity
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior durability and resistance to wear, chemicals, and UV exposure, making them ideal for long-lasting protective clothing with minimal maintenance. Hemp fabric, while naturally resistant to abrasion and mold, requires more frequent care to maintain strength and protection, including washing with gentle detergents and avoiding prolonged moisture exposure. The inherent high tensile strength and heat resistance of aramid ensure extended garment lifespan, whereas hemp's biodegradability can lead to faster degradation under harsh working conditions.
Future Trends and Innovations
Future trends in protective clothing highlight a shift towards integrating aramid fibers with sustainable materials like hemp to enhance durability and environmental impact. Innovations include bioengineered aramid composites combined with hemp fibers, offering superior heat resistance, flexibility, and biodegradability. Research focuses on developing lightweight, breathable fabrics that maintain high protective standards while reducing carbon footprints in industrial and military applications.
Infographic: Aramid vs Hemp for Protective clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com