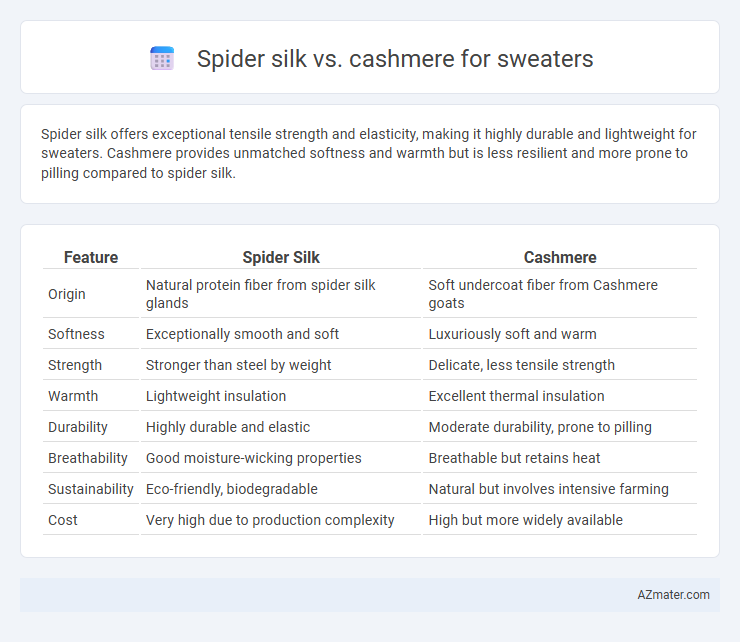
Spider silk offers exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it highly durable and lightweight for sweaters. Cashmere provides unmatched softness and warmth but is less resilient and more prone to pilling compared to spider silk.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spider Silk | Cashmere |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural protein fiber from spider silk glands | Soft undercoat fiber from Cashmere goats |
| Softness | Exceptionally smooth and soft | Luxuriously soft and warm |
| Strength | Stronger than steel by weight | Delicate, less tensile strength |
| Warmth | Lightweight insulation | Excellent thermal insulation |
| Durability | Highly durable and elastic | Moderate durability, prone to pilling |
| Breathability | Good moisture-wicking properties | Breathable but retains heat |
| Sustainability | Eco-friendly, biodegradable | Natural but involves intensive farming |
| Cost | Very high due to production complexity | High but more widely available |
Introduction to Spider Silk and Cashmere
Spider silk, renowned for its exceptional tensile strength and lightweight nature, offers unparalleled durability and elasticity in textile applications. Cashmere, derived from the undercoat of Kashmir goats, is prized for its supreme softness, thermal insulation, and luxurious feel. Both materials represent high-performance options in sweater fabrics, combining natural origin with distinctive comfort and resilience attributes.
Origin and Production Methods
Spider silk sweaters originate from the natural protein fibers produced by spiders, which are harvested through innovative biotechnological processes involving genetically engineered microorganisms that spin the silk in controlled environments. Cashmere sweaters are made from the fine undercoat fibers of cashmere goats, traditionally collected by combing or shearing during the molting season in regions like Mongolia, China, and the Himalayan highlands. The production of spider silk is a cutting-edge laboratory technique focusing on sustainability and strength, whereas cashmere relies on centuries-old pastoral methods emphasizing softness and insulation.
Fiber Structure and Composition
Spider silk fibers exhibit a highly organized, crystalline beta-sheet protein structure that provides exceptional strength and elasticity, making them lightweight yet durable. Cashmere fibers consist mainly of fine, soft keratin proteins with a hollow medulla, offering excellent insulation and moisture-wicking properties but less tensile strength compared to spider silk. The molecular composition of spider silk includes repetitive amino acid sequences such as glycine and alanine, which contribute to its remarkable toughness, whereas cashmere's keratin structure emphasizes softness and thermal retention.
Softness and Comfort Comparison
Spider silk offers exceptional softness with a smooth, lightweight texture that rivals cashmere's renowned plush feel. Cashmere provides superior warmth and a luxuriously cozy comfort due to its fine, insulating fibers, making it ideal for colder climates. While spider silk excels in breathability and durability, cashmere remains preferred for its rich softness and traditional comfort in sweaters.
Durability and Strength Differences
Spider silk outperforms cashmere in durability and strength, boasting tensile strength comparable to steel while remaining lightweight and flexible. Cashmere, derived from goat undercoat fibers, offers softness and warmth but is more prone to pilling and wear over time compared to spider silk. The molecular structure of spider silk provides superior resistance to stretching and tearing, making it an ideal material for long-lasting sweaters in high-performance and luxury apparel.
Insulation and Warmth Properties
Spider silk offers exceptional thermal regulation due to its lightweight yet strong fibers, providing excellent insulation by trapping air close to the skin while maintaining breathability. Cashmere, renowned for its fine, soft fibers, delivers superior warmth by efficiently retaining body heat but may lack the moisture-wicking properties of spider silk. Both materials excel in insulation; however, spider silk's natural ability to adapt to temperature changes gives it an edge in maintaining comfort across varying climates.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Spider silk offers a highly sustainable alternative to cashmere for sweaters, as it is biodegradable and produced through bioengineered methods that significantly reduce resource consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Cashmere production often leads to overgrazing by goats, causing soil degradation and contributing to desertification, which negatively impacts ecosystems and biodiversity. Choosing spider silk reduces the carbon footprint and environmental damage associated with traditional livestock farming, making it a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable fashion.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Spider silk sweaters require gentle hand washing with mild detergent and must be air-dried flat to preserve their delicate fibers, avoiding exposure to direct sunlight and high heat. Cashmere sweaters demand careful hand washing or dry cleaning, with cold water and a specialized cashmere detergent, followed by reshaping and flat drying to prevent stretching and pilling. Both materials necessitate proper storage in breathable containers to maintain softness and longevity, but cashmere is more prone to moth damage, requiring additional protection measures like cedar balls or lavender sachets.
Cost and Market Availability
Spider silk sweaters command significantly higher prices due to the complexity of harvesting and producing the fiber, making them a luxury niche product with limited market availability. In contrast, cashmere sweaters are more widely accessible and cost-effective, benefiting from established manufacturing processes and abundant raw material supply. While spider silk offers exceptional strength and sheen, its scarcity drives prices well above those of cashmere, which remains a popular and affordable option in the luxury sweater market.
Choosing the Right Sweater: Spider Silk vs Cashmere
Spider silk offers unparalleled strength and natural elasticity, making it a durable yet lightweight option for sweaters, while cashmere provides exceptional softness and warmth due to its fine fibers. When choosing the right sweater, consider spider silk for breathable, moisture-wicking properties ideal for active wear, whereas cashmere is preferred for luxurious comfort and insulation in colder climates. Both materials demand careful care, but spider silk's resilience often results in longer-lasting garments compared to the delicate nature of cashmere.
Infographic: Spider silk vs Cashmere for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com