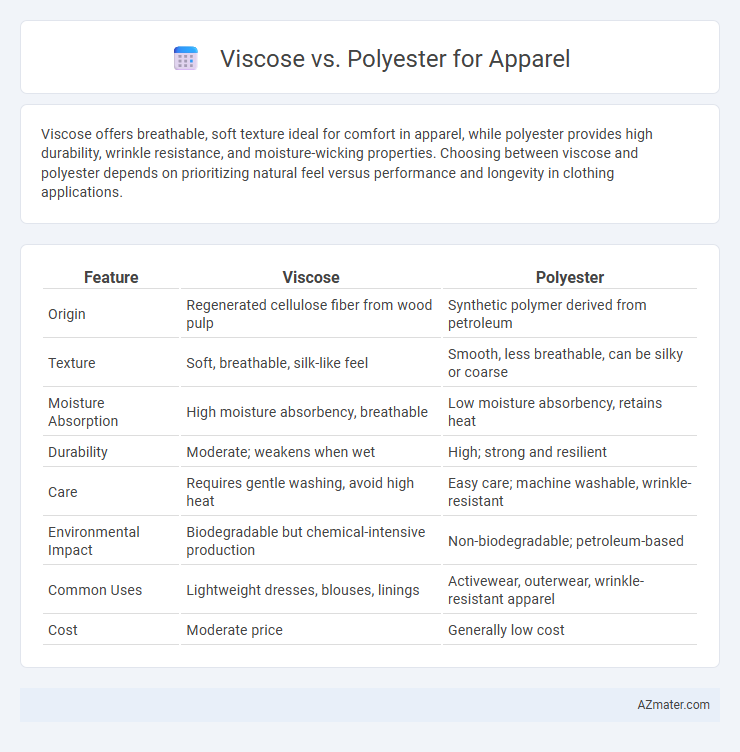
Viscose offers breathable, soft texture ideal for comfort in apparel, while polyester provides high durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties. Choosing between viscose and polyester depends on prioritizing natural feel versus performance and longevity in clothing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Viscose | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Regenerated cellulose fiber from wood pulp | Synthetic polymer derived from petroleum |
| Texture | Soft, breathable, silk-like feel | Smooth, less breathable, can be silky or coarse |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture absorbency, breathable | Low moisture absorbency, retains heat |
| Durability | Moderate; weakens when wet | High; strong and resilient |
| Care | Requires gentle washing, avoid high heat | Easy care; machine washable, wrinkle-resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable but chemical-intensive production | Non-biodegradable; petroleum-based |
| Common Uses | Lightweight dresses, blouses, linings | Activewear, outerwear, wrinkle-resistant apparel |
| Cost | Moderate price | Generally low cost |
Introduction to Viscose and Polyester
Viscose, a semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose, offers a soft, breathable, and biodegradable alternative commonly used in apparel for its silk-like feel and moisture-wicking properties. Polyester, a fully synthetic polymer made from petrochemicals, is prized in clothing for its durability, wrinkle resistance, and quick-drying capabilities, making it ideal for activewear and budget-friendly fashion. Understanding the fundamental differences in origin, texture, and performance between viscose and polyester helps consumers choose fabrics that best suit their lifestyle and environmental preferences.
Fabric Origins and Production Processes
Viscose is a semi-synthetic fiber derived from regenerated cellulose, primarily wood pulp sourced from trees like beech, pine, or eucalyptus, undergoing chemical processes involving solvents such as carbon disulfide to create a soft, breathable fabric. Polyester is a fully synthetic fiber made from petrochemicals through a polymerization process of purified terephthalic acid (PTA) and ethylene glycol, resulting in strong, durable, and wrinkle-resistant material. The production of viscose is more resource-intensive and involves hazardous chemicals, whereas polyester manufacturing relies on fossil fuels and energy-intensive extrusion techniques.
Texture and Feel: Comfort Comparison
Viscose offers a soft, breathable texture with a natural feel that enhances comfort, making it ideal for warm-weather apparel. Polyester, while less breathable, provides a smoother, slightly slick surface that resists wrinkles and retains shape but can feel less comfortable against sensitive skin. The choice between viscose and polyester heavily depends on desired comfort levels, with viscose favored for softness and moisture absorption and polyester preferred for durability and easy maintenance.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Viscose offers superior breathability compared to polyester due to its natural cellulose fibers, allowing better air circulation and moisture absorption. Polyester excels in moisture management by wicking sweat away from the skin and drying quickly, making it ideal for activewear in humid conditions. Choosing between viscose and polyester depends on prioritizing natural comfort or synthetic performance in apparel.
Durability and Strength Differences
Viscose, a semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose, offers a soft and breathable fabric but generally lacks the durability and tensile strength of polyester, a fully synthetic polymer known for its resilience and abrasion resistance. Polyester fibers maintain shape and withstand wear and tear better under frequent washing and heavy use, making it ideal for long-lasting apparel applications. While viscose provides comfort and a silky texture, polyester excels in strength and durability, essential for performance-oriented clothing.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Concerns
Viscose, derived from cellulose in wood pulp, poses sustainability concerns due to intensive water use, deforestation, and chemical pollution during production, impacting ecosystems and contributing to carbon emissions. Polyester, a synthetic fiber made from petroleum, generates significant environmental issues including non-biodegradability, microplastic pollution in oceans, and high energy consumption during manufacturing. Both materials raise critical environmental challenges, prompting the fashion industry to explore eco-friendly alternatives like recycled fibers and organic fabrics to reduce ecological footprints.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Viscose requires gentle hand washing or delicate machine cycles with cold water and mild detergent to prevent shrinkage and fabric weakening, while polyester is highly durable and can withstand regular machine washing with warm water and standard detergents without losing shape or color. Viscose garments should be air-dried flat or hung away from direct sunlight to avoid damage, whereas polyester dries quickly and resists wrinkles, reducing the need for ironing. Proper care extends the lifespan of viscose by minimizing fabric pilling and distortion, while polyester's low-maintenance nature makes it ideal for activewear and everyday apparel requiring frequent laundering.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Viscose fabric generally incurs higher production costs due to its semi-synthetic origin and reliance on wood pulp, making it less affordable than polyester for mass-market apparel. Polyester, derived from petrochemicals, benefits from lower manufacturing expenses and economies of scale, resulting in more budget-friendly pricing for both manufacturers and consumers. The durability and easy care of polyester further enhance its cost-effectiveness in apparel production compared to viscose.
Popular Uses in Apparel Industry
Viscose is widely favored in the apparel industry for its breathability and softness, making it a popular choice for summer dresses, blouses, and linings of jackets. Polyester dominates activewear and outerwear due to its durability, moisture-wicking properties, and resistance to wrinkles and shrinking. Both fibers are often blended to balance comfort and performance in fashion, optimizing fabric versatility.
Choosing the Best Fabric: Viscose vs Polyester
Viscose offers breathability, moisture absorption, and a soft, natural feel ideal for comfortable apparel, while polyester excels in durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties, making it suitable for activewear. When choosing the best fabric, consider viscose for lightweight, breathable clothing and polyester for garments requiring long-lasting color and shape retention. Balancing aesthetics, comfort, and performance is key to selecting between viscose and polyester based on specific apparel needs.
Infographic: Viscose vs Polyester for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com