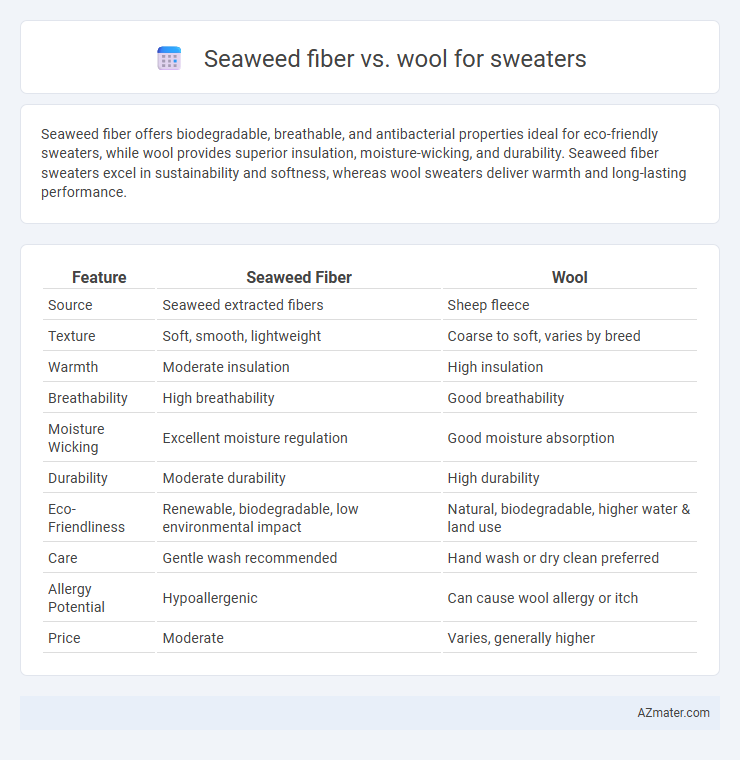
Seaweed fiber offers biodegradable, breathable, and antibacterial properties ideal for eco-friendly sweaters, while wool provides superior insulation, moisture-wicking, and durability. Seaweed fiber sweaters excel in sustainability and softness, whereas wool sweaters deliver warmth and long-lasting performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Seaweed Fiber | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Seaweed extracted fibers | Sheep fleece |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, lightweight | Coarse to soft, varies by breed |
| Warmth | Moderate insulation | High insulation |
| Breathability | High breathability | Good breathability |
| Moisture Wicking | Excellent moisture regulation | Good moisture absorption |
| Durability | Moderate durability | High durability |
| Eco-Friendliness | Renewable, biodegradable, low environmental impact | Natural, biodegradable, higher water & land use |
| Care | Gentle wash recommended | Hand wash or dry clean preferred |
| Allergy Potential | Hypoallergenic | Can cause wool allergy or itch |
| Price | Moderate | Varies, generally higher |
Introduction: Comparing Seaweed Fiber and Wool for Sweaters
Seaweed fiber and wool both offer unique benefits for sweater fabrication, with seaweed fiber providing excellent antibacterial properties, moisture-wicking capabilities, and eco-friendly sustainability. Wool remains a popular choice due to its natural insulation, breathability, and durability in cold weather. Evaluating their thermal performance, comfort, and environmental impact helps determine the best material for specific sweater applications.
Origin and Production Process
Seaweed fiber is derived from marine algae harvested sustainably from ocean beds, where it undergoes a process of extraction, drying, and blending with natural polymers to create a soft, lightweight yarn. Wool is sourced from the fleece of sheep, which is sheared, cleaned, carded, spun, and then woven into fibers suitable for warm, durable sweaters. The production of seaweed fiber emphasizes eco-friendly harvesting and minimal chemical treatment, while wool production involves animal husbandry and fiber processing that impact land use and animal welfare.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Seaweed fiber sweaters offer a sustainable alternative by utilizing renewable marine resources that require minimal water and land for cultivation, significantly reducing carbon footprint compared to traditional wool. Wool production involves high water usage, methane emissions from sheep, and land degradation, contributing to greater environmental impact. Choosing seaweed fiber supports ocean health and lowers greenhouse gas emissions, making it a more eco-friendly option in sustainable fashion.
Texture and Comfort
Seaweed fiber offers a smooth, silky texture with natural moisture-wicking properties, making sweaters breathable and soft against the skin. Wool provides a warm, slightly coarse texture that excels in insulation, ideal for colder climates but may cause itchiness for sensitive skin. Both fibers enhance comfort, with seaweed fiber suited for lightweight, comfortable wear and wool favored for durability and warmth in sweaters.
Thermal Insulation and Warmth
Seaweed fiber offers excellent thermal insulation by trapping moisture and converting it into heat, making it naturally thermoregulating and breathable. Wool provides superior warmth due to its crimped fibers that create insulating air pockets, retaining body heat even when wet. Both fibers excel in thermal performance, but wool traditionally delivers higher insulation values for cold-weather sweaters.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Seaweed fiber offers superior breathability due to its natural porous structure, which allows better air circulation and moisture wicking compared to wool. Wool fibers trap heat and moisture, making them less efficient in rapid drying and breathability under high humidity. Seaweed fiber's moisture management properties keep the skin dryer by quickly absorbing and releasing sweat, enhancing comfort during active wear.
Durability and Longevity
Seaweed fiber sweaters exhibit impressive durability due to their natural resilience against moisture and odor, making them ideal for extended wear and frequent use. Wool, renowned for its strength and elasticity, offers long-lasting performance but may require more care to prevent pilling and shrinkage over time. Comparing durability and longevity, seaweed fiber blends tend to resist wear better in humid conditions, while high-quality wool provides enduring comfort and insulation across diverse climates.
Allergies and Skin Sensitivity
Seaweed fiber sweaters provide a hypoallergenic alternative to wool, reducing irritation for individuals with sensitive skin due to their natural antimicrobial properties and smooth texture. Wool, while warm and breathable, often causes itching or allergic reactions because of lanolin and coarse fibers. Choosing seaweed fiber can help minimize allergic responses and enhance comfort for those prone to skin sensitivity.
Care, Maintenance, and Washing
Seaweed fiber sweaters require gentle washing in cold water with mild detergent to preserve their natural minerals and softness, while wool garments need careful hand washing or dry cleaning to avoid shrinkage and felting. Seaweed fiber is naturally antimicrobial and odor-resistant, reducing the frequency of washes compared to wool, which may require more frequent airing to prevent odors. Both fibers benefit from laying flat to dry and avoiding direct heat or sunlight to maintain their shape and texture.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Seaweed fiber sweaters generally cost more than wool due to limited production and the novelty of seaweed textile technology, with prices typically 20-40% higher depending on brand and sourcing. Wool remains widely available and affordable, supported by a mature global supply chain and economies of scale, making it the dominant choice in the sweater market. Seaweed fiber is gaining niche market presence with eco-conscious consumers, but its availability remains restricted compared to the extensive wool offerings.
Infographic: Seaweed fiber vs Wool for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com