Spider silk offers exceptional strength and biodegradability, making it an ideal eco-friendly material for sustainable apparel. Lyocell, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp and produced through a closed-loop process, provides breathable, biodegradable fabric with a low environmental footprint.
Table of Comparison
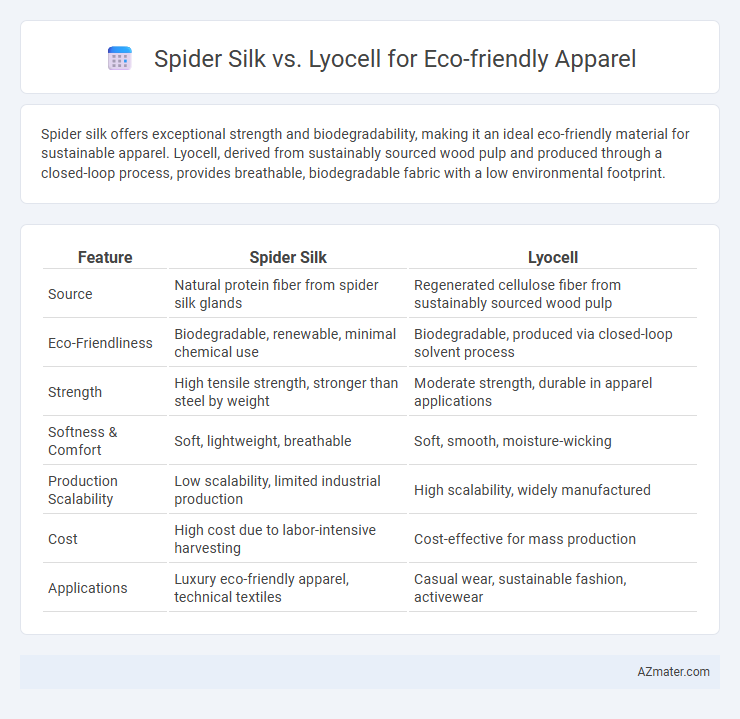
| Feature | Spider Silk | Lyocell |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural protein fiber from spider silk glands | Regenerated cellulose fiber from sustainably sourced wood pulp |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, renewable, minimal chemical use | Biodegradable, produced via closed-loop solvent process |
| Strength | High tensile strength, stronger than steel by weight | Moderate strength, durable in apparel applications |
| Softness & Comfort | Soft, lightweight, breathable | Soft, smooth, moisture-wicking |
| Production Scalability | Low scalability, limited industrial production | High scalability, widely manufactured |
| Cost | High cost due to labor-intensive harvesting | Cost-effective for mass production |
| Applications | Luxury eco-friendly apparel, technical textiles | Casual wear, sustainable fashion, activewear |
Introduction to Eco-Friendly Apparel Materials
Spider silk and Lyocell represent innovative choices in eco-friendly apparel materials due to their sustainable production methods and biodegradable properties. Spider silk, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and biodegradability, is produced through bioengineering techniques that minimize environmental impact. Lyocell, derived from wood pulp using a closed-loop process that recycles water and solvents, offers high breathability and softness, making both fibers ideal for reducing the ecological footprint of modern clothing.
What is Spider Silk?
Spider silk is a natural protein fiber produced by spiders, renowned for its exceptional strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, making it a promising material for eco-friendly apparel. Unlike conventional textiles, spider silk requires minimal water and no harmful chemicals in production, significantly reducing environmental impact compared to synthetic fibers. Innovations in bioengineering have enabled scalable production of spider silk through microbial fermentation, positioning it as a sustainable alternative to materials like lyocell.
What is Lyocell?
Lyocell is a sustainable fiber made from cellulose found in wood pulp, primarily derived from eucalyptus, beech, and spruce trees, processed through a closed-loop system that recycles water and solvents to minimize environmental impact. This biodegradable fiber offers a soft texture, breathability, and strength, making it highly suitable for eco-friendly apparel compared to synthetic textiles. Spider silk, although biodegradable and strong, remains less commercially available, positioning Lyocell as a more practical and scalable option for sustainable fashion.
Sustainability of Spider Silk Production
Spider silk stands out for its exceptional sustainability in eco-friendly apparel due to its biodegradable and renewable nature, produced by genetically engineered microbes with minimal land and water use compared to conventional fibers. The energy-efficient biofabrication process emits significantly fewer greenhouse gases than synthetic textile manufacturing, positioning spider silk as a low-impact alternative to both Lyocell and traditional cotton. Unlike Lyocell, which requires chemical-intensive processing of wood pulp, spider silk production harnesses biotechnology that reduces chemical waste and supports circular economy principles in sustainable fashion.
Sustainability of Lyocell Production
Lyocell production is highly sustainable due to its closed-loop manufacturing process that recycles over 99% of solvents, minimizing environmental pollution. Produced from sustainably sourced wood pulp, Lyocell fibers offer biodegradability and lower water consumption compared to traditional cotton farming. In contrast, spider silk, while biodegradable and robust, remains less commercially viable due to complex synthesis and higher production costs, limiting its widespread use in eco-friendly apparel.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Spider silk offers exceptional biodegradability and requires minimal water and chemical inputs during production, significantly reducing environmental pollution compared to conventional fibers. Lyocell, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp using a closed-loop solvent process, minimizes water consumption and chemical waste while maintaining soil health through responsible forestry. Both materials represent eco-friendly alternatives in apparel, with spider silk excelling in renewable biofabrication and lyocell optimizing resource efficiency and biodegradability.
Performance and Comfort: Spider Silk vs Lyocell
Spider silk excels in tensile strength and elasticity, offering superior durability and flexibility compared to lyocell, which features high moisture-wicking properties and breathability for enhanced comfort. Lyocell's smooth texture and hypoallergenic qualities make it ideal for sensitive skin, while spider silk's natural protein structure provides lightweight insulation and moisture management. Both materials support sustainable fashion, but spider silk's performance-driven advantages complement lyocell's comfort-focused attributes in eco-friendly apparel.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Spider silk exhibits exceptional biodegradability, breaking down naturally without releasing harmful residues, making it highly suitable for sustainable fashion. Lyocell, derived from wood pulp through an environmentally responsible closed-loop process, also offers strong biodegradability and ease of composting. Both materials support eco-friendly apparel end-of-life options, but spider silk's natural synthesis enhances its minimal environmental impact compared to synthetic counterparts.
Challenges in Mainstream Adoption
Spider silk faces significant production scalability challenges due to the complexity and high costs of synthetic bioengineering, limiting its widespread use in eco-friendly apparel. Lyocell benefits from a well-established manufacturing process with lower environmental impact, but struggles with water-intensive production and chemical recovery to meet true sustainability standards. Both materials require advancements in cost reduction, supply chain infrastructure, and consumer acceptance to achieve mainstream adoption in sustainable fashion markets.
Future Prospects for Eco-Friendly Fashion
Spider silk, derived from bioengineered proteins, offers exceptional strength, biodegradability, and renewable production, positioning it as a groundbreaking material for sustainable apparel. Lyocell, a cellulose-based fiber from sustainably sourced wood pulp, is already widely adopted for its eco-friendly properties, including low water usage and full biodegradability. Future prospects in eco-friendly fashion hinge on scaling spider silk production through biotechnology to complement the established benefits of lyocell, creating innovative fabrics that combine durability, comfort, and minimal environmental impact.
Infographic: Spider silk vs Lyocell for Eco-friendly apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com