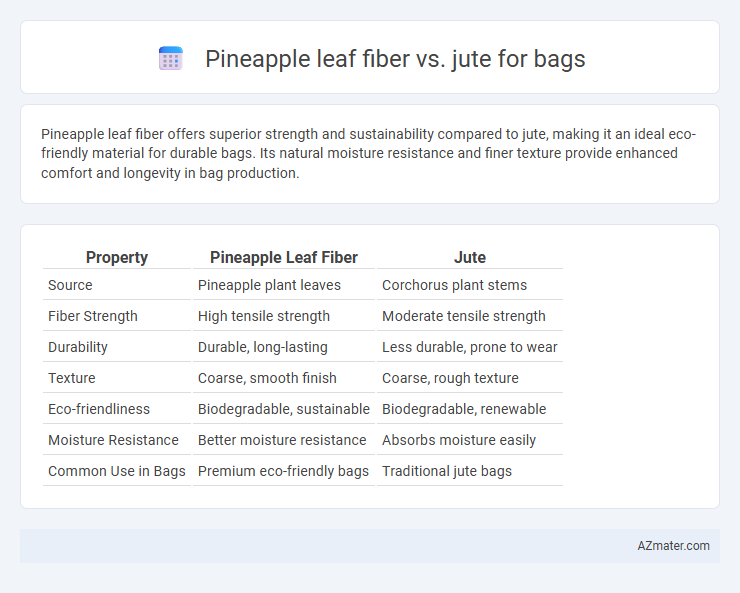
Pineapple leaf fiber offers superior strength and sustainability compared to jute, making it an ideal eco-friendly material for durable bags. Its natural moisture resistance and finer texture provide enhanced comfort and longevity in bag production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Pineapple Leaf Fiber | Jute |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Pineapple plant leaves | Corchorus plant stems |
| Fiber Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Durability | Durable, long-lasting | Less durable, prone to wear |
| Texture | Coarse, smooth finish | Coarse, rough texture |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable, sustainable | Biodegradable, renewable |
| Moisture Resistance | Better moisture resistance | Absorbs moisture easily |
| Common Use in Bags | Premium eco-friendly bags | Traditional jute bags |
Introduction to Eco-Friendly Bag Materials
Pineapple leaf fiber and jute are two sustainable materials gaining popularity in eco-friendly bag production due to their renewable nature and biodegradability. Pineapple leaf fiber, derived from agricultural waste, offers high tensile strength and a smooth texture, making it suitable for durable, lightweight bags. Jute, known as the "golden fiber," is widely cultivated and valued for its coarse texture and affordability, providing an excellent balance of strength and eco-conscious appeal in bag manufacturing.
Overview of Pineapple Leaf Fiber
Pineapple leaf fiber, derived from the long leaves of the pineapple plant, offers strong, durable, and eco-friendly material ideal for bag production. Its high tensile strength surpasses jute, providing better resistance to wear and moisture, while maintaining lightweight flexibility. This sustainable fiber supports biodegradable and renewable fashion trends by reducing environmental impact compared to synthetic alternatives and conventional jute bags.
Properties of Jute Fiber
Jute fiber is known for its remarkable strength, durability, and breathability, making it an ideal choice for bag manufacturing. It has a natural golden luster and high moisture absorption capacity, which helps in maintaining bag shape and longevity. Compared to pineapple leaf fiber, jute offers better water resistance and is more cost-effective, enhancing its popularity in eco-friendly and sustainable fashion products.
Sustainability Comparison: Pineapple Leaf vs Jute
Pineapple leaf fiber offers a sustainable alternative to jute for bag production due to its use of agricultural waste, reducing environmental impact by repurposing byproducts from pineapple farming. This fiber requires fewer pesticides and less water compared to jute, enhancing its eco-friendly profile and promoting biodiversity. While jute remains biodegradable and renewable, pineapple leaf fiber's closed-loop process and minimal resource consumption provide a stronger sustainability advantage in the textile industry.
Strength and Durability: Which Fiber Wins?
Pineapple leaf fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and resistance to wear compared to traditional jute, making it more suitable for heavy-duty bag applications requiring longevity. Jute offers moderate durability but tends to degrade faster under moisture and friction, reducing its lifespan in high-use conditions. For bags demanding superior strength and extended durability, pineapple leaf fiber consistently outperforms jute.
Visual Appeal and Texture Differences
Pineapple leaf fiber offers a unique, glossy finish with a smooth yet slightly coarse texture, giving bags a distinctive, tropical aesthetic that enhances visual appeal. In contrast, jute features a coarse, rough texture with a matte, natural brown hue that lends a rustic and earthy look to bags. Both fibers provide durability, but pineapple leaf fiber tends to create more refined, lightweight bags, whereas jute results in sturdier, heavier designs.
Processing and Manufacturing Methods
Pineapple leaf fiber (PALF) processing involves extracting fibers through decortication, followed by washing, drying, and combing to achieve fine, strong strands ideal for bag manufacturing, offering a sustainable alternative to jute. Jute fibers are extracted by retting, where stalks are soaked to separate fibers, then cleaned, dried, and spun into yarn, which is widely used for producing durable, coarse-textured bags. Manufacturing methods for both fibers leverage spinning and weaving techniques, with PALF providing superior tensile strength and finer texture, while jute benefits from cost-effective large-scale production infrastructures.
Cost Analysis: Pineapple Leaf Fiber vs Jute
Pineapple leaf fiber often incurs higher initial costs due to its complex extraction process and limited supply compared to jute, which benefits from widespread cultivation and established processing techniques. Jute's lower production expenses and greater availability make it a more economical choice for bag manufacturing in bulk. While pineapple leaf fiber can offer superior durability and eco-friendliness, its cost-effectiveness is sensitive to scale and regional sourcing efficiencies.
End-Use Applications in Bag Production
Pineapple leaf fiber offers superior tensile strength and moisture resistance compared to jute, making it ideal for producing durable and eco-friendly bags designed for heavy-duty use such as grocery or travel bags. Jute fibers, known for their coarse texture and affordability, are commonly utilized in crafting lightweight, biodegradable shopping bags and promotional tote bags that emphasize sustainability. Both fibers support biodegradable end-use applications, but pineapple leaf fiber's increased durability extends the lifespan and consumer appeal of premium bags in the eco-conscious market.
Future Trends in Natural Fiber Bags
Pineapple leaf fiber (PALF) offers superior strength, durability, and a unique texture compared to jute, positioning it as a promising alternative for sustainable bag production. Innovations in bio-composite technology and eco-friendly dyeing techniques are enhancing the appeal of PALF in the natural fiber market. As consumer demand shifts towards biodegradable and ethically sourced materials, pineapple leaf fiber is expected to gain significant traction alongside traditional jute in future bag manufacturing trends.
Infographic: Pineapple leaf fiber vs Jute for Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com