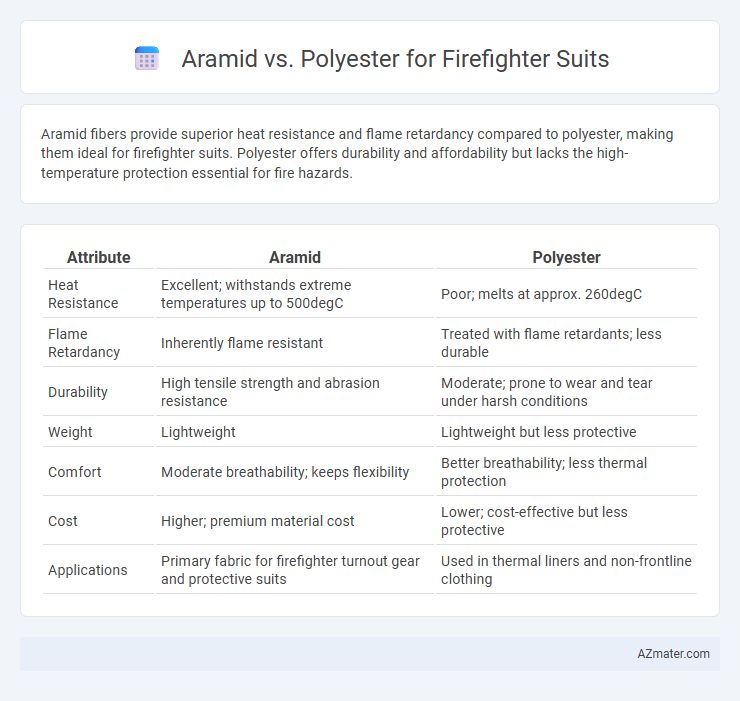
Aramid fibers provide superior heat resistance and flame retardancy compared to polyester, making them ideal for firefighter suits. Polyester offers durability and affordability but lacks the high-temperature protection essential for fire hazards.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Aramid | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Excellent; withstands extreme temperatures up to 500degC | Poor; melts at approx. 260degC |
| Flame Retardancy | Inherently flame resistant | Treated with flame retardants; less durable |
| Durability | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate; prone to wear and tear under harsh conditions |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight but less protective |
| Comfort | Moderate breathability; keeps flexibility | Better breathability; less thermal protection |
| Cost | Higher; premium material cost | Lower; cost-effective but less protective |
| Applications | Primary fabric for firefighter turnout gear and protective suits | Used in thermal liners and non-frontline clothing |
Introduction: The Importance of Material Selection in Firefighter Suits
Selecting the right material for firefighter suits is critical to ensure maximum protection against extreme heat, flames, and hazardous environments. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer exceptional thermal resistance, durability, and strength, making them ideal for high-risk fire situations. Polyester, while cost-effective and lightweight, lacks the heat resistance and flame retardant properties required for optimal firefighter safety.
Overview of Aramid and Polyester Fibers
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, are renowned for their exceptional heat resistance, durability, and flame-retardant properties, making them ideal for firefighter suits. Polyester fibers offer good mechanical strength and moisture resistance but lack the inherent flame retardancy and thermal protection required for extreme fire exposure. In firefighter gear, aramid's superior thermal stability and self-extinguishing characteristics ensure enhanced protection compared to polyester-based fabrics.
Thermal Resistance: Aramid vs Polyester
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer superior thermal resistance compared to polyester, making them essential for firefighter suits exposed to extreme heat and flame. Aramid fabrics can withstand temperatures above 370degC (700degF) without melting or igniting, while polyester begins to melt around 260degC (500degF), compromising protective performance. The inherent flame-retardant properties of aramid significantly enhance firefighter safety by preventing quick ignition and heat transfer during high-risk fire scenarios.
Flame Retardancy Comparative Analysis
Aramid fibers, widely used in firefighter suits, offer superior flame retardancy compared to polyester due to their inherent heat resistance and ability to maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 400degC. Polyester tends to melt and lose strength rapidly when exposed to high heat, increasing burn risk and compromising wearer protection. The superior thermal stability and low thermal conductivity of aramid fibers make them a more effective choice for flame-retardant protective clothing in hazardous firefighting environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, deliver superior mechanical strength and heat resistance compared to polyester, making them ideal for firefighter suits exposed to extreme conditions. Aramid fabrics maintain structural integrity under high temperatures and resist abrasion, ensuring enhanced durability and protection during intense firefighting activities. Polyester, while cost-effective and lightweight, lacks the high thermal stability and mechanical robustness necessary for prolonged exposure to fire hazards.
Comfort and Wearability in Extreme Conditions
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance and lightweight durability essential for firefighter suits, enhancing comfort during prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures. Polyester, while more affordable and flexible, lacks the thermal protection and moisture-wicking properties critical for wearability in high-heat environments. Optimal firefighter suits often integrate aramid blends to balance breathability, mobility, and protection under intense conditions.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Aramid fibers exhibit superior chemical resistance and maintain structural integrity when exposed to moisture, making them ideal for firefighter suits that require protection against hazardous substances and wet conditions. Polyester, while offering good moisture resistance and quick-drying properties, is less resistant to high temperatures and harsh chemicals compared to aramid. The optimal choice for firefighter suits prioritizes aramid's enhanced durability and chemical stability in demanding environments.
Cost and Availability Factors
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, are typically more expensive than polyester due to their superior heat resistance and durability in firefighter suits, impacting overall procurement costs. Polyester is more widely available and less costly but offers significantly lower flame resistance, which makes it less suitable for high-risk firefighting environments. Fire departments often balance the higher upfront cost of aramid suits with their longer lifespan and enhanced protection, while polyester suits may be chosen for budget-limited applications with less intense fire exposure.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Aramid fibers such as Nomex exhibit superior heat and flame resistance, resulting in a longer lifespan for firefighter suits compared to polyester, which degrades more rapidly under extreme conditions. Aramid suits require less frequent replacement due to their inherent durability and resistance to thermal damage, while polyester suits demand higher maintenance to prevent deterioration from heat exposure. Proper cleaning and inspection protocols extend the longevity of aramid materials, whereas polyester suits may suffer from loss of protective properties with routine laundering.
Summary: Best Material Choice for Firefighter Suits
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, offer superior heat resistance, flame retardancy, and durability compared to polyester, making them the preferred material for firefighter suits. Polyester, while less expensive, melts at high temperatures and provides limited thermal protection, compromising firefighter safety in extreme conditions. Choosing aramid-based suits ensures optimal protection, durability, and compliance with industry safety standards for firefighting gear.
Infographic: Aramid vs Polyester for Firefighter Suit
 azmater.com
azmater.com