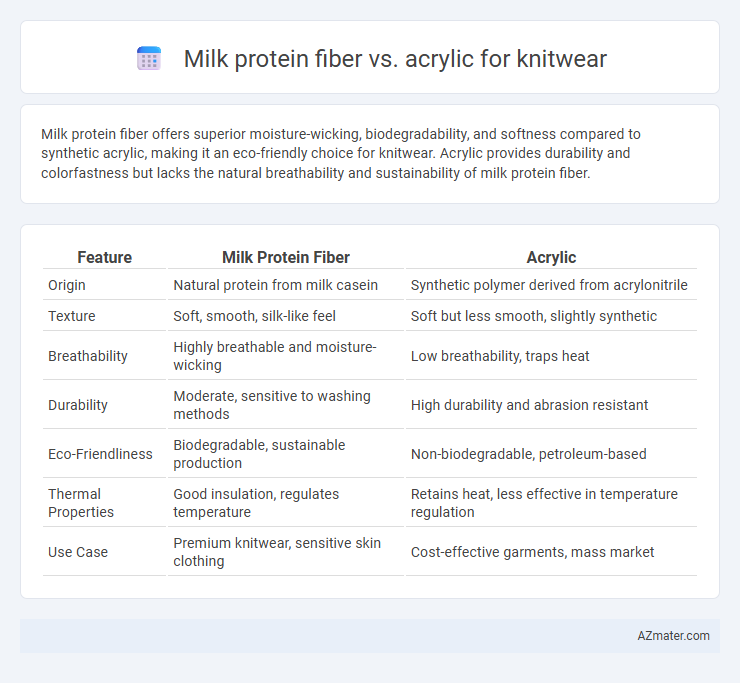
Milk protein fiber offers superior moisture-wicking, biodegradability, and softness compared to synthetic acrylic, making it an eco-friendly choice for knitwear. Acrylic provides durability and colorfastness but lacks the natural breathability and sustainability of milk protein fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Milk Protein Fiber | Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural protein from milk casein | Synthetic polymer derived from acrylonitrile |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, silk-like feel | Soft but less smooth, slightly synthetic |
| Breathability | Highly breathable and moisture-wicking | Low breathability, traps heat |
| Durability | Moderate, sensitive to washing methods | High durability and abrasion resistant |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, sustainable production | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Thermal Properties | Good insulation, regulates temperature | Retains heat, less effective in temperature regulation |
| Use Case | Premium knitwear, sensitive skin clothing | Cost-effective garments, mass market |
Introduction to Milk Protein Fiber and Acrylic in Knitwear
Milk protein fiber is a sustainable, biodegradable textile made from casein, offering softness, moisture-wicking, and antibacterial properties ideal for knitwear. Acrylic, a synthetic polymer, provides warmth, durability, and resistance to moths, making it a popular choice for affordable and easy-care knit garments. Both fibers influence texture, comfort, and performance, with milk protein fiber emphasizing eco-friendliness and natural benefits, while acrylic focuses on cost-effectiveness and resilience.
Origins and Manufacturing Processes
Milk protein fiber, derived from casein protein found in milk, undergoes a bio-based manufacturing process where liquid milk is transformed into fiber through drying, spinning, and sometimes blending with other fibers, emphasizing sustainability and biodegradability. Acrylic, a synthetic fiber made from polymerized acrylonitrile, involves a chemical process of polymerization and extrusion, producing fibers that mimic wool but rely on petrochemical resources. The contrasting origins--natural milk protein versus synthetic acrylonitrile--and their respective manufacturing stages influence the environmental footprint, texture, and performance qualities in knitwear applications.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Comparison
Milk protein fiber in knitwear offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative to acrylic, which is derived from petrochemicals and contributes to microplastic pollution. The production of milk protein fiber generates lower carbon emissions and reduces reliance on non-renewable resources, supporting a more sustainable textile industry. Acrylic fibers, while durable and cost-effective, pose significant environmental challenges due to their synthetic origin and difficulty in recycling.
Comfort and Softness: Wearer Experience
Milk protein fiber offers exceptional comfort and softness in knitwear due to its natural proteins that create a silky, smooth texture against the skin. Acrylic, while lightweight and warm, tends to be less breathable and may cause irritation or static, impacting overall wearer comfort. The moisture-wicking and hypoallergenic properties of milk protein fiber enhance the softness and comfort, making it a superior choice for sensitive skin in knitwear applications.
Durability and Longevity in Knitwear
Milk protein fiber exhibits superior durability in knitwear due to its natural elasticity and moisture-wicking properties, which reduce fiber breakage and maintain fabric integrity over time. Acrylic, while affordable and lightweight, tends to pill and lose shape with repeated wear and washing, diminishing the longevity of knit garments. Therefore, milk protein fiber offers enhanced longevity and sustained performance in knitwear compared to acrylic blends.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Milk protein fiber exhibits superior moisture absorption compared to acrylic, effectively drawing sweat away from the skin to keep the wearer dry. Its natural amino acid structure enhances breathability, promoting better air circulation and temperature regulation in knitwear. Acrylic, while durable and lightweight, tends to retain moisture and offers less breathability, making it less ideal for active or warm-weather garments.
Hypoallergenic and Skin-Friendly Properties
Milk protein fiber used in knitwear exhibits excellent hypoallergenic properties, making it ideal for sensitive skin due to its natural amino acid structure that enhances moisture retention and reduces irritation. Acrylic fibers, while durable and lightweight, often cause static build-up and may trigger skin allergies because they lack the natural protein composition found in milk fibers. Therefore, milk protein fiber is more skin-friendly and suitable for hypoallergenic knitwear compared to traditional acrylic materials.
Dyeability and Colorfastness
Milk protein fiber exhibits superior dyeability due to its natural amino acid composition, allowing vibrant and rich color absorption compared to acrylic fibers. Its excellent colorfastness ensures that hues remain stable and resistant to fading even after multiple washes and prolonged exposure to sunlight. In contrast, acrylic fibers, while capable of holding bright colors, often show decreased color retention over time and can fade more quickly under harsh conditions.
Cost and Accessibility for Consumers
Milk protein fiber offers a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional acrylic, often priced higher due to its natural and biodegradable properties, making it less accessible to budget-conscious consumers. Acrylic, derived from synthetic polymers, remains more cost-effective and widely available in the mass market, ensuring easier access for a broad range of knitwear buyers. The choice between milk protein fiber and acrylic frequently depends on consumer priorities, balancing the higher cost and niche availability of milk protein fiber against the affordability and extensive market presence of acrylic options.
Ideal Applications and Best Uses in Knitwear
Milk protein fiber offers exceptional moisture absorption and softness, making it ideal for sensitive skin and baby garments in knitwear. Acrylic provides excellent durability, elasticity, and colorfastness, suited for everyday knitwear like sweaters, scarves, and activewear. Combining milk protein fiber with acrylic enhances comfort and resilience, optimizing performance in seasonal and all-purpose knit clothing.
Infographic: Milk protein fiber vs Acrylic for Knitwear
 azmater.com
azmater.com