Pineapple leaf fiber offers superior sustainability and biodegradability compared to linen, making it an eco-friendly choice for apparel. Its natural moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties enhance comfort, while linen is known for durability and breathability but has a higher environmental impact.
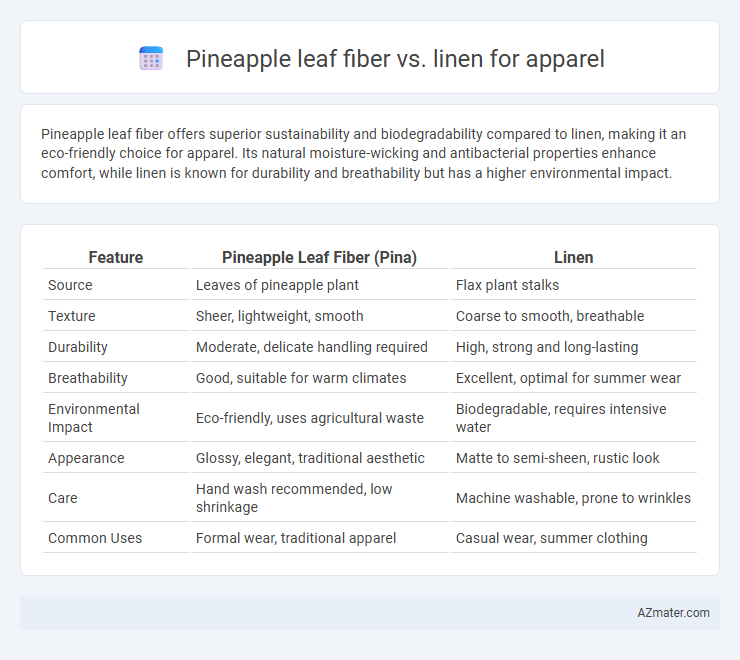
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pineapple Leaf Fiber (Pina) | Linen |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Leaves of pineapple plant | Flax plant stalks |
| Texture | Sheer, lightweight, smooth | Coarse to smooth, breathable |
| Durability | Moderate, delicate handling required | High, strong and long-lasting |
| Breathability | Good, suitable for warm climates | Excellent, optimal for summer wear |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, uses agricultural waste | Biodegradable, requires intensive water |
| Appearance | Glossy, elegant, traditional aesthetic | Matte to semi-sheen, rustic look |
| Care | Hand wash recommended, low shrinkage | Machine washable, prone to wrinkles |
| Common Uses | Formal wear, traditional apparel | Casual wear, summer clothing |
Introduction to Sustainable Fibers: Pineapple Leaf Fiber vs Linen
Pineapple leaf fiber and linen are two sustainable textile options gaining prominence in eco-friendly apparel production. Pineapple leaf fiber, derived from the agricultural byproduct of pineapple leaves, offers a biodegradable and renewable resource with a natural sheen and strong tensile strength. Linen, made from the flax plant, is highly durable, breathable, and has a low environmental impact due to minimal water and pesticide use, making both fibers ideal for sustainable fashion applications.
Source and Production Process of Pineapple Leaf Fiber
Pineapple leaf fiber, derived from the leaves of the Ananas comosus plant, is a sustainable textile material obtained through a mechanical decortication process that extracts fibers from the leaf's outer layer. Unlike linen, which comes from flax stalks and requires retting and scutching to separate fibers, pineapple leaf fiber production involves retting-free extraction, reducing water usage and chemical inputs. The fiber is known for its strength, lightweight properties, and eco-friendly sourcing, positioning it as an innovative alternative in sustainable apparel manufacturing.
How Linen is Made: From Flax Plant to Fabric
Linen is derived from the flax plant, where fibers are extracted through retting, a process that uses moisture to break down the plant's outer stalk. After retting, the fibers undergo scutching and hackling to separate and clean them before spinning into yarn. This natural, labor-intensive method produces durable and breathable fabric highly valued in apparel for its strength and moisture-wicking properties.
Environmental Impact: Comparing Pineapple Leaf Fiber and Linen
Pineapple leaf fiber offers a sustainable advantage by utilizing agricultural waste, reducing landfill waste and chemical inputs compared to traditional linen that requires extensive water and pesticide use during flax cultivation. Both fibers are biodegradable, but pineapple leaf fiber's production involves lower water consumption, making it a more eco-friendly alternative for apparel. Linen production, while renewable, has a higher environmental footprint primarily due to intensive irrigation and retting processes.
Durability and Strength: Which Fiber Lasts Longer?
Pineapple leaf fiber demonstrates exceptional tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it highly durable for apparel applications. Linen, derived from flax fibers, offers robust durability but tends to wear out faster under frequent stress compared to pineapple leaf fiber. Consequently, pineapple leaf fiber generally lasts longer than linen in garments subjected to heavy use.
Comfort and Breathability in Apparel Applications
Pineapple leaf fiber offers exceptional breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it highly suitable for comfortable apparel in warm climates. Linen is renowned for its lightweight texture and natural ability to regulate temperature, providing a cool and breathable experience ideal for summer clothing. Both fibers support sustainable fashion, but pineapple leaf fiber stands out for its softness and enhanced durability compared to traditional linen fabric.
Aesthetic Appeal: Texture, Color, and Finish
Pineapple leaf fiber offers a unique, coarse texture with a natural sheen that enhances the rustic aesthetic of apparel, while linen provides a smoother, softer hand feel with a matte finish prized for its timeless elegance. The color of pineapple leaf fiber ranges from pale yellow to light brown, lending a warm, earthy tone that contrasts with linen's typically crisp, off-white to beige hues. Both fibers absorb dye well, but pineapple leaf fiber's natural lustrous quality gives garments a subtle shimmer that differs from linen's classic, subdued appearance.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Market Availability
Pineapple leaf fiber offers a cost-effective alternative to linen, with lower raw material expenses due to its status as an agricultural byproduct, making it highly affordable for apparel production. Linen, derived from flax, typically incurs higher costs related to cultivation and processing, limiting its market availability and driving up retail prices. Pineapple leaf fiber's affordability and increasing market presence position it as a competitive sustainable option for apparel manufacturers seeking cost-efficient natural fibers.
Versatility: Uses in Modern Fashion and Apparel
Pineapple leaf fiber and linen both bring unique versatility to modern fashion, with pineapple leaf fiber prized for its eco-friendly strength and smooth texture suitable for sustainable activewear and accessories, while linen offers breathability and durability ideal for casual and formal garments. Pineapple fiber's natural sheen and lightweight properties enhance design innovation in avant-garde and everyday apparel, contrasting with linen's classic drape and moisture-wicking capabilities favored in warm-weather collections. Both fibers support diverse applications from structured outerwear to relaxed summer dresses, reflecting growing consumer demand for sustainable and functional materials in contemporary wardrobes.
Future Trends: Pineapple Leaf Fiber and Linen in Sustainable Fashion
Pineapple leaf fiber is gaining traction in sustainable fashion due to its eco-friendly production and biodegradability, offering a renewable alternative to conventional materials. Linen, derived from flax, remains a staple in sustainable apparel for its durability, breathability, and natural pest-resistant qualities that reduce pesticide use. Future trends emphasize integrating pineapple leaf fiber with linen blends to enhance fabric strength, texture, and environmental benefits, aligning with increasing consumer demand for eco-conscious, high-performance textiles.
Infographic: Pineapple leaf fiber vs Linen for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com